粘蛋白-2/上皮膜抗原2重组兔单抗
Rrmab?兔单抗
货号:bsm-60016R
产品详情
相关标记
相关产品
相关文献
常见问题
概述
产品编号
bsm-60016R
产品类型
重组兔单抗、病理级抗体
英文名称
MUC2 Recombinant Rabbit mAb
中文名称
粘蛋白-2/上皮膜抗原2重组兔单抗
英文别名
MLP; MUC-2; SMUC; 2010015E03Rik; MCM; wnn; AABR07006030.1; HH-Muc; MUC2_HUMAN; MUC2; Intestinal mucin-2; MUC2_MOUSE; Colonic mucin (MCM); Secreted gel-forming mucin; MUC2_RAT;
抗体来源
Rabbit
免疫原
KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human MUC2
亚型
IgG
性状
Liquid
纯化方法
affinity purified by Protein A
克隆类型
Recombinant
克隆号
7F9
理论分子量
570 kDa
浓度
1mg/ml
储存液
0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol.
研究领域
SWISS
Gene ID
保存条件
Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20℃ for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
注意事项
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
数据库链接
产品介绍
细胞粘附蛋白(Call Adhesion Protein)
上皮膜抗原是粘性糖蛋白家族之一,是一种膜内在糖蛋白。Muc-2表达仅限于内膜腺上皮和腔上皮,很多上皮细胞及其来源的肿瘤表达该蛋白.其合成和分泌是腺上皮组织的特征之一。MUC-2也是一种主要的肠道粘蛋白,在正常肠道和结肠癌、胃癌等肿瘤中有广泛分布。该抗体主要用于胃肠道肿瘤的研究。
上皮膜抗原是粘性糖蛋白家族之一,是一种膜内在糖蛋白。Muc-2表达仅限于内膜腺上皮和腔上皮,很多上皮细胞及其来源的肿瘤表达该蛋白.其合成和分泌是腺上皮组织的特征之一。MUC-2也是一种主要的肠道粘蛋白,在正常肠道和结肠癌、胃癌等肿瘤中有广泛分布。该抗体主要用于胃肠道肿瘤的研究。
背景资料
This gene encodes a member of the mucin protein family. Mucins are high molecular weight glycoproteins produced by many epithelial tissues. The protein encoded by this gene is secreted and forms an insoluble mucous barrier that protects the gut lumen. The protein polymerizes into a gel of which 80% is composed of oligosaccharide side chains by weight. The protein features a central domain containing tandem repeats rich in threonine and proline that varies between 50 and 115 copies in different individuals. Alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but their full-length nature is not known. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]

