脊髓灰质炎病毒受体重组兔单抗
Rrmab?兔单抗
货号:bsm-62186R
产品详情
相关标记
相关产品
相关文献
常见问题
概述
产品编号
bsm-62186R
产品类型
重组兔单抗
英文名称
CD155 Recombinant Rabbit mAb
中文名称
脊髓灰质炎病毒受体重组兔单抗
英文别名
CD155; HVED; NECL5; Necl-5; PVS; TAGE4; 3830421F03Rik; D7Ertd458e; Taa1; mE4; PVR_HUMAN; PVR; Nectin-like protein 5 (NECL-5);
抗体来源
Rabbit
免疫原
A synthesized peptide derived from human CD155: 220-350/417
亚型
IgG
性状
Liquid
纯化方法
affinity purified by Protein A
克隆类型
Recombinant
克隆号
6H7
理论分子量
45 kDa
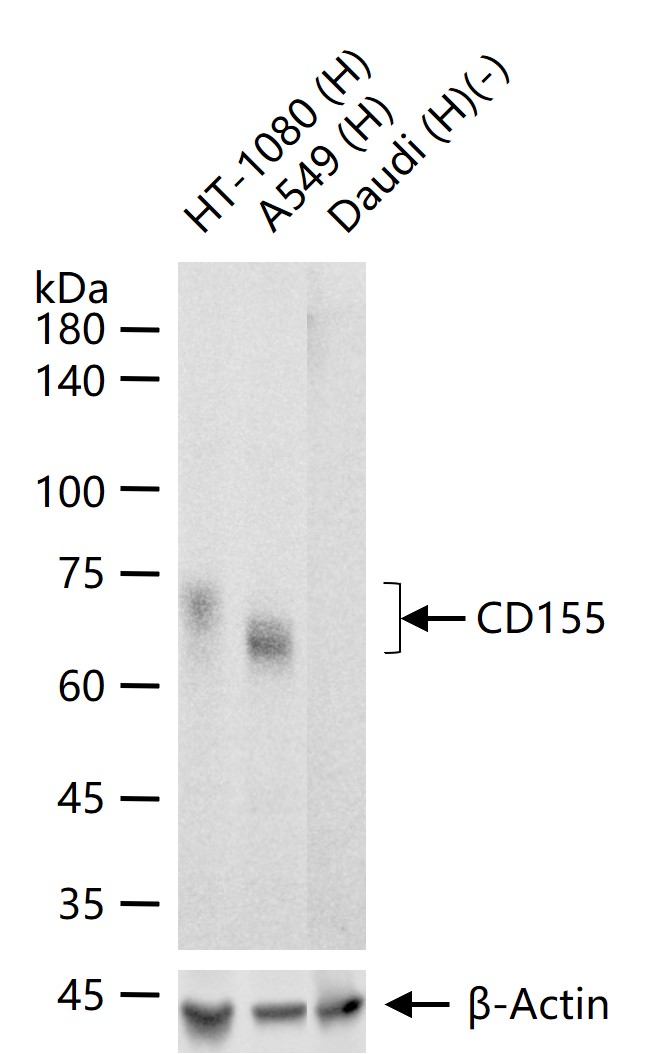
检测分子量
70 kDa
储存液
10mM phosphate buffered saline(pH 7.4) with 150mM sodium chloride, 0.05% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% glycerol.
SWISS
Gene ID
保存条件
Store at 4℃ for short term. Store at -20℃ for long term. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
注意事项
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
数据库链接
背景资料
Mediates NK cell adhesion and triggers NK cell effector functions. Binds two different NK cell receptors: CD96 and CD226. These interactions accumulates at the cell-cell contact site, leading to the formation of a mature immunological synapse between NK cell and target cell.

产品应用
| 应用 | 已检合格种属 | 预测种属 | 推荐稀释比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| WB | Human | 1:500-2000 | |
| IP | Human | 1:20-50 |
交叉反应
交叉反应: Human
相关产品
暂无相关产品
靶标
基因名
PVR
蛋白名
Poliovirus receptor
亚基
Can form trans-heterodimers with PVRL3/nectin-3. The extracellular domain interacts with VTN, CD226 and CD96. The cytoplasmic domain interacts with DYNLT1. Interacts with HHV-5 UL141. Interacts with poliovirus capsid composed of VP1, VP2 and VP3, mainly through VP3. Binds with high affinity to TIGIT.
亚细胞定位
Isoform Alpha: Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Isoform Delta: Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Isoform Beta: Secreted. Isoform Gamma: Secreted.
翻译后修饰
N-glycosylated. N-glycan at Asn-120: Hex5HexNAc4.
相似性
Belongs to the nectin family.
Contains 2 Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains.
Contains 1 Ig-like V-type (immunoglobulin-like) domain.
Contains 2 Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains.
Contains 1 Ig-like V-type (immunoglobulin-like) domain.
功能
Mediates NK cell adhesion and triggers NK cell effector functions. Binds two different NK cell receptors: CD96 and CD226. These interactions accumulates at the cell-cell contact site, leading to the formation of a mature immunological synapse between NK cell and target cell. This may trigger adhesion and secretion of lytic granules and IFN-gamma and activate cytoxicity of activated NK cells. May also promote NK cell-target cell modular exchange, and PVR transfer to the NK cell. This transfer is more important in some tumor cells expressing a lot of PVR, and may trigger fratricide NK cell activation, providing tumors with a mechanism of immunoevasion. Plays a role in mediating tumor cell invasion and migration. Serves as a receptor for poliovirus attachment to target cells. May play a role in axonal transport of poliovirus, by targeting virion-PVR-containing endocytic vesicles to the microtubular network through interaction with DYNLT1. This interaction would drive the virus-containing vesicle to the axonal retrograde transport.
标记抗体
暂无标记数据
同靶标产品
暂无同靶标产品
相关文献
提示: 发表研究结果有使用 bsm-62186R 时请让我们知道,以便我们可以引用参考文章。作为回馈,资料提供者将获得我们送上的小礼品。
暂无相关文献
常见问题
暂无常见问题