载脂蛋白E重组兔单抗
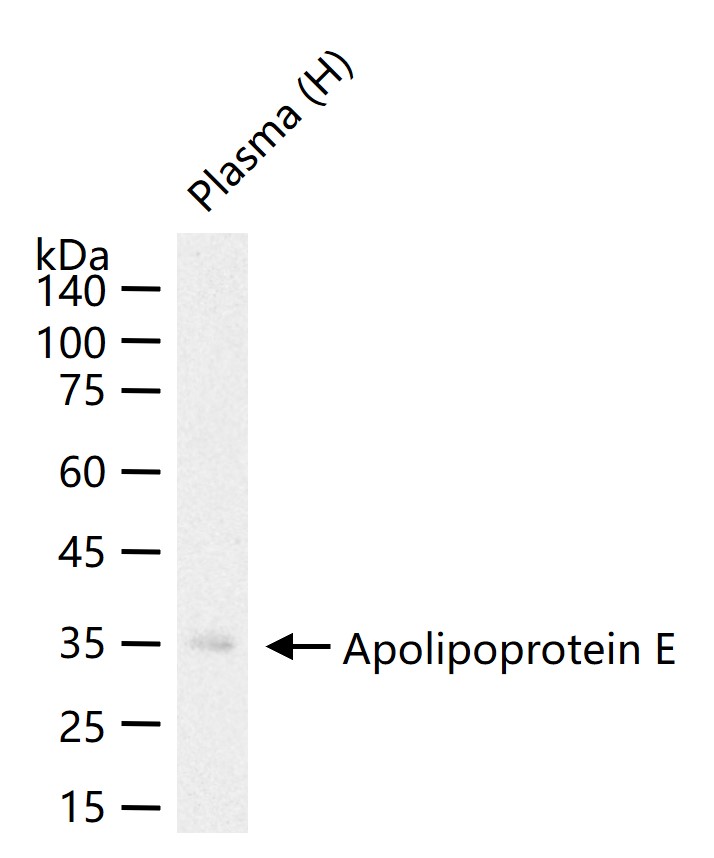
概述
Cancer > Cancer Metabolism > Metabolic signaling pathway > Metabolism of lipids and lipoproteins
Cardiovascular > Atherosclerosis > Lipid transport
Cardiovascular > Lipids / Lipoproteins > Lipid Metabolism > Cholesterol Metabolism
Cardiovascular > Lipids / Lipoproteins > Lipoproteins/Apolipoproteins
Developmental Biology > Lineage specification > Endoderm
Metabolism > Pathways and Processes > Metabolic signaling pathways > Lipid and lipoprotein metabolism > Cholesterol Metabolism