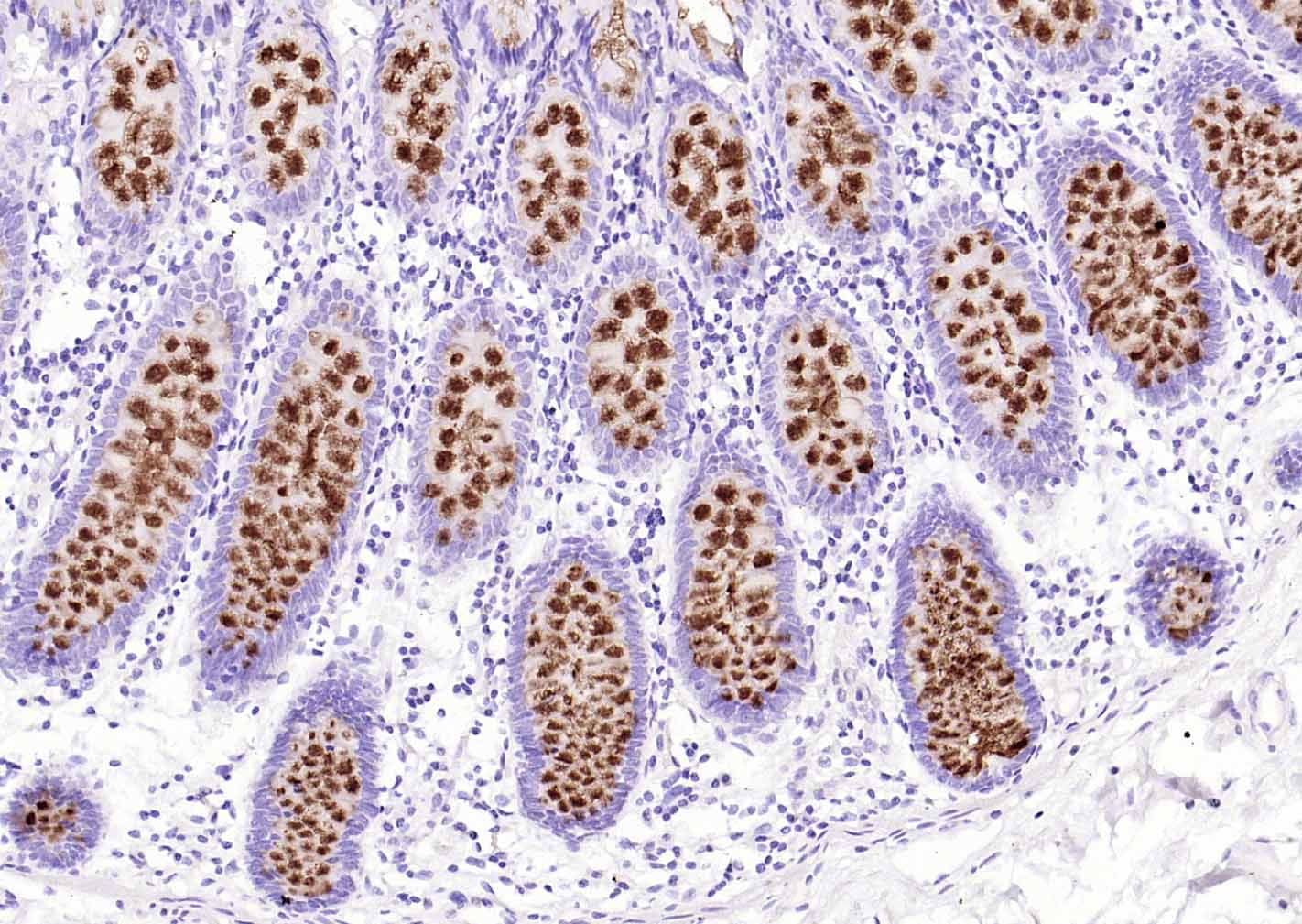
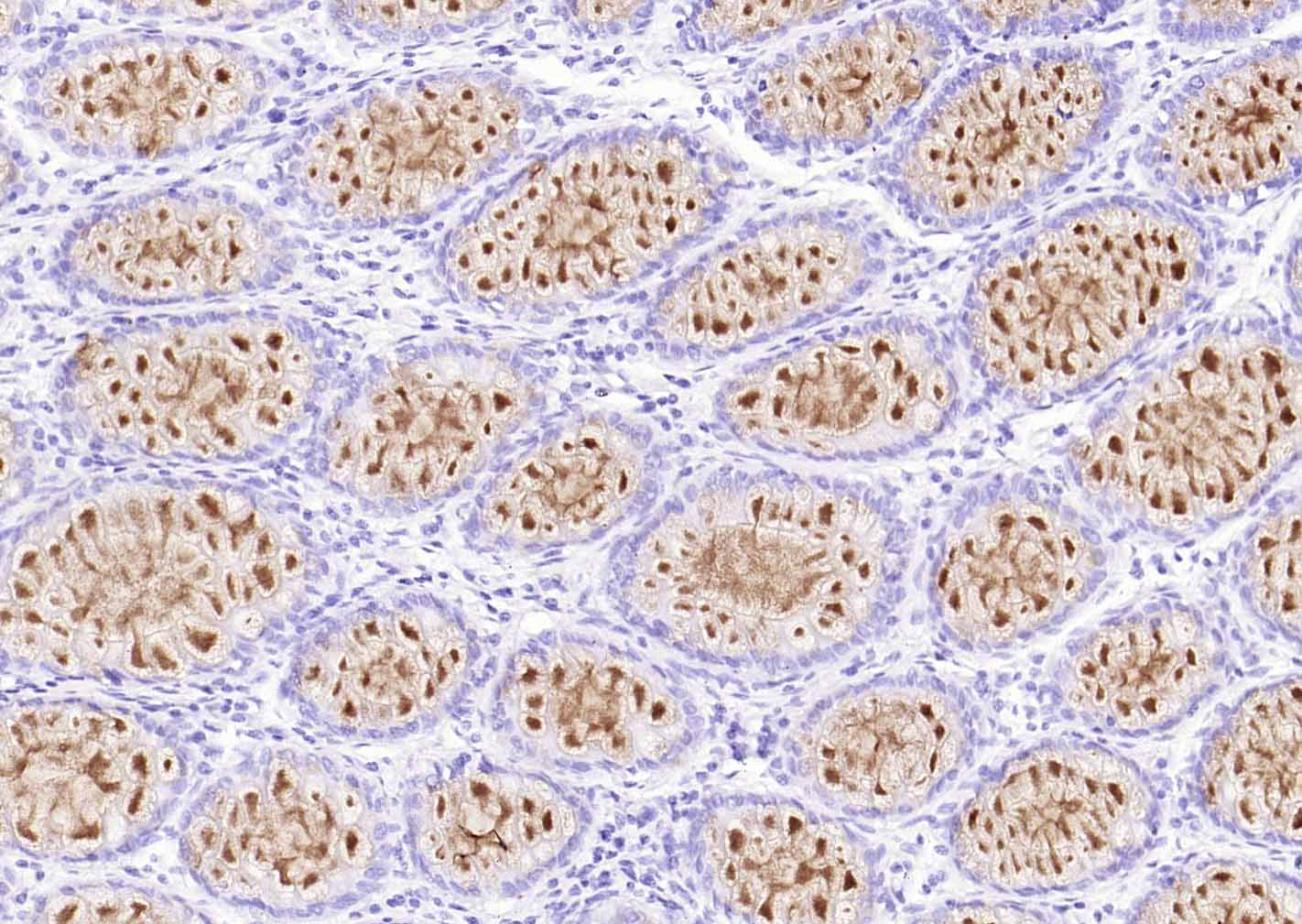
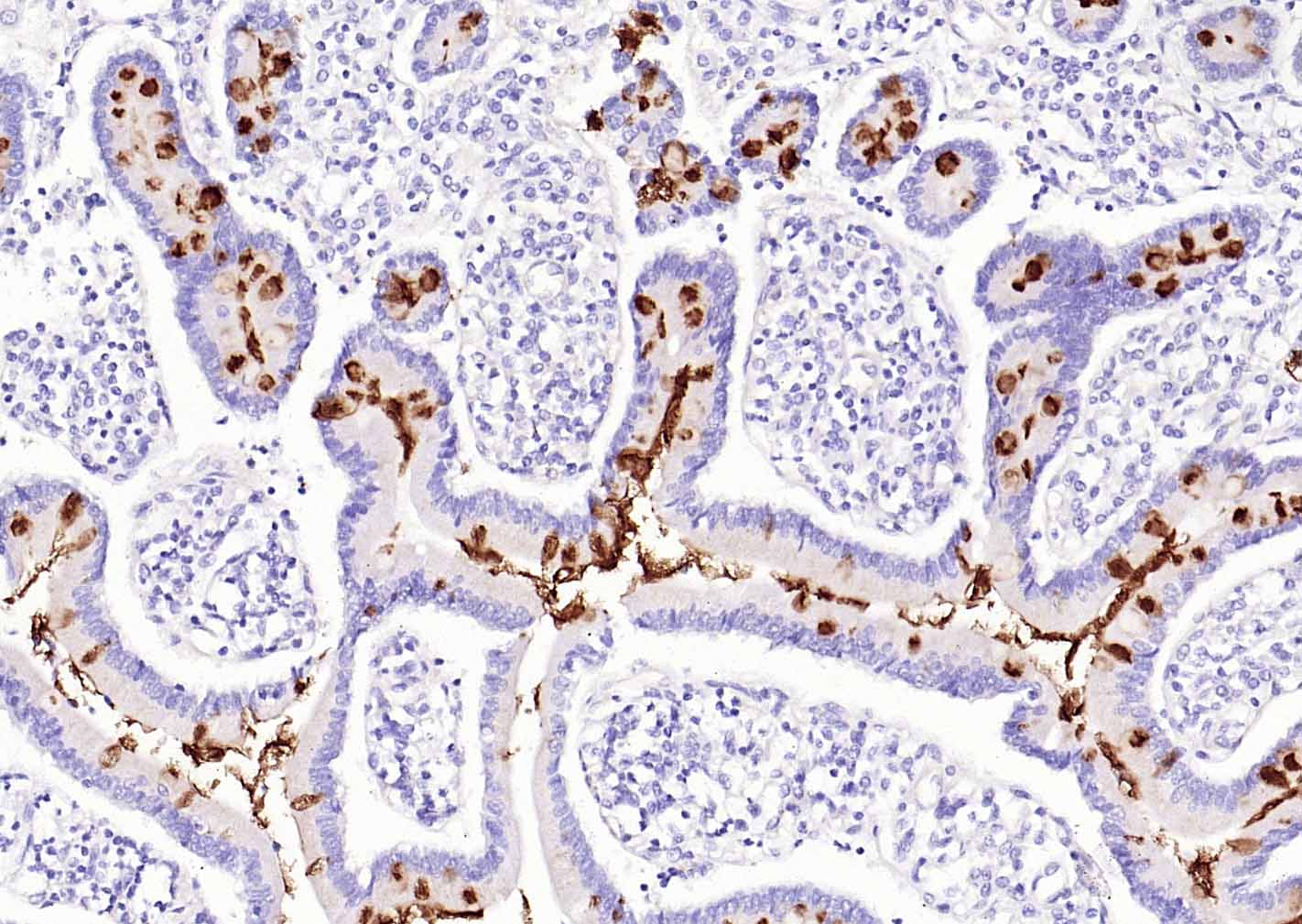
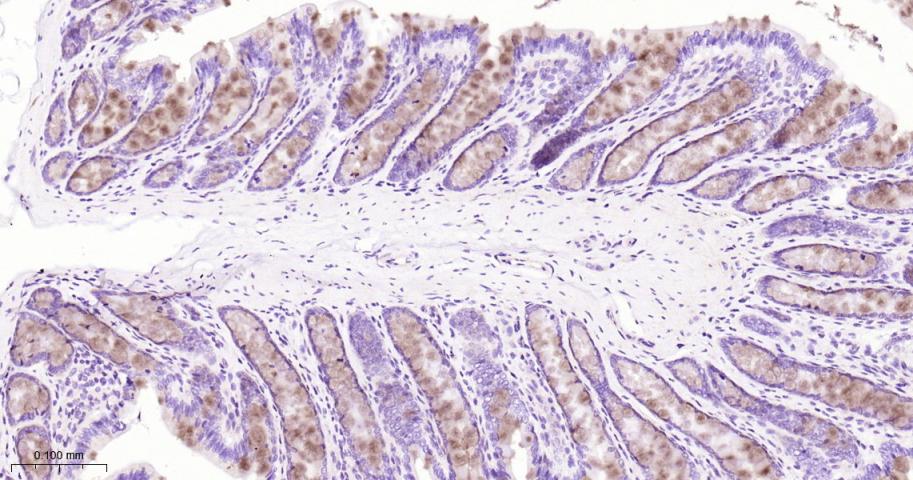
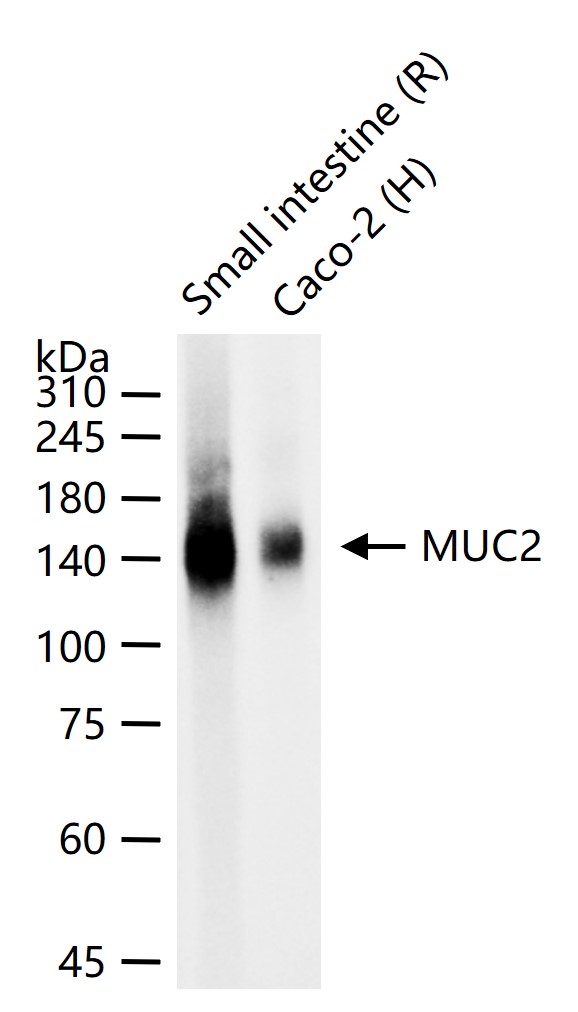
产品应用
| 应用 | 已检合格种属 | 预测种属 | 推荐稀释比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| WB | Human, Rat | 1:500-2000 | |
| IHC-P | Human, Rat | 1:100-500 | |
| IHC-F | Human, Rat | 1:100-500 | |
| IF | Human, Rat | 1:100-500 | |
| Flow-Cyt | Human, Rat | 1:50-100 |
交叉反应
交叉反应: Human, Rat
相关产品
暂无相关产品
靶标
基因名
MUC2
蛋白名
Mucin-2
亚基
Homotrimer; disulfide-linked. Dimerizes in the endoplasmic reticulum via its C-terminal region and polymerizes via its N-terminal region by disulfide-linked trimerization. Interacts with FCGBP. Interacts with AGR2; disulfide-linked.
亚细胞定位
Secreted. Note=In the intestine, secreted into the inner and outer mucus layers.
组织特异性
