酸性成纤维细胞生长因子重组兔单抗
Rrmab?兔单抗
货号:bsm-61826R
产品详情
相关标记
相关产品
相关文献
常见问题
概述
产品编号
bsm-61826R
产品类型
重组兔单抗
英文名称
FGF1 Recombinant Rabbit mAb
中文名称
酸性成纤维细胞生长因子重组兔单抗
英文别名
AFGF; ECGF; ECGF-beta; ECGFA; ECGFB; FGF-1; FGF-alpha; FGFA; GLIO703; HBGF-1; HBGF1; Fgf2b; Dffrx; Fam; FGF1_HUMAN; FGF1; Acidic fibroblast growth factor (aFGF); Endothelial cell growth factor (ECGF); Heparin-binding growth factor 1 (HBGF-1); FGF1_RAT; FGF1_MOUSE;
抗体来源
Rabbit
免疫原
A synthesized peptide derived from human FGF1: 130-155
亚型
IgG
性状
Liquid
纯化方法
affinity purified by Protein A
克隆类型
Recombinant
克隆号
6H8
理论分子量
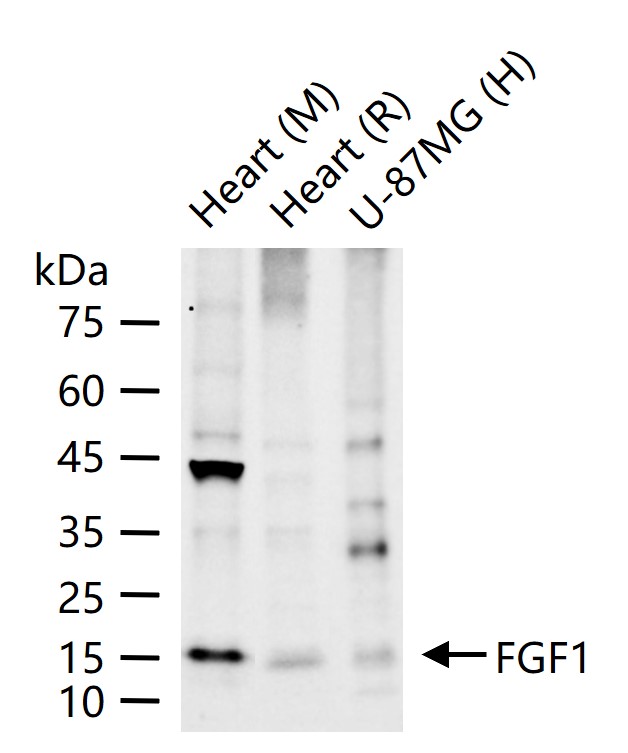
17 kDa
检测分子量
17 kDa
储存液
10mM phosphate buffered saline(pH 7.4) with 150mM sodium chloride, 0.05% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% glycerol.
研究领域
SWISS
Gene ID
保存条件
Store at 4℃ for short term. Store at -20℃ for long term. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
注意事项
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
数据库链接
产品介绍
生长因子和激素( Growth Factor and Hormones)
肝素结合生长因子(FGF1)可与肝素结合是血管生成剂,还是多种细胞强的促细胞分裂剂,可刺激多种中胚层细胞的生长包括软骨细胞、粒细胞和内皮细胞,在创伤愈合及动物肢体再生中可能起作用。在不同的组织中分布和含量不同,以单体形式存在,属于肝素结合生长因子家族成员之一。
肝素结合生长因子(FGF1)可与肝素结合是血管生成剂,还是多种细胞强的促细胞分裂剂,可刺激多种中胚层细胞的生长包括软骨细胞、粒细胞和内皮细胞,在创伤愈合及动物肢体再生中可能起作用。在不同的组织中分布和含量不同,以单体形式存在,属于肝素结合生长因子家族成员之一。
背景资料
Plays an important role in the regulation of cell survival, cell division, angiogenesis, cell differentiation and cell migration. Functions as a potent mitogen in vitro.

产品应用
| 应用 | 已检合格种属 | 预测种属 | 推荐稀释比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| WB | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:500-2000 |
交叉反应
交叉反应: Human, Mouse, Rat
相关产品
暂无相关产品
靶标
基因名
FGF1
蛋白名
Fibroblast growth factor 1
亚基
Monomer. Homodimer. Interacts with FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3 and FGFR4. Affinity between fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) and their receptors is increased by heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycans that function as coreceptors. Found in a complex with FGFBP1, FGF1 and FGF2. Interacts with FGFBP1. Part of a Cu(2+)-dependent multiprotein aggregate containing FGF1, S100A13 and SYT1. Interacts with SYT1. Interacts with S100A13. Interacts with LRRC59. Interacts with CSNKA, CSNKB and FIBP. While binding with LRRC59, CSNKA and FIBP seem mutually exclusive, CSNKB and FIBP may cooperatively interact with FGF1.
亚细胞定位
Secreted. Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm, cell cortex. Cytoplasm, cytosol. Nucleus. Note=Lacks a cleavable signal sequence. Within the cytoplasm, it is transported to the cell membrane and then secreted by a non-classical pathway that requires Cu(2+) ions and S100A13. Secreted in a complex with SYT1 (By similarity). Binding of exogenous FGF1 to FGFR facilitates endocytosis followed by translocation of FGF1 across endosomal membrane into the cytosol. Nuclear import from the cytosol requires the classical nuclear import machinery, involving proteins KPNA1 and KPNB1, as well as LRRC59.
组织特异性
Predominantly expressed in kidney and brain. Detected at much lower levels in heart and skeletal muscle.
翻译后修饰
In the nucleus, phosphorylated by PKC/PRKCD.
相似性
Belongs to the heparin-binding growth factors family.
功能
The heparin-binding fibroblast growth factors play important roles in the regulation of cell survival, cell division, angiogenesis, cell differentiation and cell migration. They are potent mitogens in vitro.
标记抗体
暂无标记数据
同靶标产品
暂无同靶标产品
相关文献
提示: 发表研究结果有使用 bsm-61826R 时请让我们知道,以便我们可以引用参考文章。作为回馈,资料提供者将获得我们送上的小礼品。
暂无相关文献
常见问题
暂无常见问题