CD105重组兔单抗
Rrmab?兔单抗
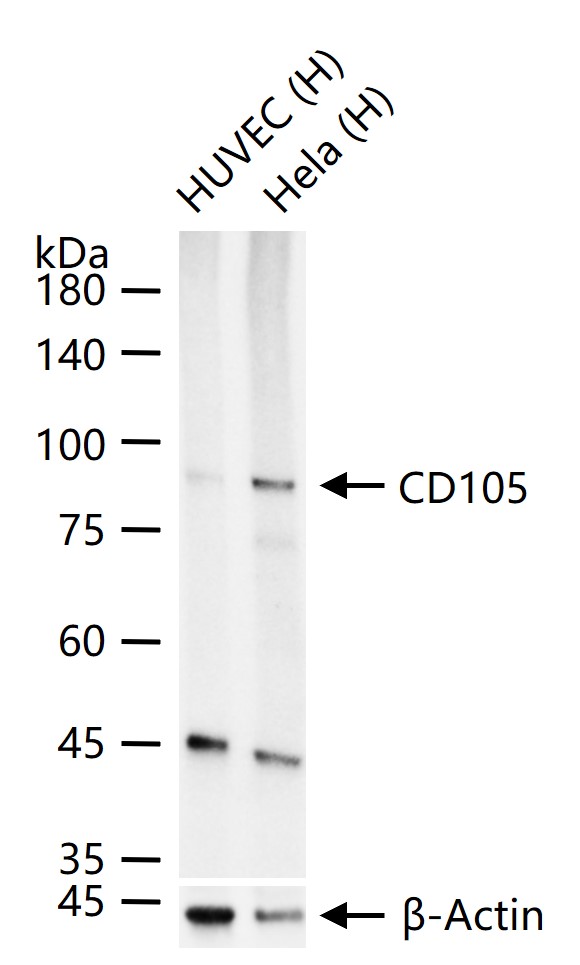
货号:bsm-41201R
产品详情
相关标记
相关产品
相关文献
常见问题
概述
产品编号
bsm-41201R
产品类型
重组兔单抗
英文名称
CD105 Recombinant Rabbit mAb
中文名称
CD105重组兔单抗
英文别名
END; HHT1; ORW1; EGLN_HUMAN; ENG; EGLN_MOUSE; Cell surface MJ7/18 antigen; Edg; CD105; Endo; S-endoglin;
抗体来源
Rabbit
免疫原
Recombinant human CD105 Protein: 26-586/658
亚型
IgG
性状
Liquid
纯化方法
affinity purified by Protein A
克隆类型
Recombinant
克隆号
3A8
理论分子量
70 kDa
浓度
1mg/ml
储存液
0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol.
研究领域
SWISS
Gene ID
保存条件
Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20℃ for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
注意事项
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
数据库链接
产品介绍
细胞膜受体(Membrane Receptors)
CD105(Endoglin):CD105是一种存在于细胞表面的同源二聚体跨膜糖蛋白,是TGF-β受体复合物的组成部分,是TGF-β的附属受体,能与多种TGF-β超家族成员结合尤其与TGF-β1、TGF-β3有很高的亲和力,调节TGF-βs与其受体结合而参与信号传导,是内皮细胞增殖相关膜抗原,在培养的高增殖活性内皮细胞和许多恶性肿瘤组织血管内皮细胞中高表达,参与血管生成,但其在血管生成调节中的作用机制尚未阐明。主要用于各种恶性肿瘤组织中的血管生成的研究.
CD105(Endoglin):CD105是一种分子量为180kDa的存在于细胞表面的同源二聚体跨膜糖蛋白,是TGF-β受体复合物的组成部分,是TGF-β的附属受体,能与多种TGF-β超家族成员结合尤其与TGF-β1、TGF-β3有很高的亲和力,调节TGF-βs与其受体结合而参与信号传导,是内皮细胞增殖相关膜抗原,在培养的高增殖活性内皮细胞和许多恶性肿瘤组织血管内皮细胞中高表达,参与血管生成,但其在血管生成调节中的作用机制尚未阐明。CD105基因定位于人9号染色体,是Ⅰ型遗传性出血性毛细血管扩张症的相关基因。CD105基因敲除小鼠胚胎因血管生成缺陷而于受精后平均11.5天死亡,故有学者认为,CD105可能与血管生成启动有关,可用于标记肿瘤新生血管。 Endoglin是内皮细胞表面与细胞增殖相关的膜抗原,也是转化生长因子β超家族受体复合物成分之一。其具有调节内皮细胞对TGF的反应、促内皮细胞增殖和促血管形成等功能,与肿瘤血管的发生密切相关。近年来,Endoglin在肿瘤诊断、判断预后和疗效及抗肿瘤血管靶向治疗等方面的作用得到重视。
背景资料
This gene encodes a homodimeric transmembrane protein which is a major glycoprotein of the vascular endothelium. This protein is a component of the transforming growth factor beta receptor complex and it binds to the beta1 and beta3 peptides with high affinity. Mutations in this gene cause hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, also known as Osler-Rendu-Weber syndrome 1, an autosomal dominant multisystemic vascular dysplasia. This gene may also be involved in preeclampsia and several types of cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013]

产品应用
| 应用 | 已检合格种属 | 预测种属 | 推荐稀释比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| WB | Human | 1:500-2000 |
交叉反应
交叉反应: Human
相关产品
暂无相关产品
靶标
基因名
ENG
蛋白名
Endoglin
亚基
Homodimer that forms an heteromeric complex with the signaling receptors for transforming growth factor-beta: TGFBR1 and/or TGFBR2. It is able to bind TGF-beta 1, and 3 efficiently and TGF-beta 2 less efficiently. Interacts with TCTEX1D4. Interacts with ARRB2.
亚细胞定位
Membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.
组织特异性
Endoglin is restricted to endothelial cells in all tissues except bone marrow.
疾病
Defects in ENG are the cause of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia type 1 (HHT1) [MIM:187300]; also known as Osler-Rendu-Weber syndrome 1 (ORW1). HHT1 is an autosomal dominant multisystemic vascular dysplasia, characterized by recurrent epistaxis, muco-cutaneous telangiectases, gastro-intestinal hemorrhage, and pulmonary (PAVM), cerebral (CAVM) and hepatic arteriovenous malformations; all secondary manifestations of the underlying vascular dysplasia. Although the first symptom of HHT1 in children is generally nose bleed, there is an important clinical heterogeneity.
功能
Major glycoprotein of vascular endothelium. May play a critical role in the binding of endothelial cells to integrins and/or other RGD receptors.
标记抗体
暂无标记数据
同靶标产品
暂无同靶标产品
相关文献
提示: 发表研究结果有使用 bsm-41201R 时请让我们知道,以便我们可以引用参考文章。作为回馈,资料提供者将获得我们送上的小礼品。
暂无相关文献
常见问题
暂无常见问题