胰岛素重组兔单抗
Rrmab?兔单抗
货号:bsm-60010R
产品详情
相关标记
相关产品
相关文献
常见问题
概述
产品编号
bsm-60010R
产品类型
重组兔单抗、mIHC精品抗体
英文名称
Insulin Recombinant Rabbit mAb
中文名称
胰岛素重组兔单抗
英文别名
IDDM; IDDM1; IDDM2; ILPR; IRDN; MODY10; PNDM4; Ins-1; Ins2-rs1; Ins-2; InsII; Mody; Mody4; INS_HUMAN; INS; INS1_MOUSE; Ins1; INS1_RAT; INS_PIG;
抗体来源
Rabbit
免疫原
A synthesized peptide derived from human Insulin: 25-110
亚型
IgG
性状
Liquid
纯化方法
affinity purified by Protein A
克隆类型
Recombinant
克隆号
2F3
CAS
11061-68-0
理论分子量
12 kDa
浓度
1mg/ml
储存液
0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol.
研究领域
SWISS
Gene ID
保存条件
Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20℃ for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
注意事项
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
数据库链接
产品介绍
胰岛素(Insulin)是胰岛beta细胞分泌的一种激素,可以减低血糖浓度。
背景资料
Insulin is one of the major regulatory hormones of intermediate metabolism throughout the body. The biological actions of this hormone involve integration of carbohydrate, protein, and lipid metabolism. Insulin enhances membrane transport of glucose, amino acids, and certain ions. It also promotes glycogen storage, formation of triglycerides and synthesis of proteins and nucleic acids. Immunocytochemical investigations have localized insulin in the B cells of pancreatic islets of Langerhans. Deficiency of insulin results in diabetes mellitus, one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in the general population. Insulin is also present in tumors of B cell origin such as insulinoma.

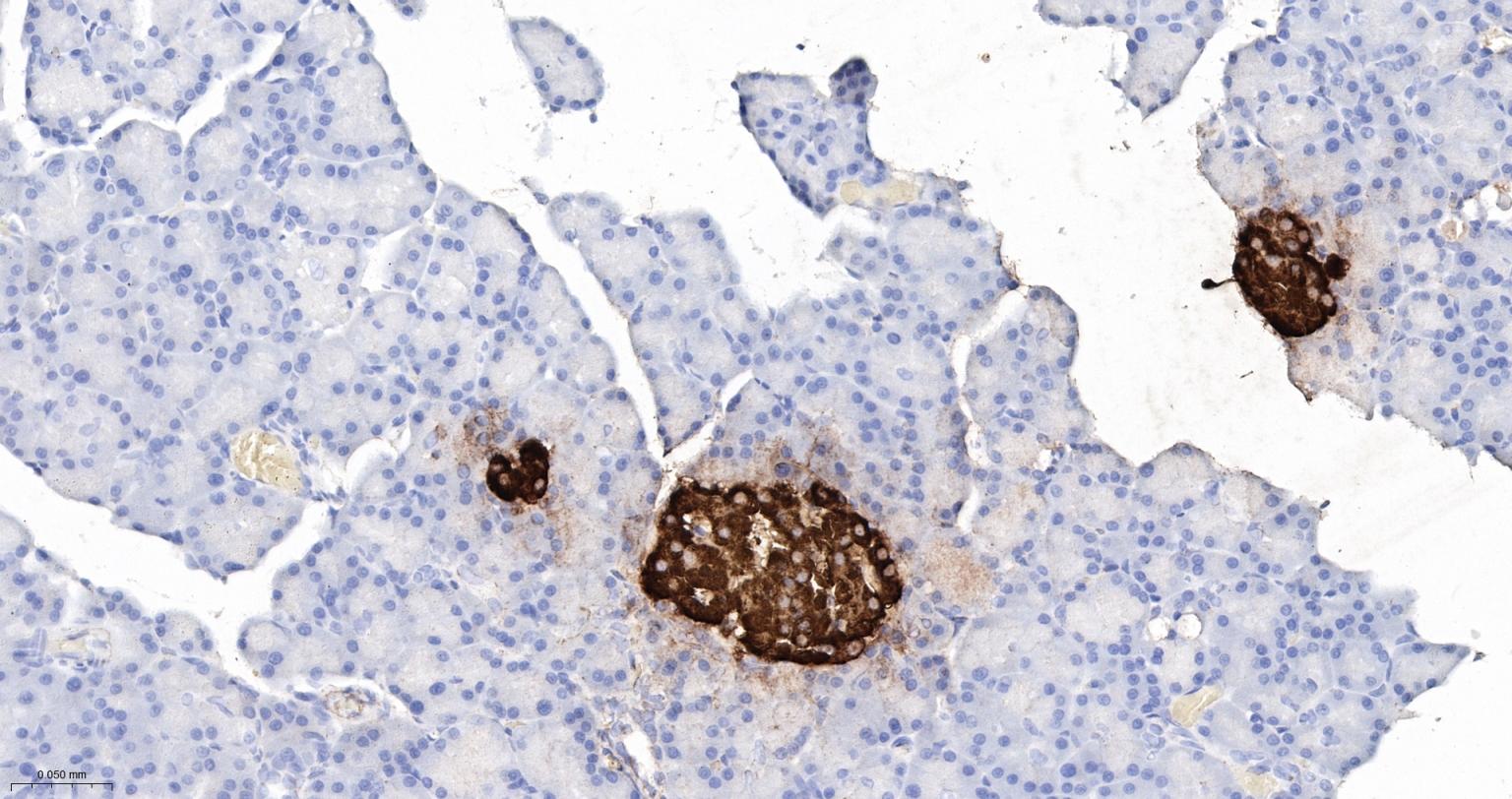
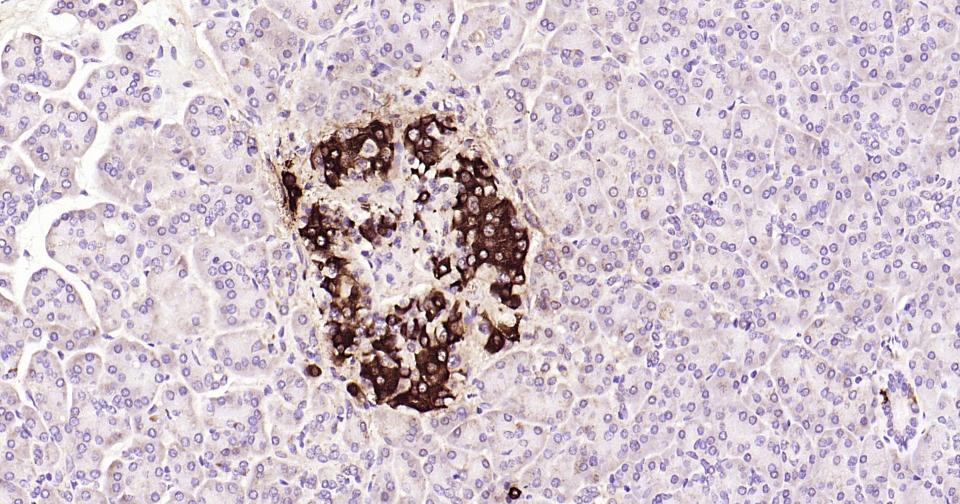
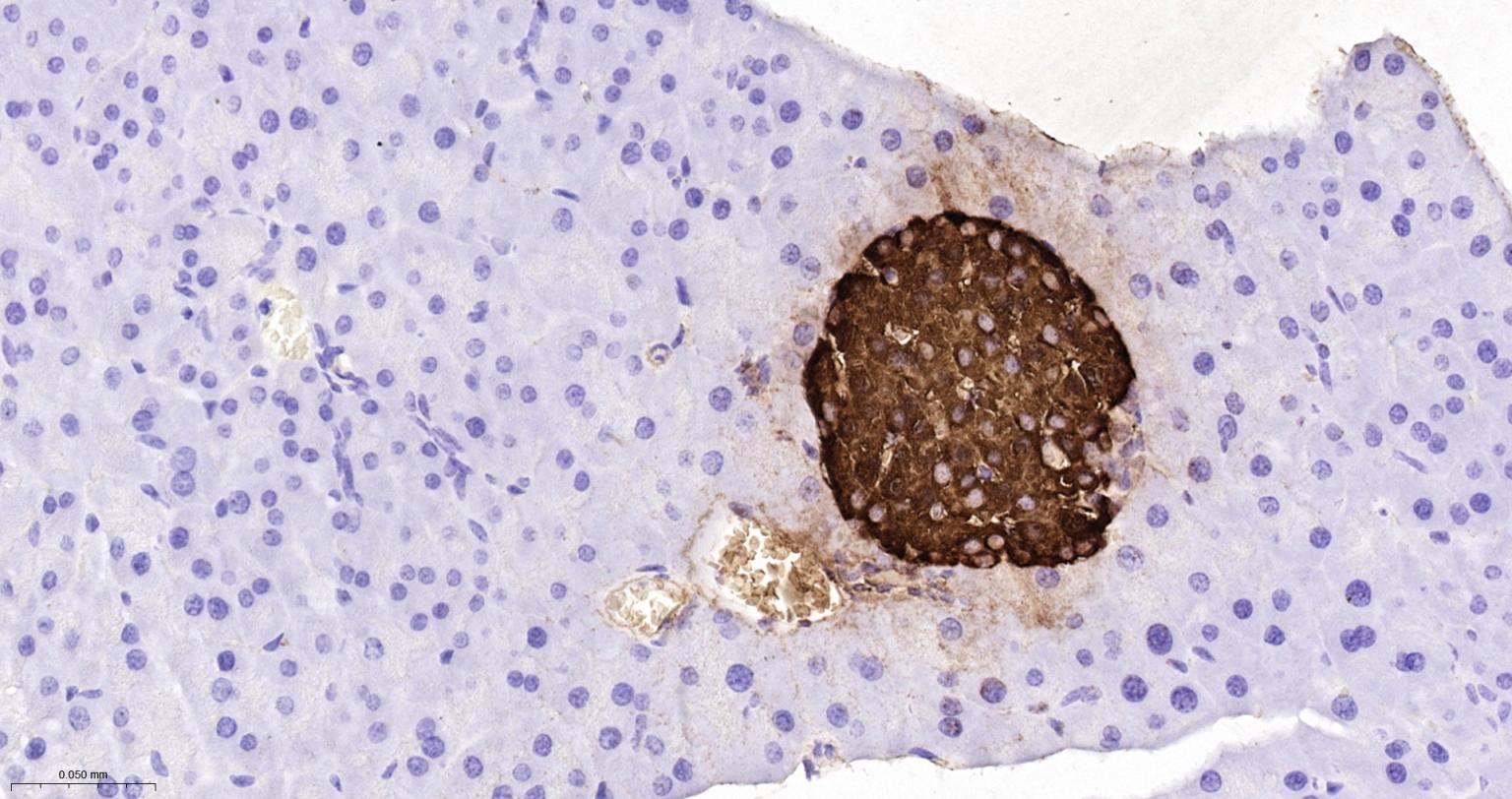
产品应用
| 应用 | 已检合格种属 | 预测种属 | 推荐稀释比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IHC-P | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:1000-5000 | |
