补体因子H重组兔单抗
Rrmab?兔单抗
货号:bsm-54051R
产品详情
相关标记
相关产品
相关文献
常见问题
概述
产品编号
bsm-54051R
产品类型
重组兔单抗
英文名称
CFH Recombinant Rabbit mAb
中文名称
补体因子H重组兔单抗
英文别名
AHUS1; AMBP1; ARMD4; ARMS1; CFHL3; FH; FHL1; HF; HF1; HF2; HUS; Mud-1; NOM; Sas-1; Sas1; AMBP-1; CFAH_HUMAN; CFH; H factor 1; CFAH_MOUSE; Protein beta-1-H;
抗体来源
Rabbit
免疫原
A synthesized peptide derived from human Complement factor H: 150-200/1231
亚型
IgG
性状
Liquid
纯化方法
affinity purified by Protein A
克隆类型
Recombinant
克隆号
6F11
理论分子量
51/137 kDa
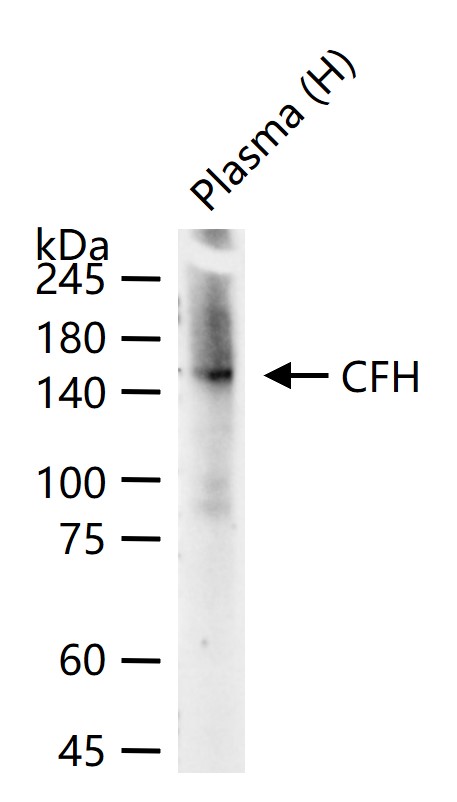
检测分子量
150 kDa
浓度
1mg/ml
储存液
0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol.
SWISS
Gene ID
保存条件
Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20℃ for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
注意事项
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
数据库链接
背景资料
This gene is a member of the Regulator of Complement Activation (RCA) gene cluster and encodes a protein with twenty short consensus repeat (SCR) domains. This protein is secreted into the bloodstream and has an essential role in the regulation of complement activation, restricting this innate defense mechanism to microbial infections. Mutations in this gene have been associated with hemolytic-uremic syndrome (HUS) and chronic hypocomplementemic nephropathy. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]

产品应用
| 应用 | 已检合格种属 | 预测种属 | 推荐稀释比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| WB | Human | 1:500-2000 |
交叉反应
交叉反应: Human
相关产品
暂无相关产品
靶标
基因名
CFH
蛋白名
Complement factor H
亚细胞定位
Secreted.
组织特异性
Expressed by the liver and secreted in plasma.
疾病
Genetic variations in CFH are associated with basal laminar drusen (BLD) [MIM:126700]; also known as drusen of Bruch membrane or cuticular drusen or grouped early adult-onset drusen. Drusen are extracellular deposits that accumulate below the retinal pigment epithelium on Bruch membrane. Basal laminar drusen refers to an early adult-onset drusen phenotype that shows a pattern of uniform small, slightly raised yellow subretinal nodules randomly scattered in the macula. In later stages, these drusen often become more numerous, with clustered groups of drusen scattered throughout the retina. In time these small basal laminar drusen may expand and ultimately lead to a serous pigment epithelial detachment of the macula that may result in vision loss.
Defects in CFH are the cause of complement factor H deficiency (CFHD) [MIM:609814]. A disorder that can manifest as several different phenotypes, including asymptomatic, recurrent bacterial infections, and renal failure. Laboratory features usually include decreased serum levels of factor H, complement component C3, and a decrease in other terminal complement components, indicating activation of the alternative complement pathway. It is associated with a number of renal diseases with variable clinical presentation and progression, including membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome.
Defects in CFH are a cause of susceptibility to hemolytic uremic syndrome atypical type 1 (AHUS1) [MIM:235400]. An atypical form of hemolytic uremic syndrome. It is a complex genetic disease characterized by microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, renal failure and absence of episodes of enterocolitis and diarrhea. In contrast to typical hemolytic uremic syndrome, atypical forms have a poorer prognosis, with higher death rates and frequent progression to end-stage renal disease. Note=Susceptibility to the development of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome can be conferred by mutations in various components of or regulatory factors in the complement cascade system. Other genes may play a role in modifying the phenotype.
Genetic variation in CFH is associated with age-related macular degeneration type 4 (ARMD4) [MIM:610698]. ARMD is a multifactorial eye disease and the most common cause of irreversible vision loss in the developed world. In most patients, the disease is manifest as ophthalmoscopically visible yellowish accumulations of protein and lipid (known as drusen) that lie beneath the retinal pigment epithelium and within an elastin-containing structure known as Bruch membrane.
Defects in CFH are the cause of complement factor H deficiency (CFHD) [MIM:609814]. A disorder that can manifest as several different phenotypes, including asymptomatic, recurrent bacterial infections, and renal failure. Laboratory features usually include decreased serum levels of factor H, complement component C3, and a decrease in other terminal complement components, indicating activation of the alternative complement pathway. It is associated with a number of renal diseases with variable clinical presentation and progression, including membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome.
Defects in CFH are a cause of susceptibility to hemolytic uremic syndrome atypical type 1 (AHUS1) [MIM:235400]. An atypical form of hemolytic uremic syndrome. It is a complex genetic disease characterized by microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, renal failure and absence of episodes of enterocolitis and diarrhea. In contrast to typical hemolytic uremic syndrome, atypical forms have a poorer prognosis, with higher death rates and frequent progression to end-stage renal disease. Note=Susceptibility to the development of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome can be conferred by mutations in various components of or regulatory factors in the complement cascade system. Other genes may play a role in modifying the phenotype.
Genetic variation in CFH is associated with age-related macular degeneration type 4 (ARMD4) [MIM:610698]. ARMD is a multifactorial eye disease and the most common cause of irreversible vision loss in the developed world. In most patients, the disease is manifest as ophthalmoscopically visible yellowish accumulations of protein and lipid (known as drusen) that lie beneath the retinal pigment epithelium and within an elastin-containing structure known as Bruch membrane.
相似性
Contains 20 Sushi (CCP/SCR) domains.
功能
Factor H functions as a cofactor in the inactivation of C3b by factor I and also increases the rate of dissociation of the C3bBb complex (C3 convertase) and the (C3b)NBB complex (C5 convertase) in the alternative complement pathway.
标记抗体
暂无标记数据
同靶标产品
暂无同靶标产品
相关文献
提示: 发表研究结果有使用 bsm-54051R 时请让我们知道,以便我们可以引用参考文章。作为回馈,资料提供者将获得我们送上的小礼品。
暂无相关文献
常见问题
暂无常见问题