Metabolism > Pathways and Processes > Metabolic signaling pathways > Lipid and lipoprotein metabolism > Lipid metabolism
Metabolism > Types of disease > Heart disease
Metabolism > Types of disease > Neurodegenerative disease
Neuroscience > Neurology process > Neurodegenerative disease
Neuroscience > Neurology process > Neurodegenerative disease > Alzheimer's disease

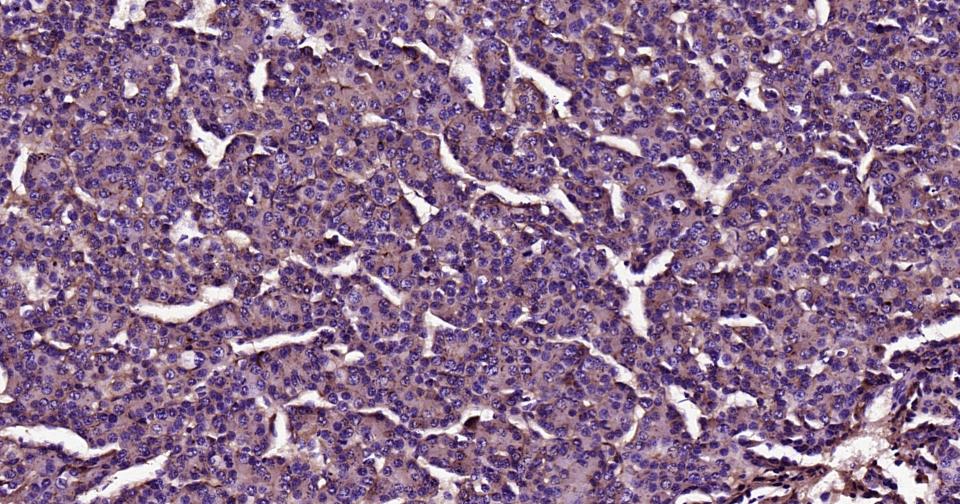
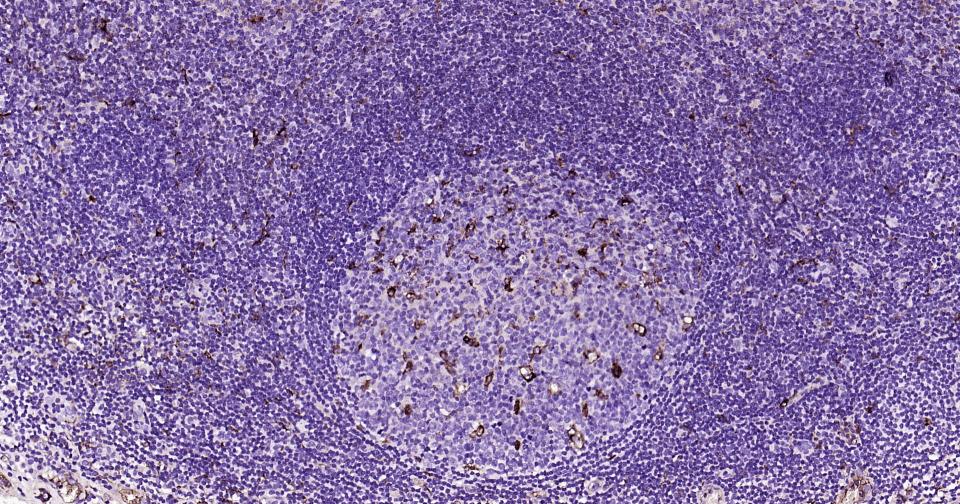
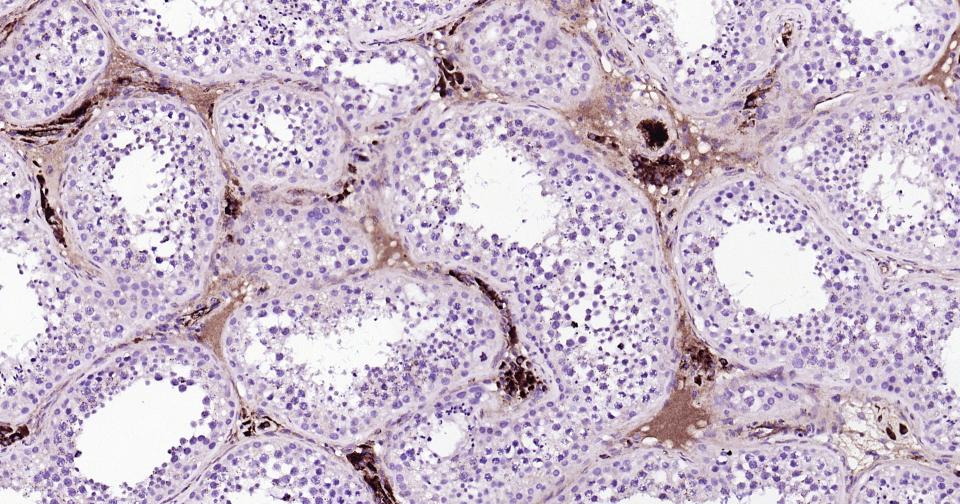
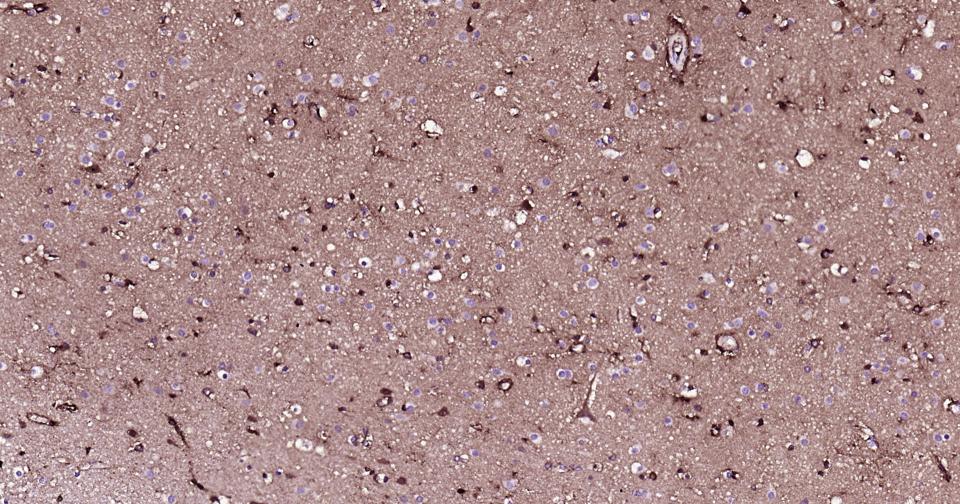
