苯丙氨酸羟化酶4重组兔单抗
Rrmab?兔单抗
货号:bsm-62685R
产品详情
相关标记
相关产品
相关文献
常见问题
概述
产品编号
bsm-62685R
产品类型
重组兔单抗、mIHC精品抗体
英文名称
PAH Recombinant Rabbit mAb
中文名称
苯丙氨酸羟化酶4重组兔单抗
英文别名
PH; PKU; PKU1; PH4H_HUMAN; PAH; Phe-4-monooxygenase; 1.14.16.1; PH4H_MOUSE; PH4H_RAT;
抗体来源
Rabbit
免疫原
A synthesized peptide derived from human PAH: 50-100
亚型
IgG
性状
Liquid
纯化方法
affinity purified by Protein A
克隆类型
Recombinant
克隆号
4H12
理论分子量
52 kDa
检测分子量
48 kDa
储存液
10mM phosphate buffered saline(pH 7.4) with 150mM sodium chloride, 0.05% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% glycerol.
研究领域
SWISS
Gene ID
保存条件
Store at 4℃ for short term. Store at -20℃ for long term. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
注意事项
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
数据库链接
背景资料
Catalyzes the hydroxylation of L-phenylalanine to L-tyrosine.

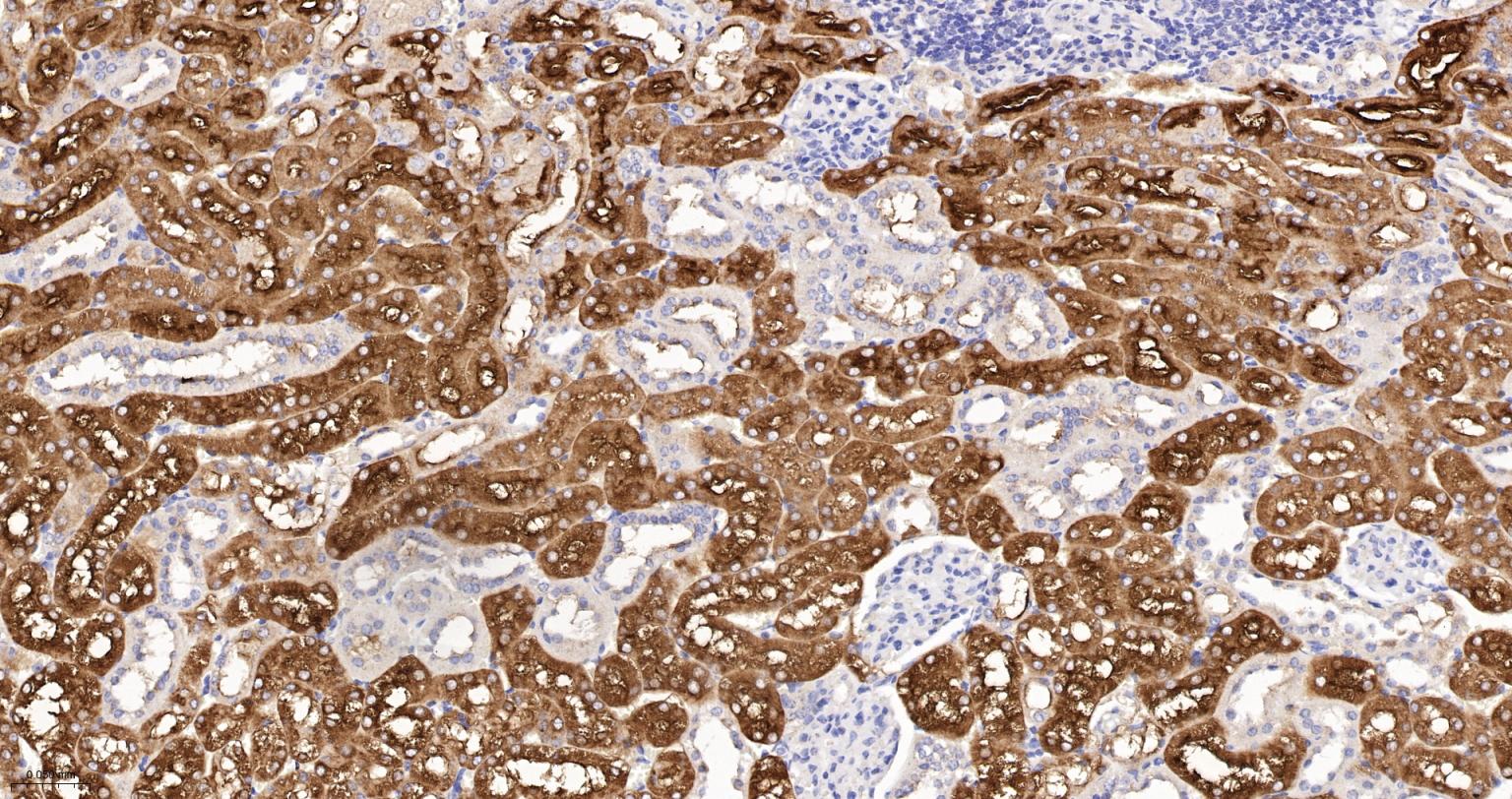
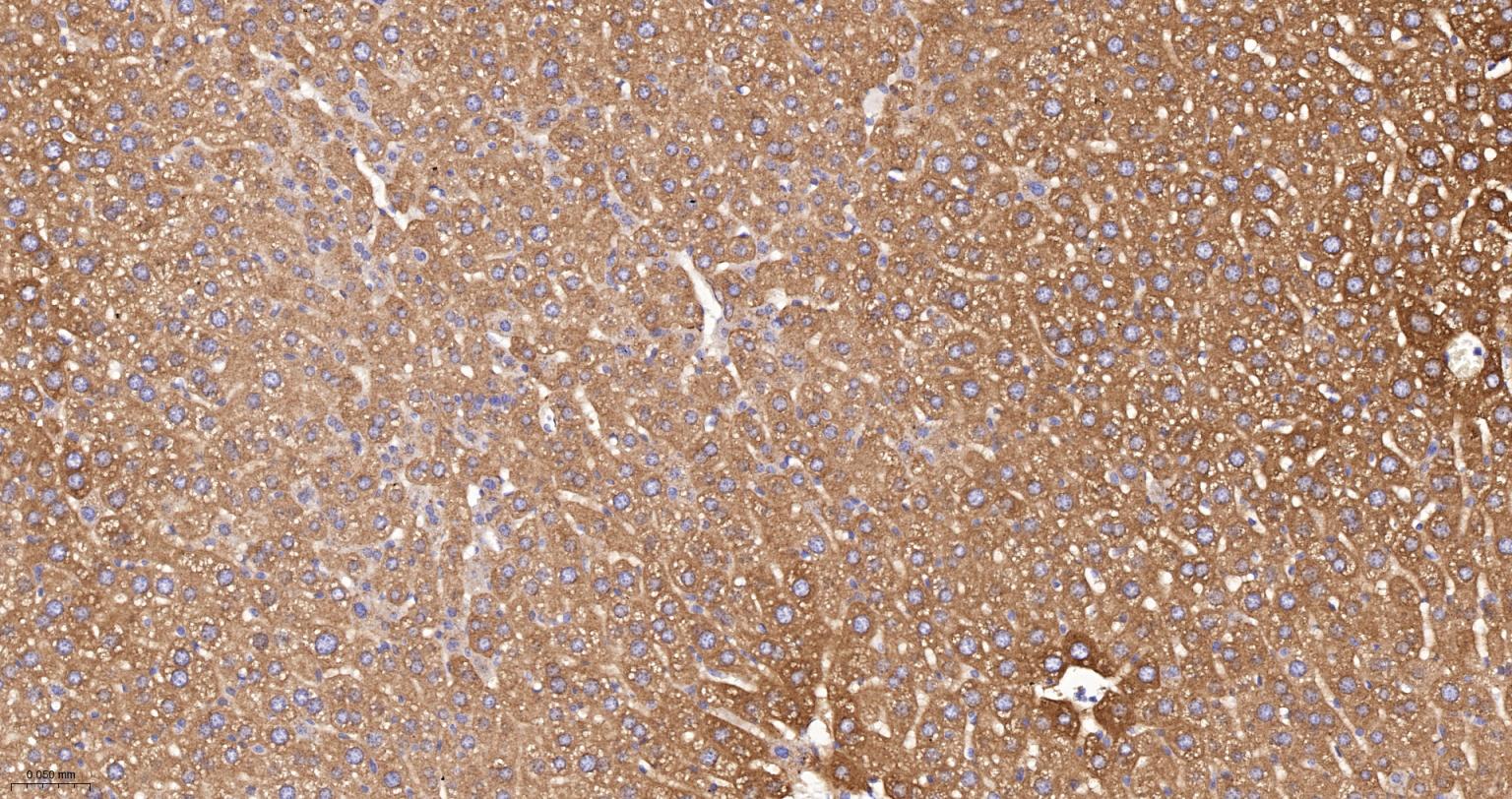
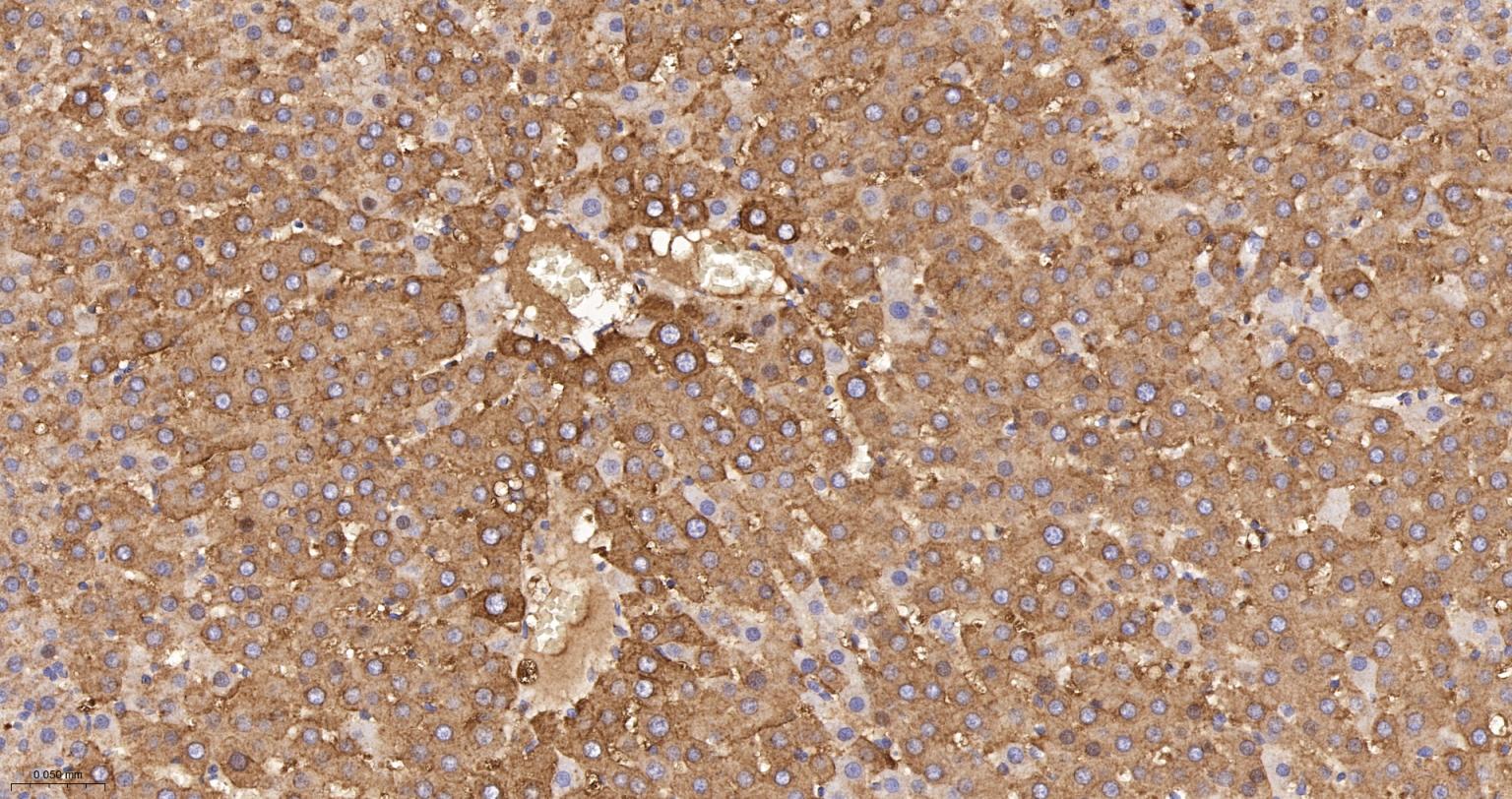
