血栓调节蛋白重组兔单抗
Rrmab?兔单抗
货号:bsm-62575R
产品详情
相关标记
相关产品
相关文献
常见问题
概述
产品编号
bsm-62575R
产品类型
重组兔单抗
英文名称
Thrombomodulin Recombinant Rabbit mAb
中文名称
血栓调节蛋白重组兔单抗
英文别名
AHUS6; BDCA-3; BDCA3; CD141; THPH12; THRM; TM; TRBM_HUMAN; THBD; Fetomodulin; TRBM_MOUSE;
抗体来源
Rabbit
免疫原
A synthesized peptide derived from mouse Thrombomodulin: 300-550
亚型
IgG
性状
Liquid
纯化方法
affinity purified by Protein A
克隆类型
Recombinant
克隆号
6E1
理论分子量
62 kDa
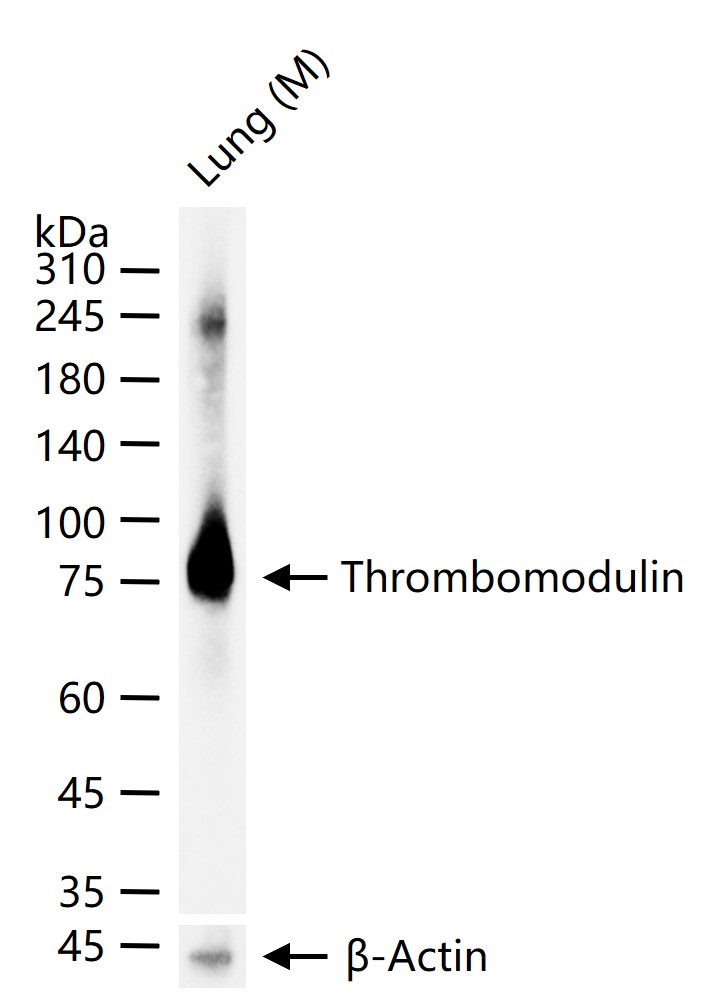
检测分子量
105,70 kDa
储存液
10mM phosphate buffered saline(pH 7.4) with 150mM sodium chloride, 0.05% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% glycerol.
研究领域
SWISS
Gene ID
保存条件
Store at 4℃ for short term. Store at -20℃ for long term. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
注意事项
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
数据库链接
产品介绍
血栓调节蛋白(thrombomodulin,TM)是一种分布于静脉、动脉和毛细血管内皮细胞表面的质膜蛋白。 一般认为:TM是血管内皮损伤的重要参数,也是凝血酶的受体,已知在人类多种正常组织中表达,亦可表达于许多肿瘤组织,TM可能类似于钙粘蛋白,是具有凝集素样活性的新一类细胞粘附分子的成员。TM是血管内皮细胞膜上的凝血酶受体之一。与凝血酶结合后可降低凝血酶的凝血活性,而加强其激活蛋白C的活性。由于被激活的蛋白C具有抗凝作用,因此,TM是使凝血酶由促凝转向抗凝的重要的血管内凝血抑制因子。
背景资料
Thrombomodulin is a specific endothelial cell receptor that forms a 1:1 stoichiometric complex with thrombin. This complex is responsible for the conversion of protein C to the activated protein C (protein Ca). Once evolved, protein Ca scissions the activated cofactors of the coagulation mechanism, factor Va and factor VIIIa, and thereby reduces the amount of thrombin generated.