Colon, small intestine, colonic tumors, bronchus, cervix and gall bladder.
翻译后修饰
O-glycosylated.
May undergo proteolytic cleavage in the outer mucus layer of the colon, contributing to the expanded volume and loose nature of this layer which allows for bacterial colonization in contrast to the inner mucus layer which is dense and devoid of bacteria.
At low pH of 6 and under, undergoes autocatalytic cleavage in vitro in the N-terminal region of the fourth VWD domain. It is likely that this also occurs in vivo and is triggered by the low pH of the late secretory pathway.
May undergo proteolytic cleavage in the outer mucus layer of the colon, contributing to the expanded volume and loose nature of this layer which allows for bacterial colonization in contrast to the inner mucus layer which is dense and devoid of bacteria.
At low pH of 6 and under, undergoes autocatalytic cleavage in vitro in the N-terminal region of the fourth VWD domain. It is likely that this also occurs in vivo and is triggered by the low pH of the late secretory pathway.
相似性
Contains 1 CTCK (C-terminal cystine knot-like) domain.
Contains 1 TIL (trypsin inhibitory-like) domain.
Contains 2 VWFC domains.
Contains 1 TIL (trypsin inhibitory-like) domain.
Contains 2 VWFC domains.
功能
Coats the epithelia of the intestines, airways, and other mucus membrane-containing organs. Thought to provide a protective, lubricating barrier against particles and infectious agents at mucosal surfaces. Major constituent of both the inner and outer mucus layers of the colon and may play a role in excluding bacteria from the inner mucus layer.
标记抗体
暂无标记数据
同靶标产品
暂无同靶标产品
相关文献
提示: 发表研究结果有使用 bsm-60016R 时请让我们知道,以便我们可以引用参考文章。作为回馈,资料提供者将获得我们送上的小礼品。
具体参考文献:bsm-60016R 被引用于5文献中
暂无相关文献
常见问题
暂无常见问题