细胞周期检测点激酶2重组兔单抗
Rrmab?兔单抗
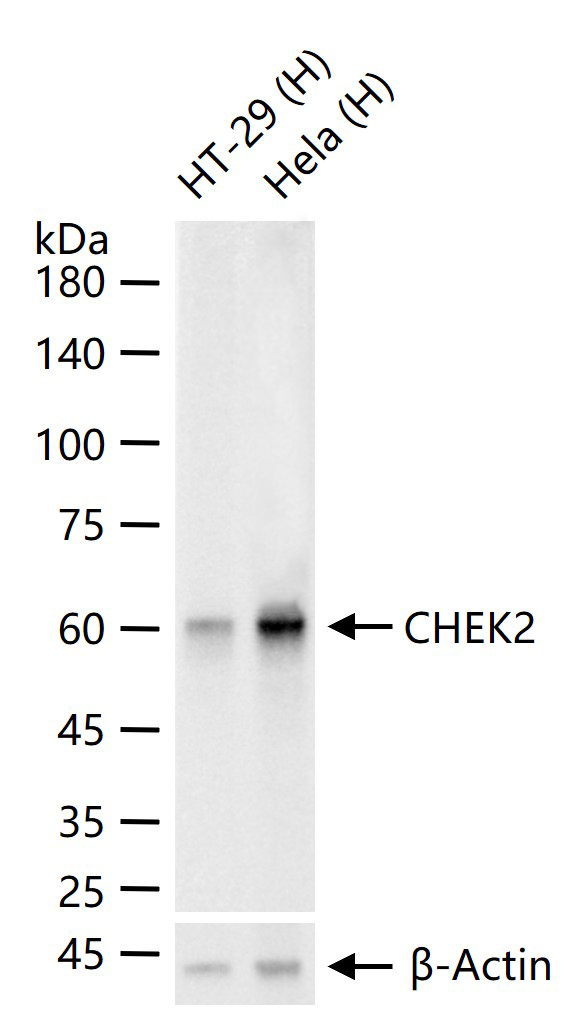
货号:bsm-61562R
产品详情
相关标记
相关产品
相关文献
常见问题
概述
产品编号
bsm-61562R
产品类型
重组兔单抗、mIHC精品抗体
英文名称
CHEK2 Recombinant Rabbit mAb
中文名称
细胞周期检测点激酶2重组兔单抗
英文别名
CDS1; CHK2; HuCds1; LFS2; PP1425; RAD53; TPDS4; hCds1; CHK2_HUMAN; CHEK2; CHK2 checkpoint homolog; Cds1 homolog (Hucds1 | hCds1); Checkpoint kinase 2; 2.7.11.1; CHK2_MOUSE; Q9R019_RAT;
抗体来源
Rabbit
免疫原
A synthesized peptide derived from human Chk2: 30-180
亚型
IgG
性状
Liquid
纯化方法
affinity purified by Protein A
克隆类型
Recombinant
克隆号
7D13
理论分子量
61 kDa
检测分子量
62 kDa
储存液
10mM phosphate buffered saline(pH 7.4) with 150mM sodium chloride, 0.05% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% glycerol.
研究领域
SWISS
Gene ID
保存条件
Store at 4℃ for short term. Store at -20℃ for long term. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
注意事项
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
数据库链接
产品介绍
Chk2作为Cdks的调节参与细胞周期调节过程,是生物进化过程中非常保守的蛋白激酶,在DNA损伤引起的细胞周期检测点调节中有着非常重要的作用。
背景资料
Serine/threonine-protein kinase which is required for checkpoint-mediated cell cycle arrest, activation of DNA repair and apoptosis in response to the presence of DNA double-strand breaks.

