相关死亡促进因子BAD重组兔单抗
Rrmab?兔单抗
货号:bsm-63058R
产品详情
相关标记
相关产品
相关文献
常见问题
概述
产品编号
bsm-63058R
产品类型
重组兔单抗、mIHC精品抗体
英文名称
BAD Recombinant Rabbit mAb
中文名称
相关死亡促进因子BAD重组兔单抗
英文别名
BBC2; BCL2L8; Bad_v1; Bad_v2; BAD_HUMAN; BAD; Bcl-2-binding component 6; Bcl-2-like protein 8 (Bcl2-L-8); Bcl-xL/Bcl-2-associated death promoter; Bcl2 antagonist of cell death; BBC6; BAD_MOUSE; BAD_RAT;
抗体来源
Rabbit
免疫原
A synthesized peptide derived from human BAD: 1-42
亚型
IgG
性状
Liquid
纯化方法
affinity purified by Protein A
克隆类型
Recombinant
克隆号
12H7
理论分子量
18 kDa
储存液
10mM phosphate buffered saline , pH 7.4, 150mM sodium chloride, 0.05% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% glycerol.
研究领域
SWISS
Gene ID
保存条件
Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20℃ for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
注意事项
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
数据库链接
产品介绍
BAD是BCL2/BAX、BCL-XL/BAX异二聚体的负调节基因。BAD是BCL2/BCL-XL相关死亡促进因子,作为BCL2、 bCL-XL异二聚体伴分子而促进细胞凋亡。
有学者认为:BAD缺乏典型的羧基端跨膜结构,提示其并非一完整膜蛋白。与同BCL2作用相比,BAD与BCL-XL的结合更强,BAD以浓度依赖性方式替换BCL-XL/BAX、BCL2/BAX异二聚体中的BAX,使BAX游离而促进细胞凋亡。当一细胞系的所有细胞内异二聚体(BCL-XL/BAX和BCL2/BAX)的含量≥50%时,则细胞耐受凋亡;而当细胞内BAX同二聚体>80%时且在适当信号诱导下则细胞出现凋亡。这表明BAD通过调节BAX同二聚体与异二聚体量的比值而介导凋亡。
有学者认为:BAD缺乏典型的羧基端跨膜结构,提示其并非一完整膜蛋白。与同BCL2作用相比,BAD与BCL-XL的结合更强,BAD以浓度依赖性方式替换BCL-XL/BAX、BCL2/BAX异二聚体中的BAX,使BAX游离而促进细胞凋亡。当一细胞系的所有细胞内异二聚体(BCL-XL/BAX和BCL2/BAX)的含量≥50%时,则细胞耐受凋亡;而当细胞内BAX同二聚体>80%时且在适当信号诱导下则细胞出现凋亡。这表明BAD通过调节BAX同二聚体与异二聚体量的比值而介导凋亡。
背景资料
Bad is a member of the Bcl2 family and acts to promote apoptosis by forming heterodimers with the survival proteins Bcl2 and BclxL, thus preventing them from binding with BAX. Bad is found on the outer mitochondrial membrane and, once phosphorylated in response to growth stimuli, translocates to the cytoplasm. The phosphorylation status of Bad represents a key checkpoint for death or cell survival. JNK-induced phosphorylation of BAD serine 128 promotes the apoptotic role of Bad by opposing the inhibitory effect of growth factor on Bad-mediated apoptosis. Cdc2-induced phosphorylation of Bad serine 128 has an inhibitory effect on its interaction with 14-3-3 proteins. The latter interaction is critical for Bad phosphorylation at serine 155, a site within the BH3 domain that leads to the release of BclxL and the promotion of cell survival. Alternative splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants which encode the same isoform.