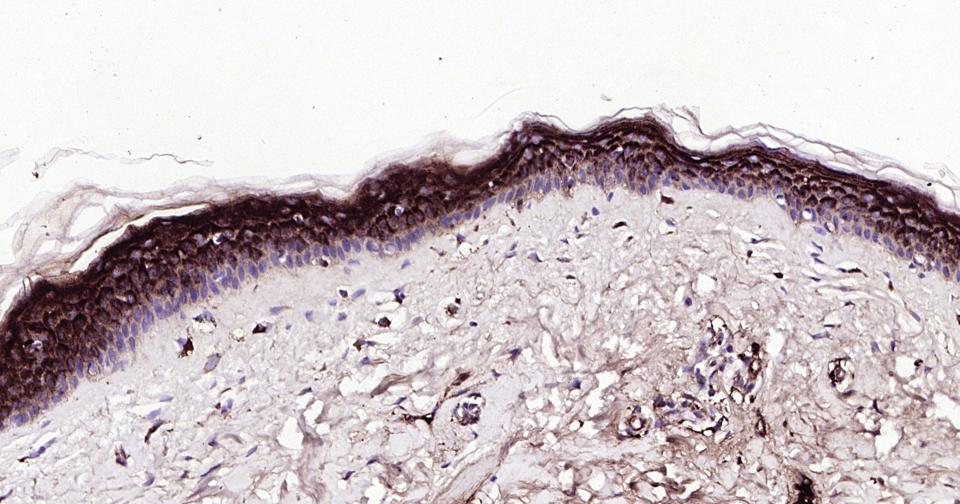
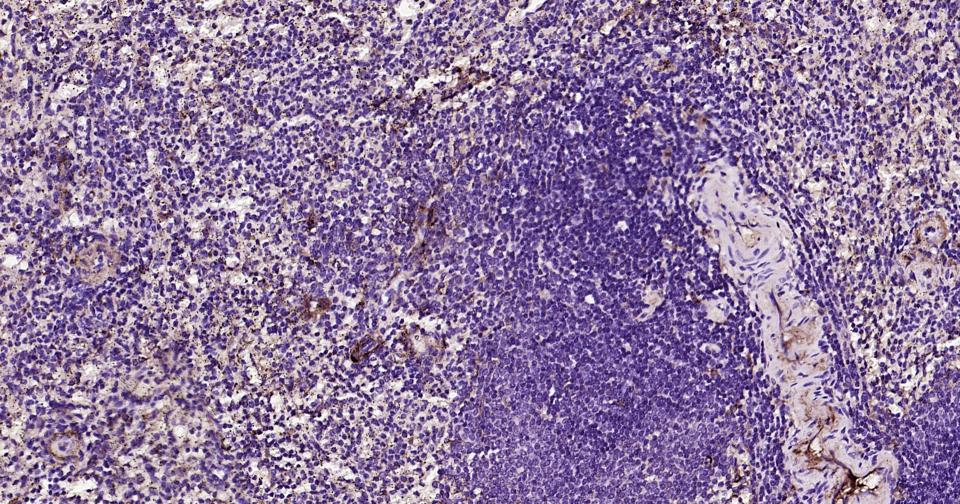
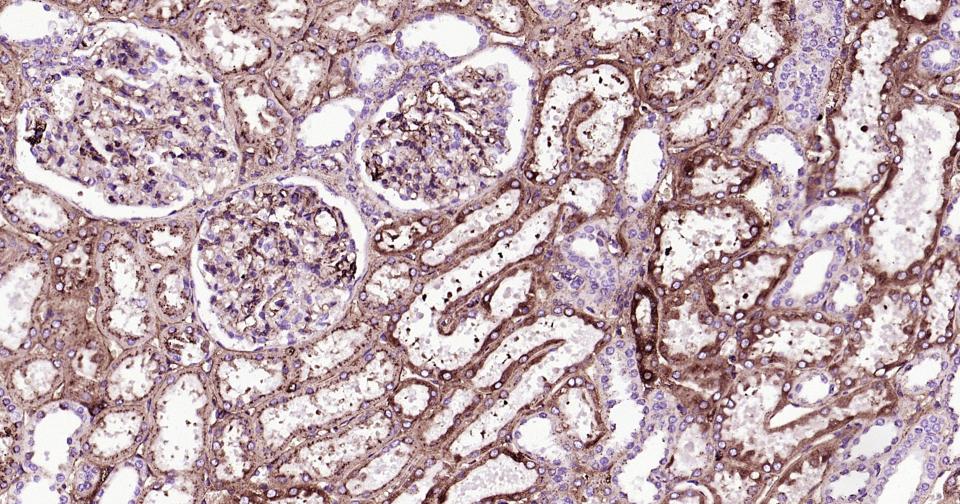
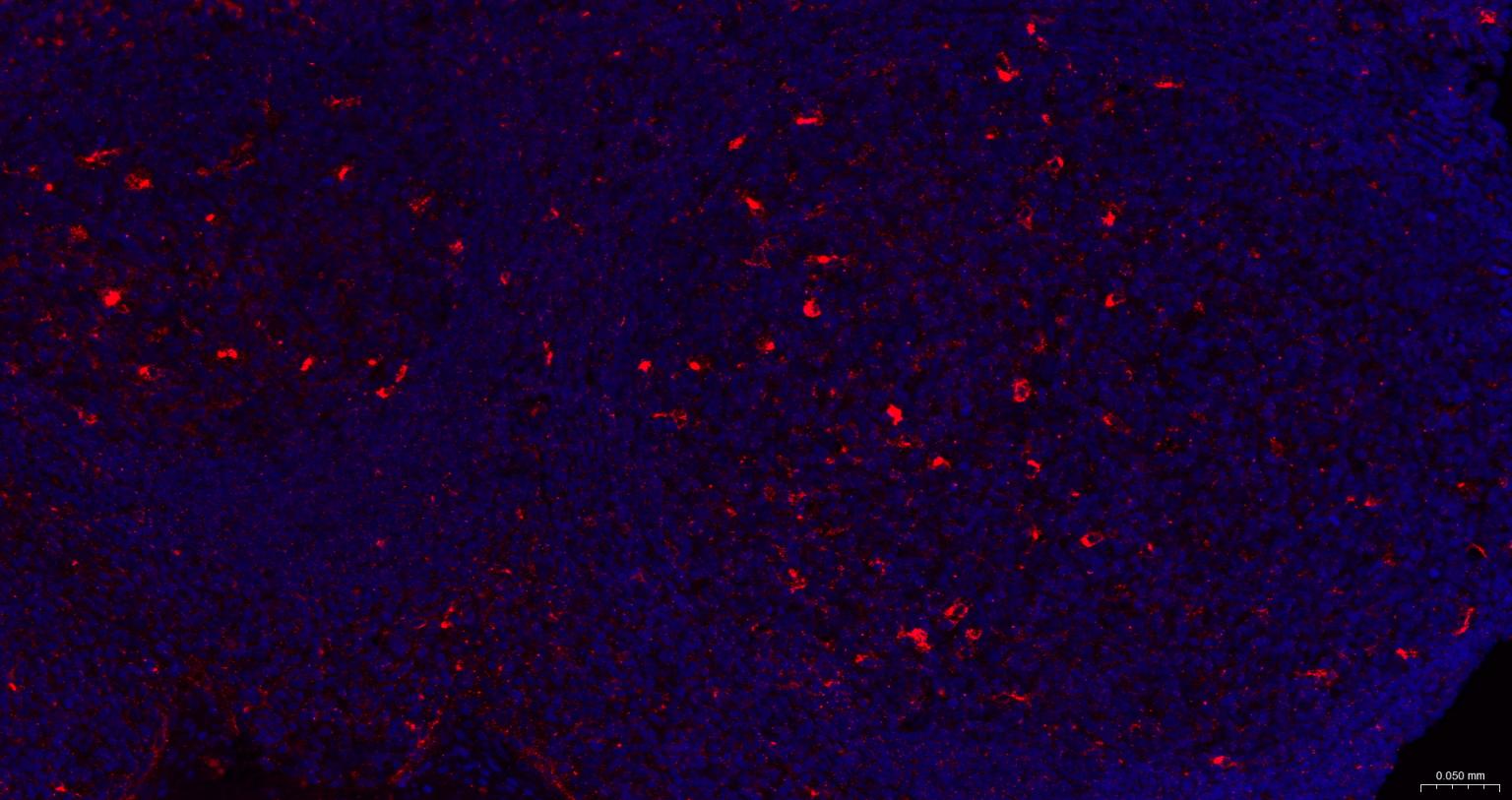
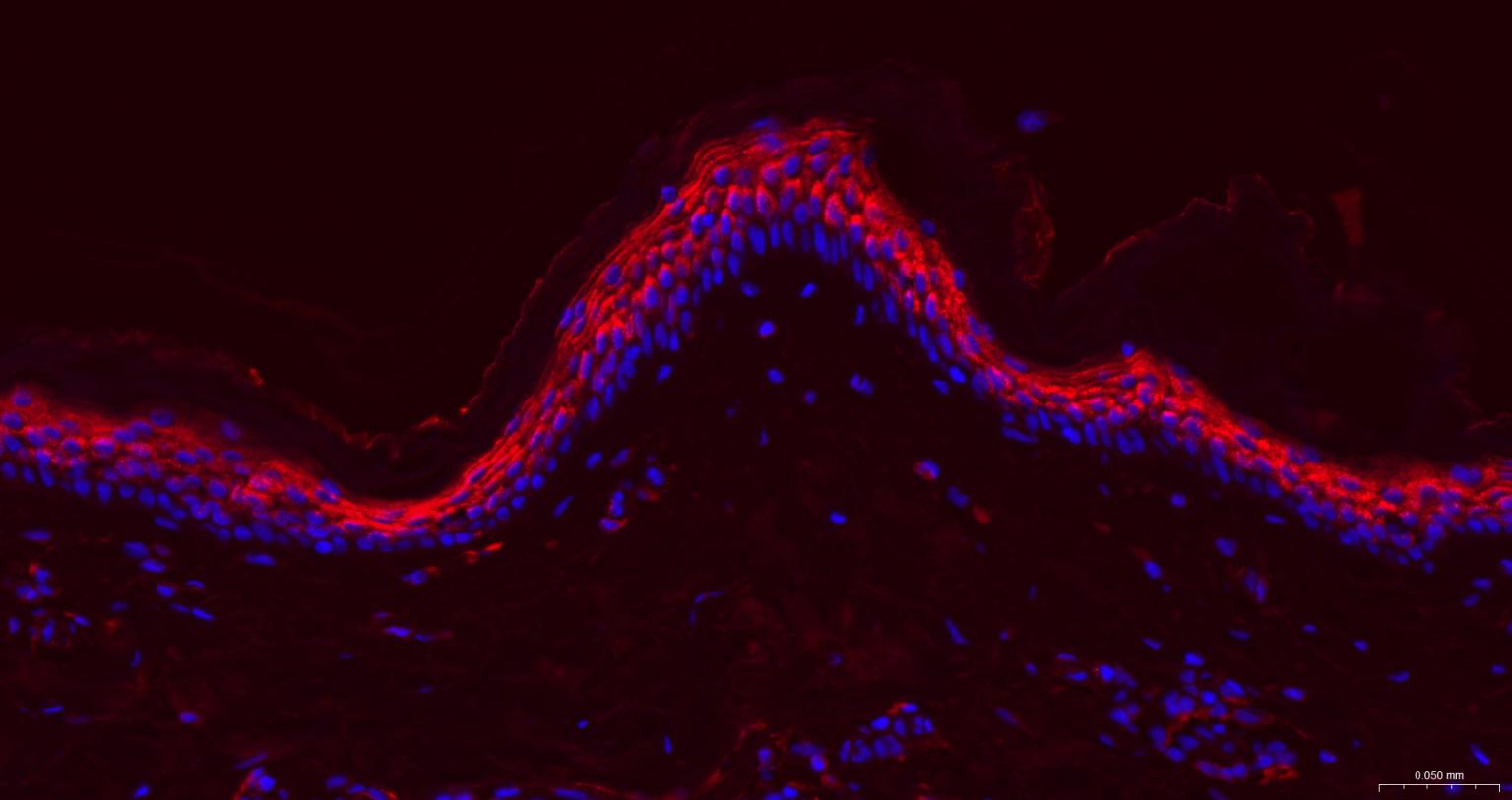
产品应用
| 应用 | 已检合格种属 | 预测种属 | 推荐稀释比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| WB | Human | 1:500-2000 | |
| IHC-P | Human | 1:100-500 | |
| IHC-F | Human | 1:100-500 | |
| IF | Human | 1:100-500 | |
| ICC/IF | Human | 1:50-200 | |
| IP | Human | 1:20-50 |
交叉反应
交叉反应: Human
相关产品
暂无相关产品
靶标