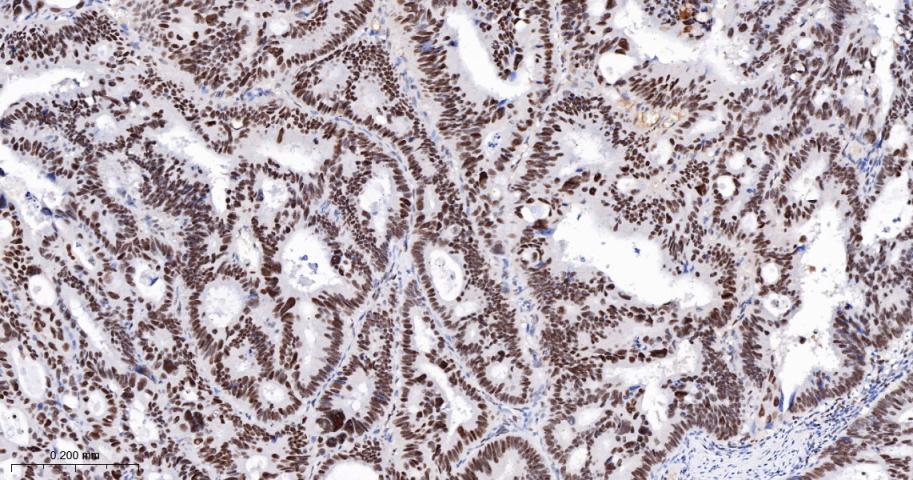
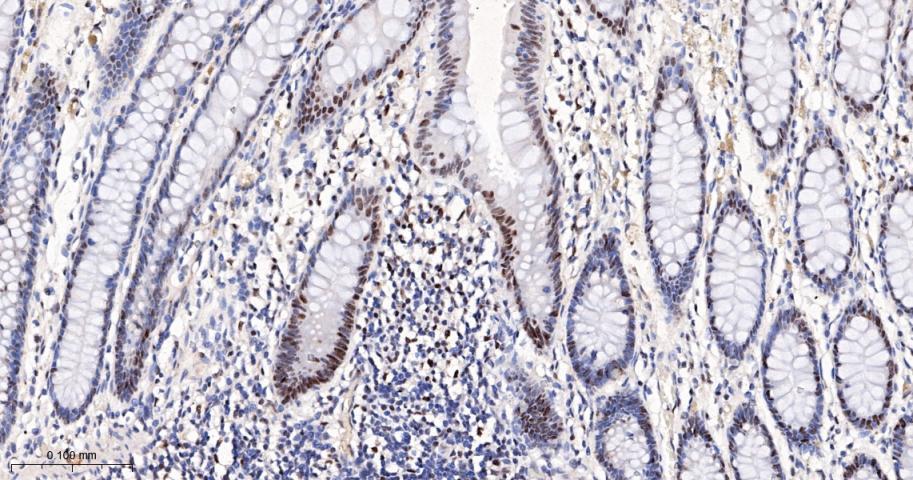
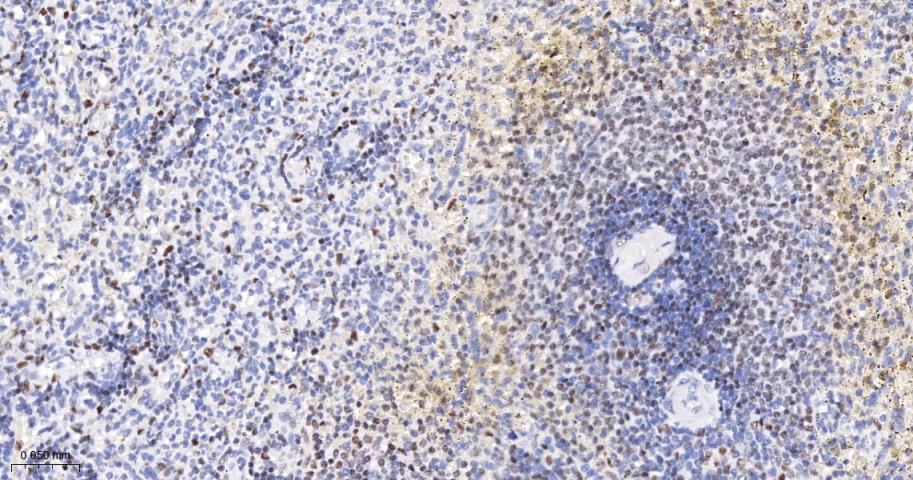
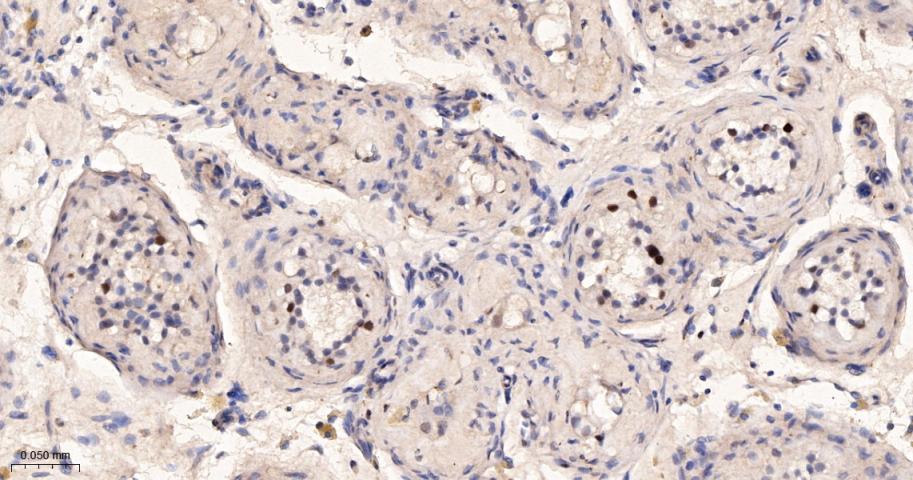
产品应用
| 应用 | 已检合格种属 | 预测种属 | 推荐稀释比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| WB | Human | 1:500-2000 | |
| IHC-P | Human | 1:100-500 | |
| IHC-F | Human | 1:100-500 | |
| IF | Human | 1:100-500 | |
| ICC/IF | Human | 1:50-200 | |
| IP | Human | 1:20-50 |
交叉反应
交叉反应: Human
相关产品
暂无相关产品
靶标
基因名
CHEK2
蛋白名
Serine/threonine-protein kinase Chk2
亚基
Homodimer. Homodimerization is part of the activation process but the dimer may dissociate following activation. Interacts with PML. Interacts with TP53. Interacts with RB1; phosphorylates RB1. Interacts with BRCA1. Interacts (phosphorylated at Thr-68) with MDC1; requires ATM-mediated phosphorylation of CHEK2. Interacts with TP53BP1; modulates CHEK2 phosphorylation at Thr-68 in response to ionizing radiation. Interacts with CDC25A; phosphorylates CDC25A and mediates its degradation in response to ionizing radiation. Interacts with CUL1; mediates CHEK2 ubiquitination and regulation.
亚细胞定位
Isoform 2: Nucleus. Note=Isoform 10 is present throughout the cell.
Isoform 4: Nucleus.
Isoform 7: Nucleus.
Isoform 9: Nucleus.
Isoform 12: Nucleus.
Nucleus, PML body. Nucleus, nucleoplasm. Note=Recruited into PML bodies together with TP53.
Isoform 4: Nucleus.