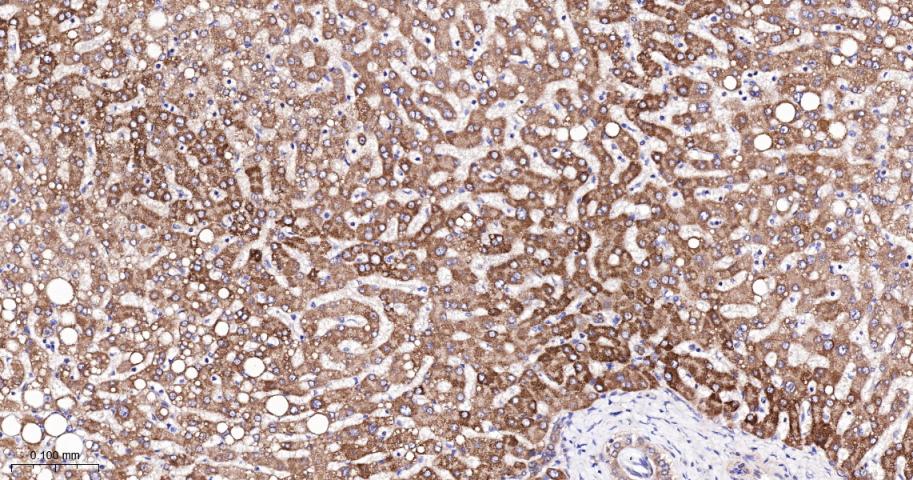
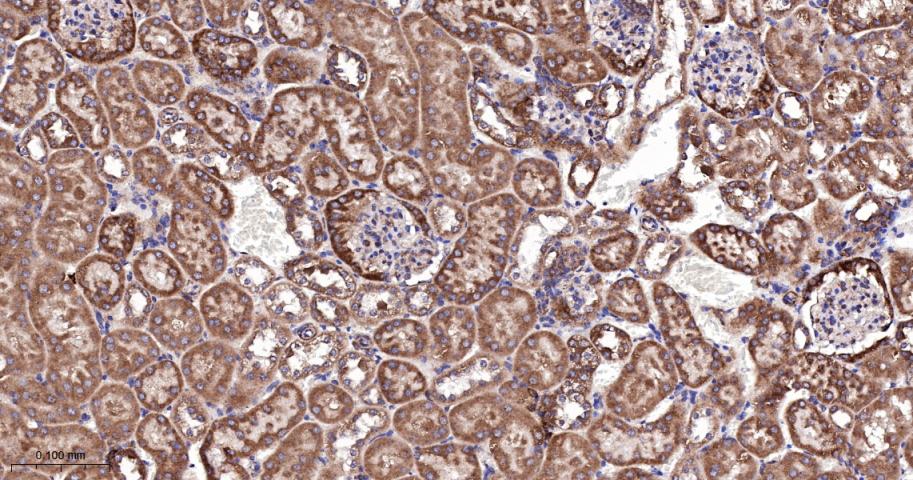
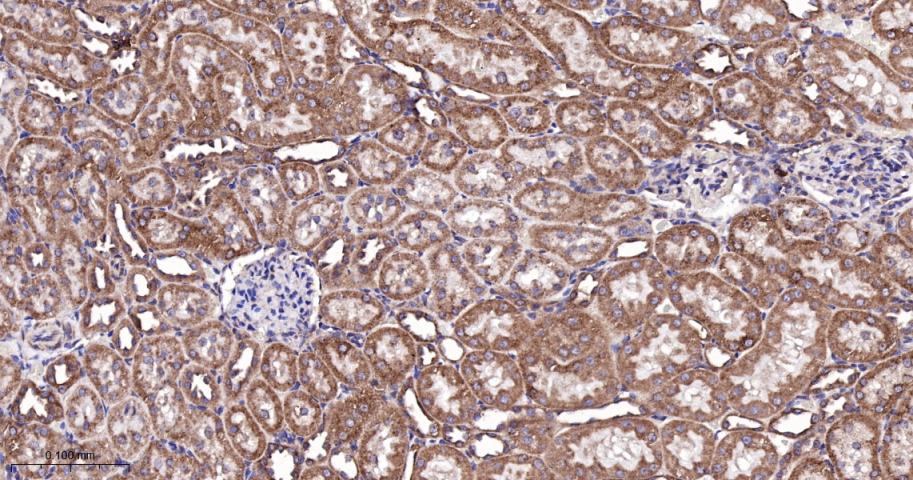
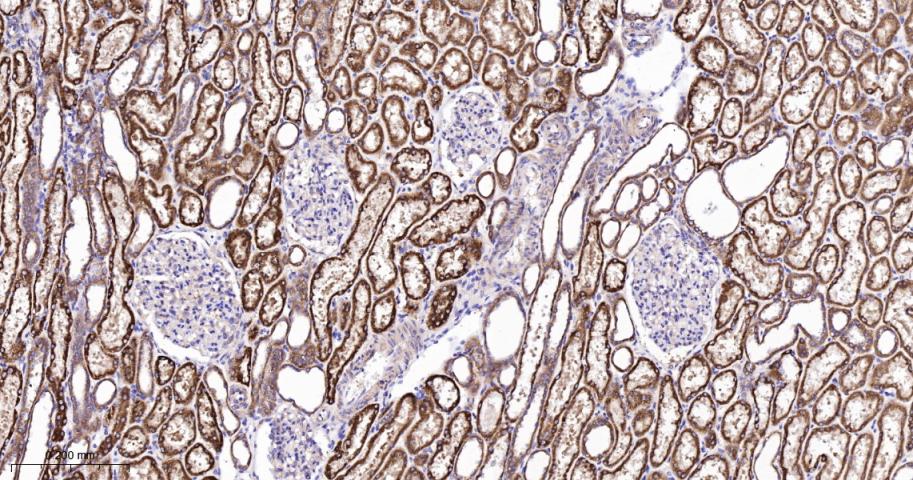
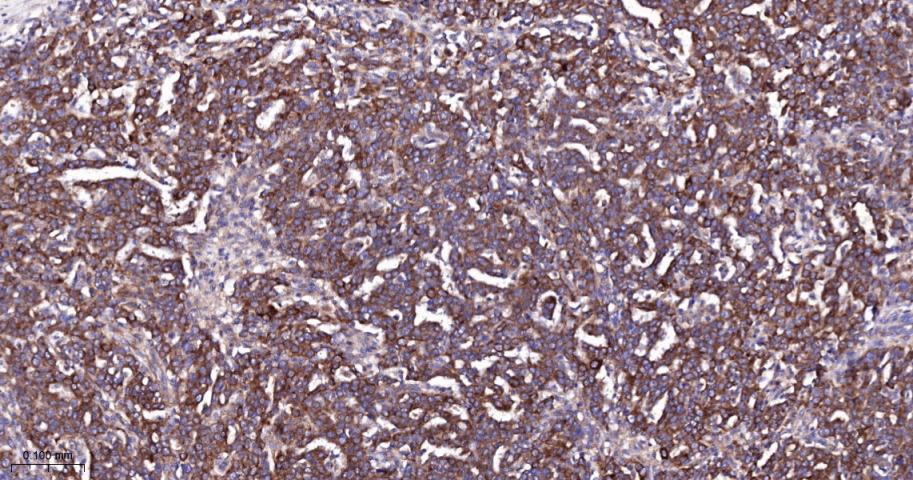
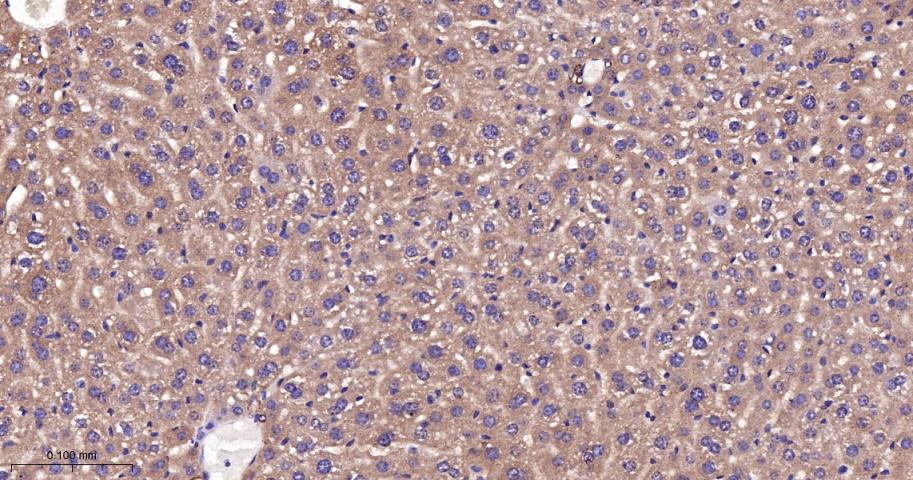
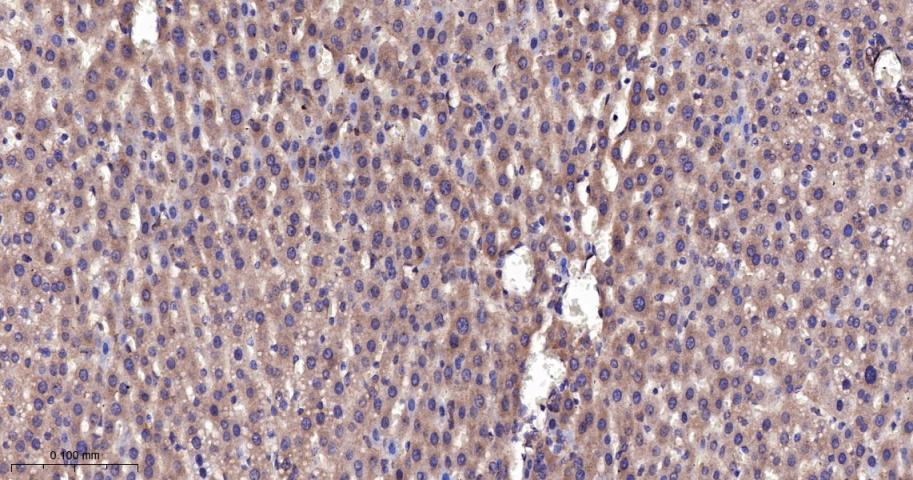
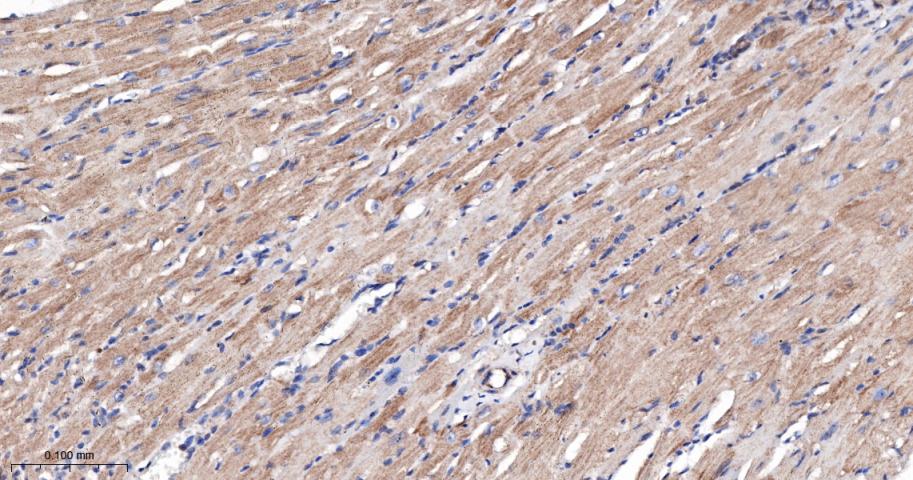
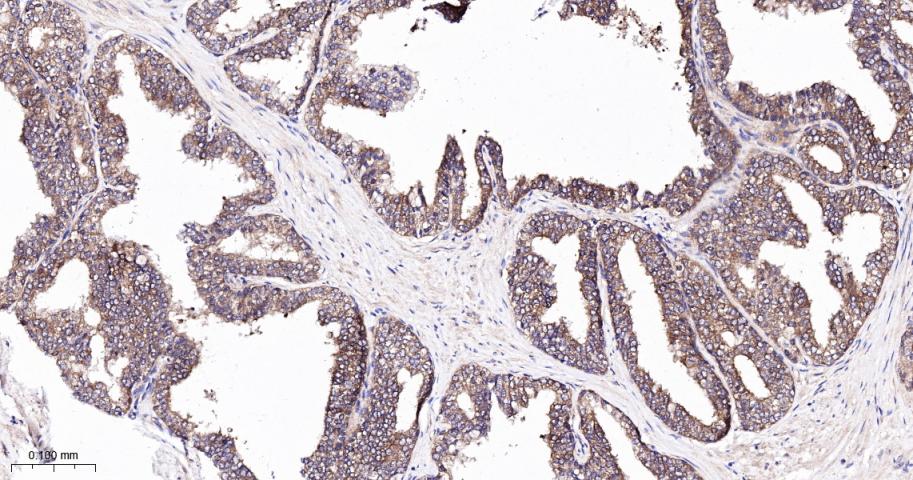
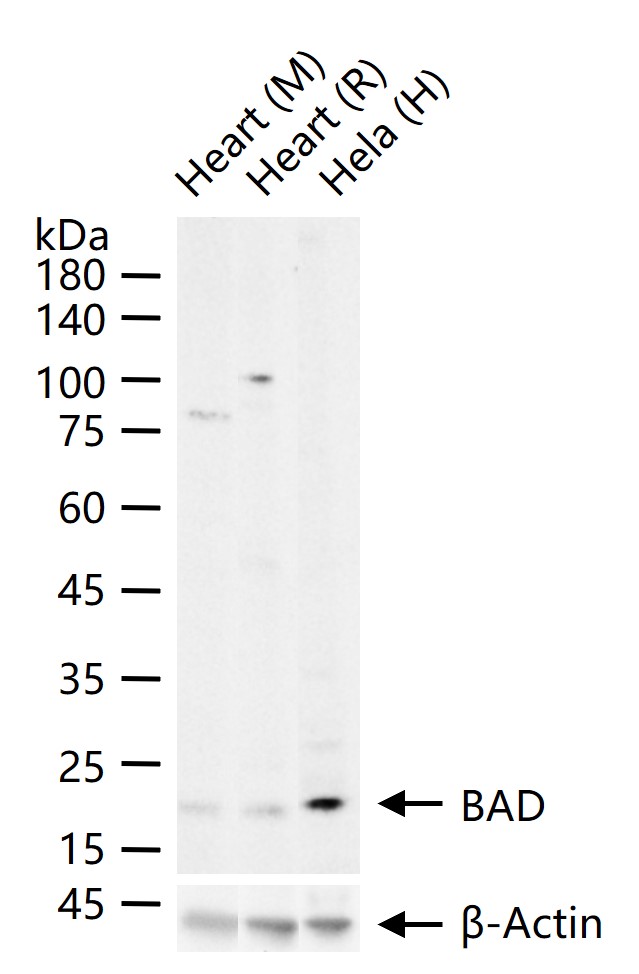
产品应用
| 应用 | 已检合格种属 | 预测种属 | 推荐稀释比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| WB | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:500-2000 | |
| IHC-P | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:100-500 | |
| IHC-F | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:100-500 | |