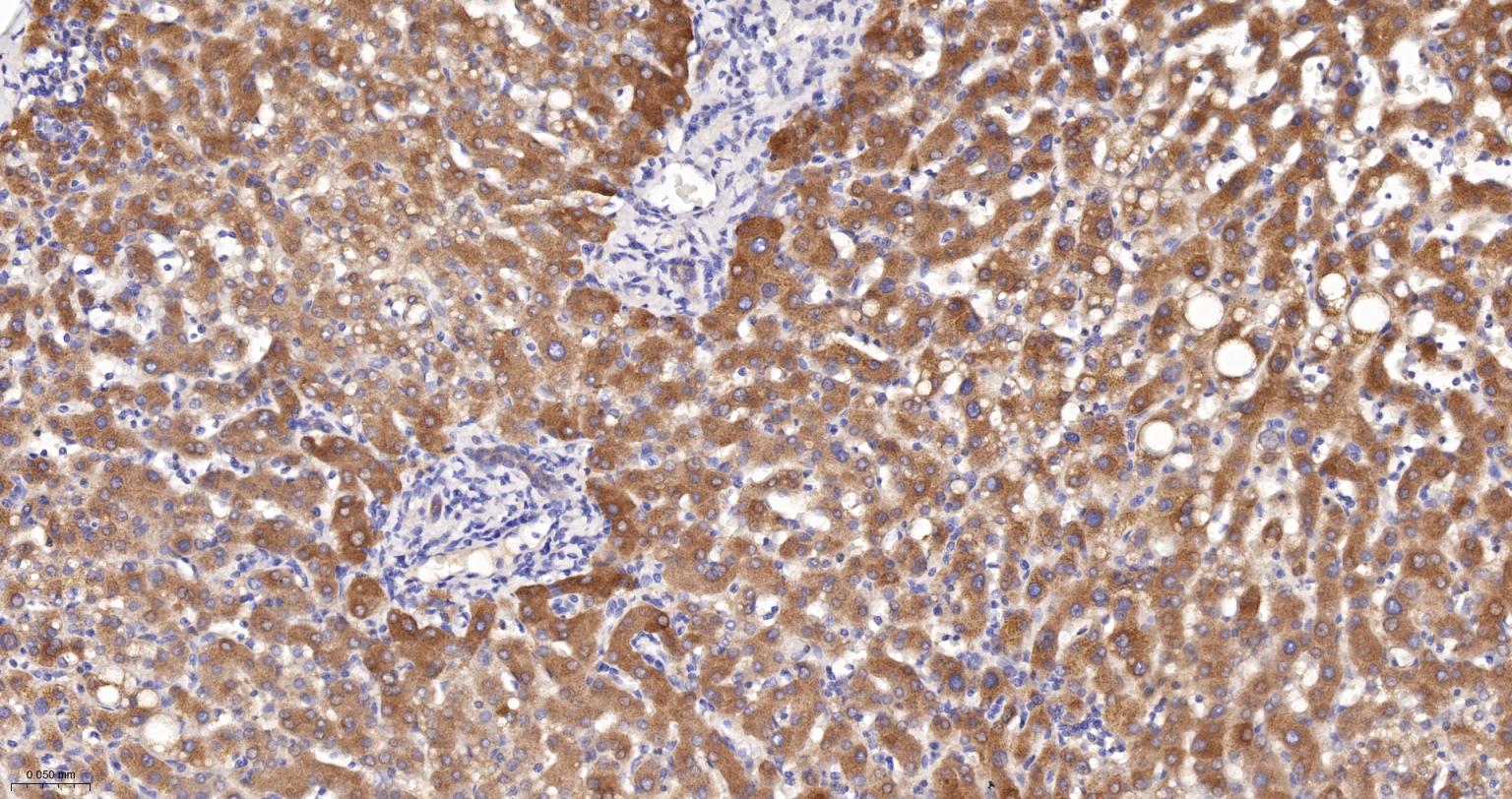
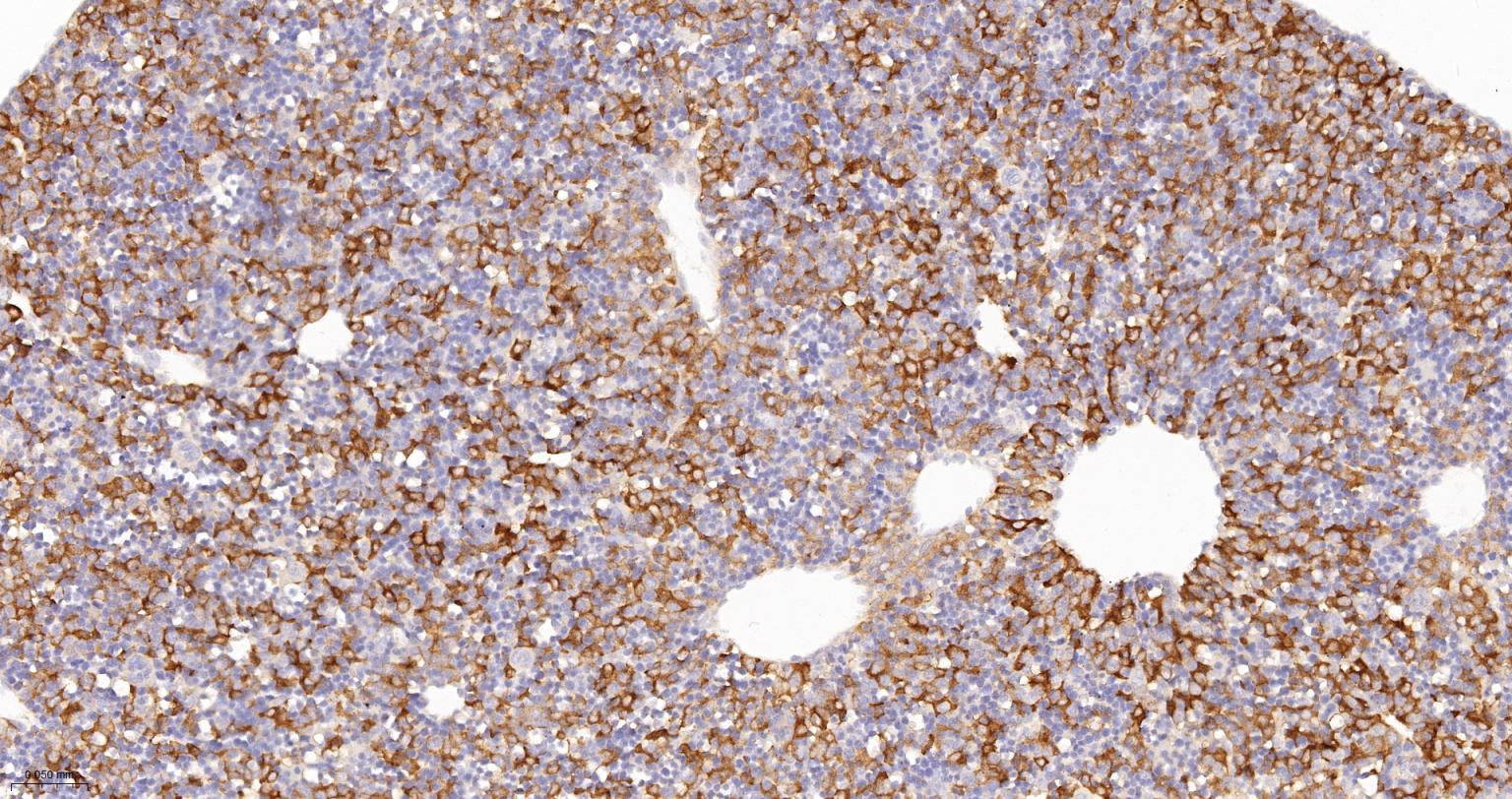
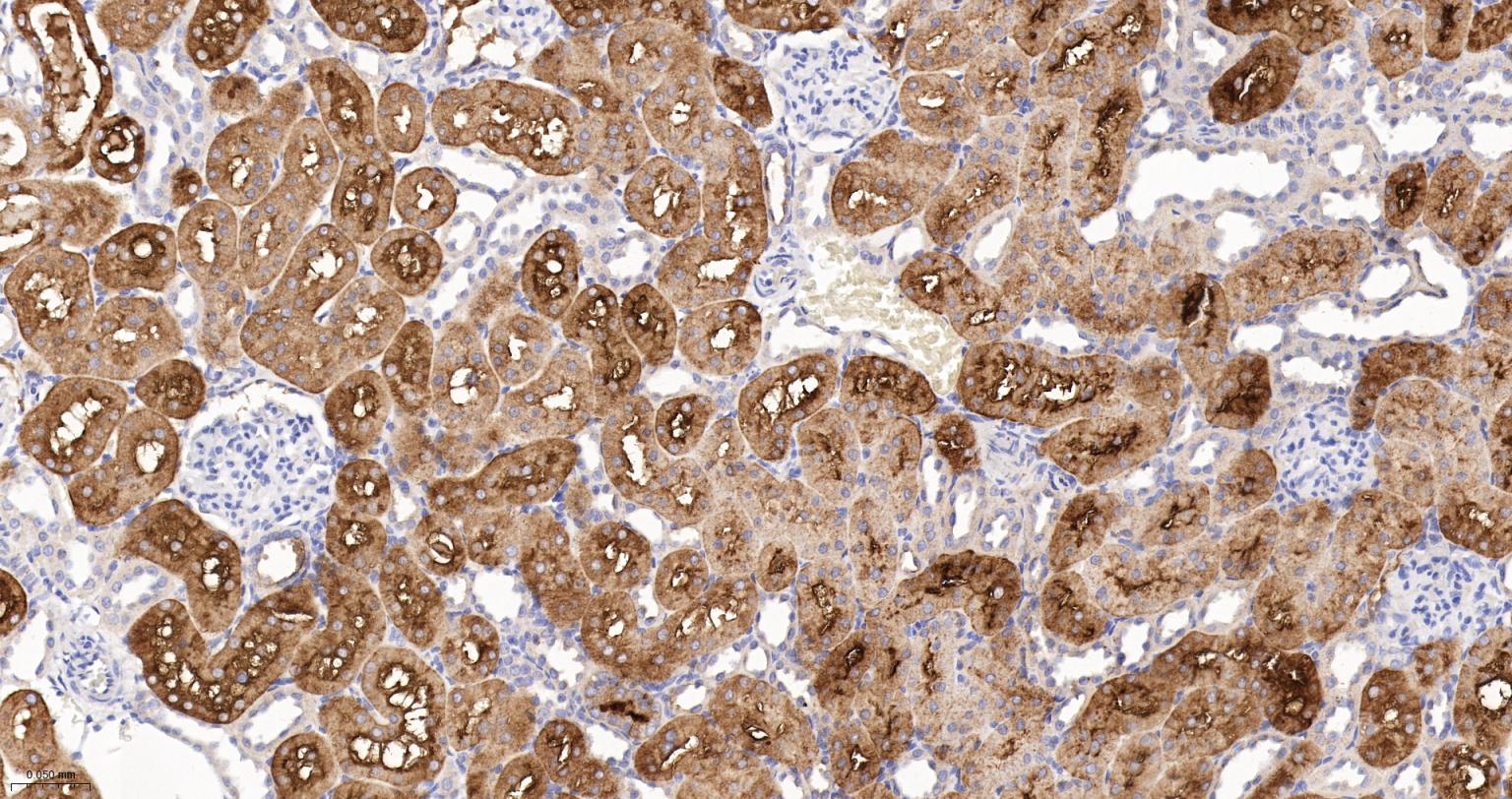
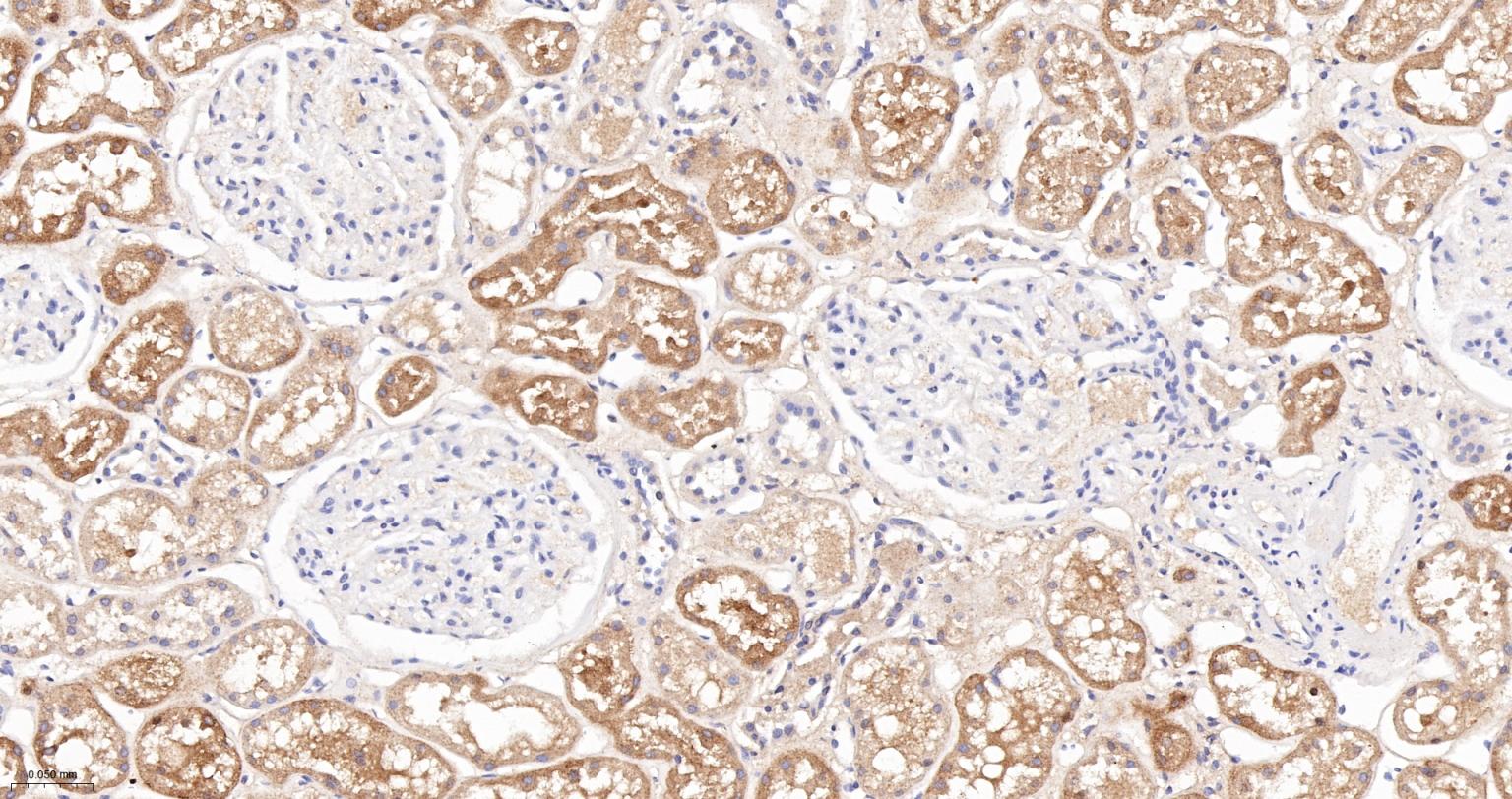
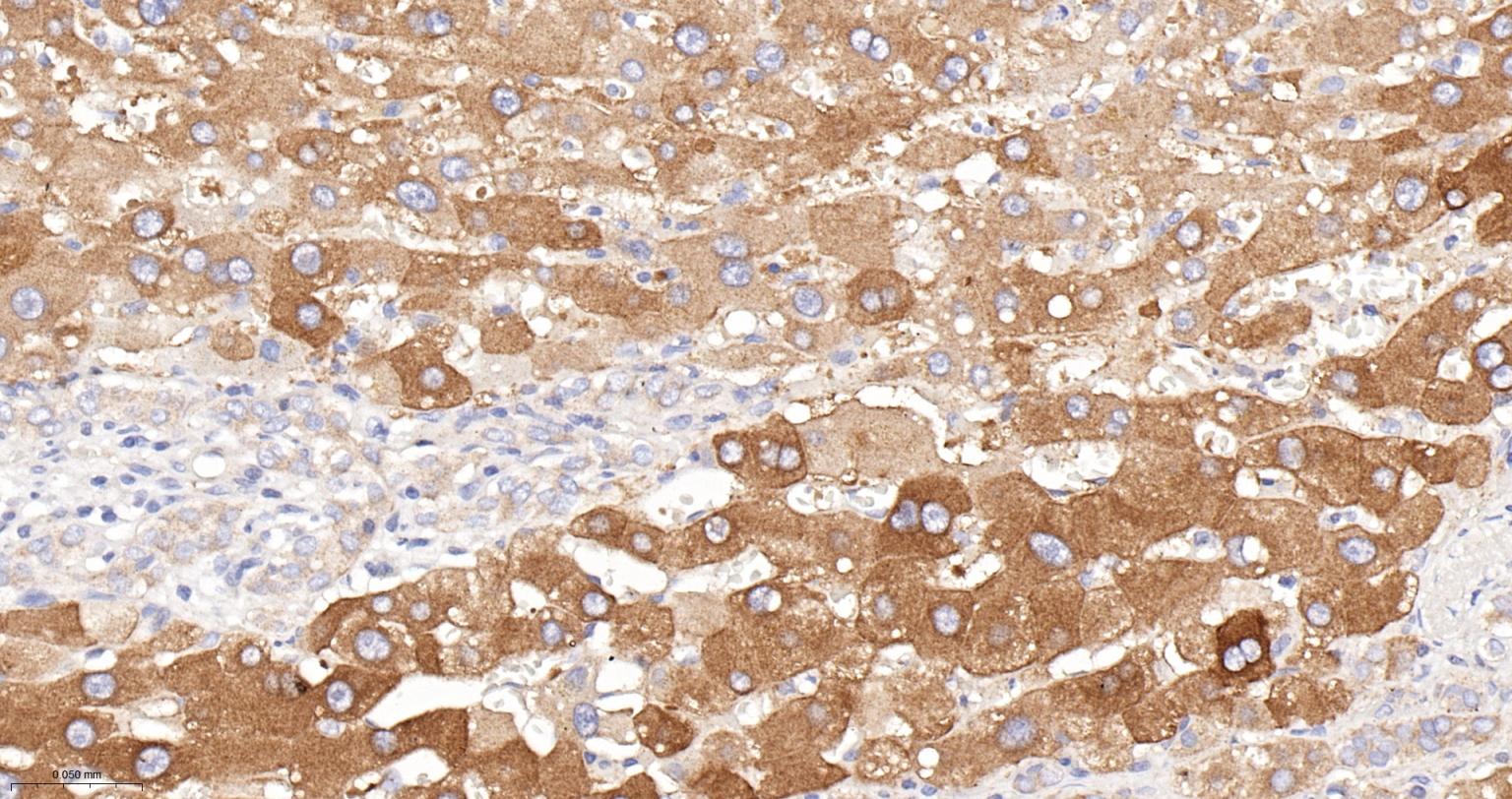
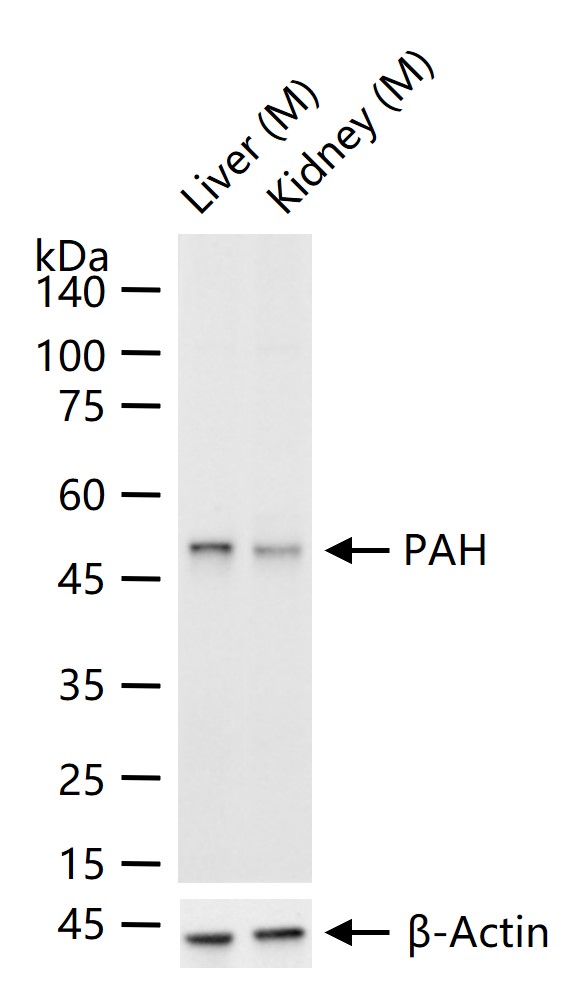
产品应用
| 应用 | 已检合格种属 | 预测种属 | 推荐稀释比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| WB | Mouse | Human, Rat | 1:500-2000 |
| IHC-P | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:100-200 | |