Isoform 7: Nucleus.
Isoform 9: Nucleus.
Isoform 12: Nucleus.
Nucleus, PML body. Nucleus, nucleoplasm. Note=Recruited into PML bodies together with TP53.
组织特异性
High expression is found in testis, spleen, colon and peripheral blood leukocytes. Low expression is found in other tissues.
翻译后修饰
Phosphorylated. Phosphorylated at Ser-73 by PLK3 in response to DNA damage, promoting phosphorylation at Thr-68 by ATM and the G2/M transition checkpoint. Phosphorylation at Thr-68 induces homodimerization. Autophosphorylates at Thr-383 and Thr-387 in the T-loop/activation segment upon dimerization to become fully active and phosphorylate its substrates like for instance CDC25C. DNA damage-induced autophosphorylation at Ser-379 induces CUL1-mediated ubiquitination and regulates the pro-apoptotic function. Phosphorylation at Ser-456 also regulates ubiquitination. Phosphorylated by PLK4.
Ubiquitinated. CUL1-mediated ubiquitination regulates the pro-apoptotic function. Ubiquitination may also regulate protein stability (PubMed:17715138).
Ubiquitinated. CUL1-mediated ubiquitination regulates the pro-apoptotic function. Ubiquitination may also regulate protein stability (PubMed:17715138).
疾病
Defects in CHEK2 are associated with Li-Fraumeni syndrome 2 (LFS2) [MIM:609265]; a highly penetrant familial cancer phenotype usually associated with inherited mutations in p53/TP53.