| IF | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:100-500 |
交叉反应
交叉反应: Human, Mouse, Rat
相关产品
暂无相关产品
靶标
基因名
BAD
蛋白名
Bcl2-associated agonist of cell death
亚基
Forms heterodimers with the anti-apoptotic proteins, Bcl-X(L), Bcl-2 and Bcl-W. Also binds protein S100A10 (By similarity). The Ser-75/Ser-99 phosphorylated form binds 14-3-3 proteins (By similarity). Interacts with AKT1 and PIM3.
亚细胞定位
Mitochondrion outer membrane. Cytoplasm. Note=Upon phosphorylation, locates to the cytoplasm.
组织特异性
Expressed in a wide variety of tissues.
翻译后修饰
Phosphorylated on one or more of Ser-75, Ser-99, Ser-118 and Ser-134 in response to survival stimuli, which blocks its pro-apoptotic activity.
Phosphorylation on Ser-99 or Ser-75 promotes heterodimerization with 14-3-3 proteins. This interaction then facilitates the phosphorylation at Ser-118, a site within the BH3 motif, leading to the release of Bcl-X(L) and the promotion of cell survival. Ser-99 is the major site of AKT/PKB phosphorylation, Ser-118 the major site of protein kinase A (CAPK) phosphorylation. Ser-75 is phosphorylated by AKT/PKB, protein kinase A and PIM2.
Phosphorylation on Ser-99 or Ser-75 promotes heterodimerization with 14-3-3 proteins. This interaction then facilitates the phosphorylation at Ser-118, a site within the BH3 motif, leading to the release of Bcl-X(L) and the promotion of cell survival. Ser-99 is the major site of AKT/PKB phosphorylation, Ser-118 the major site of protein kinase A (CAPK) phosphorylation. Ser-75 is phosphorylated by AKT/PKB, protein kinase A and PIM2.
相似性
Belongs to the Bcl-2 family.
功能
Promotes cell death. Successfully competes for the binding to Bcl-X(L), Bcl-2 and Bcl-W, thereby affecting the level of heterodimerization of these proteins with BAX. Can reverse the death repressor activity of Bcl-X(L), but not that of Bcl-2 (By similarity). Appears to act as a link between growth factor receptor signaling and the apoptotic pathways.
标记抗体
暂无标记数据
同靶标产品
暂无同靶标产品
相关文献
提示: 发表研究结果有使用 bsm-63058R 时请让我们知道,以便我们可以引用参考文章。作为回馈,资料提供者将获得我们送上的小礼品。
暂无相关文献
常见问题
暂无常见问题