| IHC-F | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:100-200 | |
| IF | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:100-200 |
交叉反应
交叉反应: Human, Mouse, Rat
相关产品
暂无相关产品
靶标
基因名
PAH
蛋白名
Phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase
亚基
Homodimer and homotetramer.
组织特异性
Optimum temperature is 50 degrees Celsius.
疾病
Defects in PAH are the cause of phenylketonuria (PKU) [MIM:261600]. PKU is an autosomal recessive inborn error of phenylalanine metabolism, due to severe phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. It is characterized by blood concentrations of phenylalanine persistently above 1200 mumol (normal concentration 100 mumol) which usually causes mental retardation (unless low phenylalanine diet is introduced early in life). They tend to have light pigmentation, rashes similar to eczema, epilepsy, extreme hyperactivity, psychotic states and an unpleasant 'mousy' odor.
Defects in PAH are the cause of non-phenylketonuria hyperphenylalaninemia (Non-PKU HPA) [MIM:261600]. Non-PKU HPA is a mild form of phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency characterized by phenylalanine levels persistently below 600 mumol, which allows normal intellectual and behavioral development without treatment. Non-PKU HPA is usually caused by the combined effect of a mild hyperphenylalaninemia mutation and a severe one.
Defects in PAH are the cause of hyperphenylalaninemia (HPA) [MIM:261600]. HPA is the mildest form of phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency.
Defects in PAH are the cause of non-phenylketonuria hyperphenylalaninemia (Non-PKU HPA) [MIM:261600]. Non-PKU HPA is a mild form of phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency characterized by phenylalanine levels persistently below 600 mumol, which allows normal intellectual and behavioral development without treatment. Non-PKU HPA is usually caused by the combined effect of a mild hyperphenylalaninemia mutation and a severe one.
Defects in PAH are the cause of hyperphenylalaninemia (HPA) [MIM:261600]. HPA is the mildest form of phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency.
相似性
Belongs to the biopterin-dependent aromatic amino acid hydroxylase family.
Contains 1 ACT domain.
标记抗体
暂无标记数据
同靶标产品
暂无同靶标产品
相关文献
提示: 发表研究结果有使用 bsm-62685R 时请让我们知道,以便我们可以引用参考文章。作为回馈,资料提供者将获得我们送上的小礼品。
暂无相关文献
常见问题
暂无常见问题