Defects in CHEK2 may be a cause of susceptibility to prostate cancer (PC) [MIM:176807]. It is a malignancy originating in tissues of the prostate. Most prostate cancers are adenocarcinomas that develop in the acini of the prostatic ducts. Other rare histopathologic types of prostate cancer that occur in approximately 5% of patients include small cell carcinoma, mucinous carcinoma, prostatic ductal carcinoma, transitional cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, adenoid cystic carcinoma (basaloid), signet-ring cell carcinoma and neuroendocrine carcinoma.
Defects in CHEK2 are found in some patients with osteogenic sarcoma (OSRC) [MIM:259500].
Defects in CHEK2 is a cause of susceptibility to breast cancer (BC) [MIM:114480]. A common malignancy originating from breast epithelial tissue. Breast neoplasms can be distinguished by their histologic pattern. Invasive ductal carcinoma is by far the most common type. Breast cancer is etiologically and genetically heterogeneous. Important genetic factors have been indicated by familial occurrence and bilateral involvement. Mutations at more than one locus can be involved in different families or even in the same case. Note=CHEK2 variants are associated with susceptibility to breast cancer and contribute to a substantial fraction of familial breast cancer (PubMed:12094328).
Defects in CHEK2 may be a cause of susceptibility to prostate cancer (PC) [MIM:176807]. It is a malignancy originating in tissues of the prostate. Most prostate cancers are adenocarcinomas that develop in the acini of the prostatic ducts. Other rare histopathologic types of prostate cancer that occur in approximately 5% of patients include small cell carcinoma, mucinous carcinoma, prostatic ductal carcinoma, transitional cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, adenoid cystic carcinoma (basaloid), signet-ring cell carcinoma and neuroendocrine carcinoma.
Defects in CHEK2 are found in some patients with osteogenic sarcoma (OSRC) [MIM:259500].
Defects in CHEK2 is a cause of susceptibility to breast cancer (BC) [MIM:114480]. A common malignancy originating from breast epithelial tissue. Breast neoplasms can be distinguished by their histologic pattern. Invasive ductal carcinoma is by far the most common type. Breast cancer is etiologically and genetically heterogeneous. Important genetic factors have been indicated by familial occurrence and bilateral involvement. Mutations at more than one locus can be involved in different families or even in the same case. Note=CHEK2 variants are associated with susceptibility to breast cancer and contribute to a substantial fraction of familial breast cancer (PubMed:12094328).
相似性
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. CAMK Ser/Thr protein kinase family. CHK2 subfamily.
Contains 1 FHA domain.
Contains 1 protein kinase domain.
Contains 1 FHA domain.
Contains 1 protein kinase domain.
功能
Serine/threonine-protein kinase which is required for checkpoint-mediated cell cycle arrest, activation of DNA repair and apoptosis in response to the presence of DNA double-strand breaks. May also negatively regulate cell cycle progression during unperturbed cell cycles. Following activation, phosphorylates numerous effectors preferentially at the consensus sequence [L-X-R-X-X-S/T]. Regulates cell cycle checkpoint arrest through phosphorylation of CDC25A, CDC25B and CDC25C, inhibiting their activity. Inhibition of CDC25 phosphatase activity leads to increased inhibitory tyrosine phosphorylation of CDK-cyclin complexes and blocks cell cycle progression. May also phosphorylate NEK6 which is involved in G2/M cell cycle arrest. Regulates DNA repair through phosphorylation of BRCA2, enhancing the association of RAD51 with chromatin which promotes DNA repair by homologous recombination. Also stimulates the transcription of genes involved in DNA repair (including BRCA2) through the phosphorylation and activation of the transcription factor FOXM1. Regulates apoptosis through the phosphorylation of p53/TP53, MDM4 and PML. Phosphorylation of p53/TP53 at 'Ser-20' by CHEK2 may alleviate inhibition by MDM2, leading to accumulation of active p53/TP53. Phosphorylation of MDM4 may also reduce degradation of p53/TP53. Also controls the transcription of pro-apoptotic genes through phosphorylation of the transcription factor E2F1. Tumor suppressor, it may also have a DNA damage-independent function in mitotic spindle assembly by phosphorylating BRCA1. Its absence may be a cause of the chromosomal instability observed in some cancer cells.
标记抗体
暂无标记数据
同靶标产品
暂无同靶标产品
相关文献
提示: 发表研究结果有使用 bsm-61562R 时请让我们知道,以便我们可以引用参考文章。作为回馈,资料提供者将获得我们送上的小礼品。
暂无相关文献
常见问题
暂无常见问题