整合素连接激酶ILK重组兔单抗
Rrmab?兔单抗
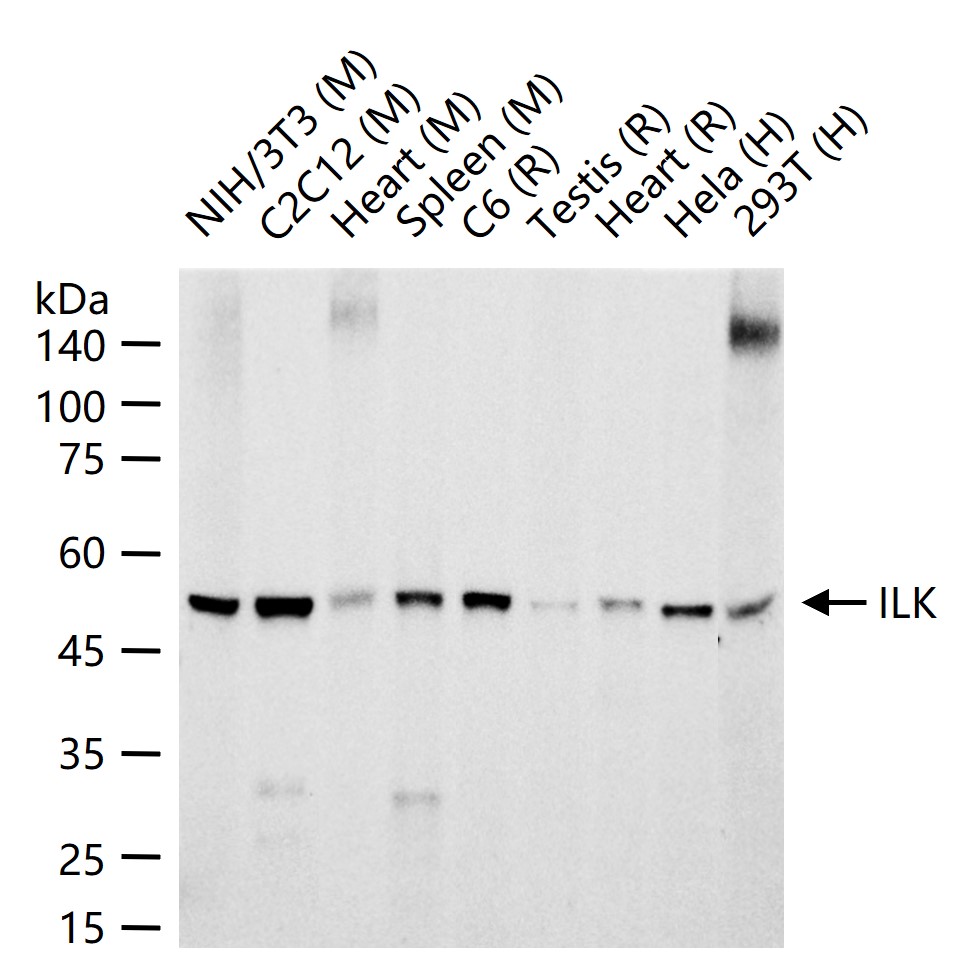
货号:bsm-61287R
产品详情
相关标记
相关产品
相关文献
常见问题
概述
产品编号
bsm-61287R
产品类型
重组兔单抗
英文名称
ILK Recombinant Rabbit mAb
中文名称
整合素连接激酶ILK重组兔单抗
英文别名
HEL-S-28; ILK-1; ILK-2; P59; p59ILK; ESTM24; ILK_HUMAN; ILK; Inactive integrin-linked kinase; ILK1; ILK2; ILK_MOUSE; ILK_RAT;
抗体来源
Rabbit
免疫原
A synthesized peptide derived from human ILK: 401-452/452
亚型
IgG
性状
Liquid
纯化方法
affinity purified by Protein A
克隆类型
Recombinant
克隆号
10G2
理论分子量
51 kDa
检测分子量
51 kDa
储存液
10mM phosphate buffered saline(pH 7.4) with 150mM sodium chloride, 0.05% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% glycerol.
SWISS
Gene ID
保存条件
Store at 4℃ for short term. Store at -20℃ for long term. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
注意事项
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
数据库链接
产品介绍
ILK 是一种新发现的Ser/Thr蛋白激酶。ILK能够通过与整合素β1亚单位的结合介导细胞与胞外基质的连接,以依赖于PI3K的方式激活,并通过磷酸化下游底物PKB/AKT,GSK3等胞外信号的一项下游传递,对细胞的生长,分化,迁移等进行调控。由于ILK在胞内外信号传导中起着重要的作用。并且抑制ILK的活性能够导致细胞周期的停滞和细胞程序性死亡的启动,使其成为肿瘤治疗和肿瘤药物的理想靶位点。
背景资料
Integrin-linked kinases (ILKs) couple integrins and growth factors to downstream pathways involved in cell survival, cell cycle control, cell-cell adhesion and cell motility. ILK functions as a scaffold bridging the extracellular matrix (ECM) and growth factor receptors to the actin cytoskeleton through interactions with integrin, PINCH (which links ILK to the RTKs via Nck2), CH-ILKBP and affixin.

产品应用
| 应用 | 已检合格种属 | 预测种属 | 推荐稀释比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| WB | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:500-2000 | |
| Flow-Cyt | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:50-100 | |
| ICC/IF | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:50-200 | |
| IP | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:20-50 |
交叉反应
交叉反应: Human, Mouse, Rat
相关产品
暂无相关产品
靶标
基因名
ILK
蛋白名
Integrin-linked protein kinase
亚基
Interacts with cytoplasmic domain of beta 1 subunit of integrin. Could also interacts with beta 2, beta 3 and/or beta 5 subunit of integrin. Interacts (via ANK repeats) with LIMS1 and LIMS2. Interacts with parvins and probably TGFB1I1. Interacts (via ANK repeats) with EPHA1 (via SAM domain); stimulated by EFNA1 but independent of the kinase activity of EPHA1.
亚细胞定位
Cell junction, focal adhesion. Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side.
组织特异性
Highly expressed in heart followed by skeletal muscle, pancreas and kidney. Weakly expressed in placenta, lung and liver.
翻译后修饰
Autophosphorylated on serine residues.
相似性
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. TKL Ser/Thr protein kinase family.
Contains 5 ANK repeats.
Contains 1 protein kinase domain.
Contains 5 ANK repeats.
Contains 1 protein kinase domain.
功能
Receptor-proximal protein kinase regulating integrin-mediated signal transduction. May act as a mediator of inside-out integrin signaling. Focal adhesion protein part of the complex ILK-PINCH. This complex is considered to be one of the convergence points of integrin- and growth factor-signaling pathway. Could be implicated in mediating cell architecture, adhesion to integrin substrates and anchorage-dependent growth in epithelial cells. Phosphorylates beta-1 and beta-3 integrin subunit on serine and threonine residues, but also AKT1 and GSK3B.
标记抗体
暂无标记数据
同靶标产品
暂无同靶标产品
相关文献
提示: 发表研究结果有使用 bsm-61287R 时请让我们知道,以便我们可以引用参考文章。作为回馈,资料提供者将获得我们送上的小礼品。
暂无相关文献
常见问题
暂无常见问题