| IHC-F | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:1000-5000 | |
| IF | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:1000-5000 |
交叉反应
交叉反应: Human, Mouse, Rat
相关产品
暂无相关产品
靶标
基因名
INS
蛋白名
Insulin
亚基
Heterodimer of a B chain and an A chain linked by two disulfide bonds.
亚细胞定位
Secreted.
疾病
Hyperproinsulinemia, familial (FHPRI) [MIM:176730]: An autosomal dominant condition characterized by elevated levels of serum proinsulin-like material. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.
Diabetes mellitus, insulin-dependent, 2 (IDDM2) [MIM:125852]: A multifactorial disorder of glucose homeostasis that is characterized by susceptibility to ketoacidosis in the absence of insulin therapy. Clinical fetaures are polydipsia, polyphagia and polyuria which result from hyperglycemia-induced osmotic diuresis and secondary thirst. These derangements result in long-term complications that affect the eyes, kidneys, nerves, and blood vessels. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.
Diabetes mellitus, permanent neonatal (PNDM) [MIM:606176]: A rare form of diabetes distinct from childhood-onset autoimmune diabetes mellitus type 1. It is characterized by insulin-requiring hyperglycemia that is diagnosed within the first months of life. Permanent neonatal diabetes requires lifelong therapy. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.
Maturity-onset diabetes of the young 10 (MODY10) [MIM:613370]: A form of diabetes that is characterized by an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance, onset in childhood or early adulthood (usually before 25 years of age), a primary defect in insulin secretion and frequent insulin-independence at the beginning of the disease. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.