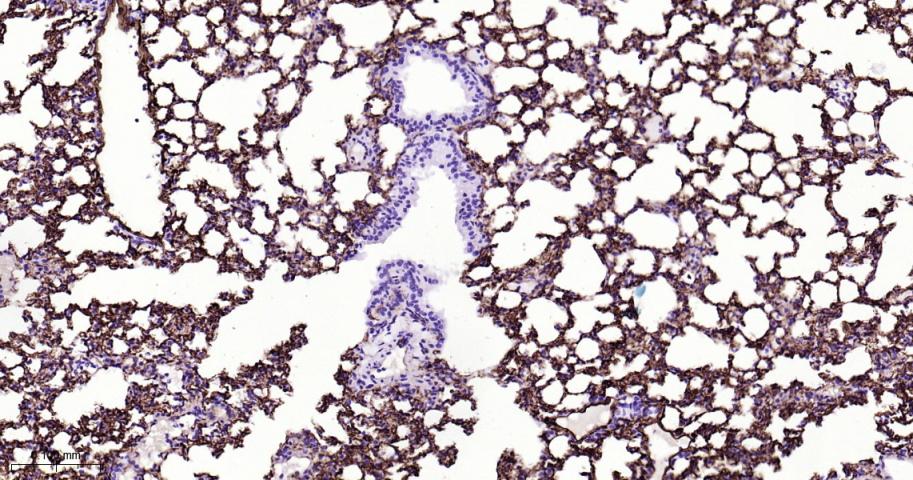
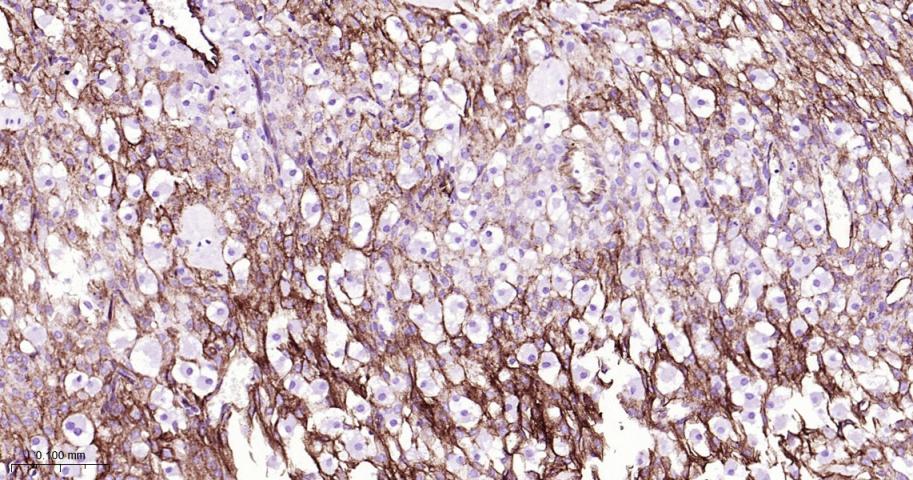
产品应用
| 应用 | 已检合格种属 | 预测种属 | 推荐稀释比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| WB | Mouse | 1:500-2000 | |
| IHC-P | Mouse | 1:100-500 | |
| IHC-F | Mouse | 1:100-500 | |
| IF | Mouse | 1:100-500 | |
| Flow-Cyt | Mouse | 1:50-100 |
交叉反应
交叉反应: Mouse
相关产品
暂无相关产品
靶标
基因名
THBD
蛋白名
Thrombomodulin
亚细胞定位
Membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.
组织特异性
Endothelial cells are unique in synthesizing thrombomodulin.
翻译后修饰
N-glycosylated.
The iron and 2-oxoglutarate dependent 3-hydroxylation of aspartate and asparagine is (R) stereospecific within EGF domains.
The iron and 2-oxoglutarate dependent 3-hydroxylation of aspartate and asparagine is (R) stereospecific within EGF domains.
疾病
Defects in THBD are the cause of thrombophilia due to thrombomodulin defect (THPH12) [MIM:614486]. A hemostatic disorder characterized by a tendency to thrombosis.
Defects in THBD are a cause of susceptibility to hemolytic uremic syndrome atypical type 6 (AHUS6) [MIM:612926]. An atypical form of hemolytic uremic syndrome. It is a complex genetic disease characterized by microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, renal failure and absence of episodes of enterocolitis and diarrhea. In contrast to typical hemolytic uremic syndrome, atypical forms have a poorer prognosis, with higher death rates and frequent progression to end-stage renal disease. Note=Susceptibility to the development of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome can be conferred by mutations in various components of or regulatory factors in the complement cascade system. Other genes may play a role in modifying the phenotype.
Defects in THBD are a cause of susceptibility to hemolytic uremic syndrome atypical type 6 (AHUS6) [MIM:612926]. An atypical form of hemolytic uremic syndrome. It is a complex genetic disease characterized by microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, renal failure and absence of episodes of enterocolitis and diarrhea. In contrast to typical hemolytic uremic syndrome, atypical forms have a poorer prognosis, with higher death rates and frequent progression to end-stage renal disease. Note=Susceptibility to the development of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome can be conferred by mutations in various components of or regulatory factors in the complement cascade system. Other genes may play a role in modifying the phenotype.
相似性
Contains 1 C-type lectin domain.
Contains 6 EGF-like domains.
Contains 6 EGF-like domains.
功能
Thrombomodulin is a specific endothelial cell receptor that forms a 1:1 stoichiometric complex with thrombin. This complex is responsible for the conversion of protein C to the activated protein C (protein Ca). Once evolved, protein Ca scissions the activated cofactors of the coagulation mechanism, factor Va and factor VIIIa, and thereby reduces the amount of thrombin generated.
标记抗体
暂无标记数据
同靶标产品
暂无同靶标产品
相关文献
提示: 发表研究结果有使用 bsm-62575R 时请让我们知道,以便我们可以引用参考文章。作为回馈,资料提供者将获得我们送上的小礼品。
暂无相关文献
常见问题
暂无常见问题