Diabetes mellitus, insulin-dependent, 2 (IDDM2) [MIM:125852]: A multifactorial disorder of glucose homeostasis that is characterized by susceptibility to ketoacidosis in the absence of insulin therapy. Clinical fetaures are polydipsia, polyphagia and polyuria which result from hyperglycemia-induced osmotic diuresis and secondary thirst. These derangements result in long-term complications that affect the eyes, kidneys, nerves, and blood vessels. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.
Diabetes mellitus, permanent neonatal (PNDM) [MIM:606176]: A rare form of diabetes distinct from childhood-onset autoimmune diabetes mellitus type 1. It is characterized by insulin-requiring hyperglycemia that is diagnosed within the first months of life. Permanent neonatal diabetes requires lifelong therapy. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.
Maturity-onset diabetes of the young 10 (MODY10) [MIM:613370]: A form of diabetes that is characterized by an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance, onset in childhood or early adulthood (usually before 25 years of age), a primary defect in insulin secretion and frequent insulin-independence at the beginning of the disease. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.
相似性
Belongs to the insulin family.
功能
Insulin decreases blood glucose concentration. It increases cell permeability to monosaccharides, amino acids and fatty acids. It accelerates glycolysis, the pentose phosphate cycle, and glycogen synthesis in liver.
标记抗体
暂无标记数据
同靶标产品
暂无同靶标产品
相关文献
提示: 发表研究结果有使用 bsm-60010R 时请让我们知道,以便我们可以引用参考文章。作为回馈,资料提供者将获得我们送上的小礼品。
具体参考文献:bsm-60010R 被引用于2文献中
暂无相关文献
常见问题
暂无常见问题