Glycated in plasma VLDL of normal subjects, and of hyperglycemic diabetic patients at a higher level (2-3 fold).
Phosphorylation sites are present in the extracellular medium.
Genetic variations in APOE are associated with Alzheimer disease type 2 (AD2) [MIM:104310]. It is a late-onset neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive dementia, loss of cognitive abilities, and deposition of fibrillar amyloid proteins as intraneuronal neurofibrillary tangles, extracellular amyloid plaques and vascular amyloid deposits. The major constituent of these plaques is the neurotoxic amyloid-beta-APP 40-42 peptide (s), derived proteolytically from the transmembrane precursor protein APP by sequential secretase processing. The cytotoxic C-terminal fragments (CTFs) and the caspase-cleaved products such as C31 derived from APP, are also implicated in neuronal death. Note=The APOE*4 allele is genetically associated with the common late onset familial and sporadic forms of Alzheimer disease. Risk for AD increased from 20% to 90% and mean age at onset decreased from 84 to 68 years with increasing number of APOE*4 alleles in 42 families with late onset AD. Thus APOE*4 gene dose is a major risk factor for late onset AD and, in these families, homozygosity for APOE*4 was virtually sufficient to cause AD by age 80. The mechanism by which APOE*4 participates in pathogenesis is not known.
Defects in APOE are a cause of sea-blue histiocyte disease (SBHD) [MIM:269600]; also known as sea-blue histiocytosis. This disorder is characterized by splenomegaly, mild thrombocytopenia and, in the bone marrow, numerous histiocytes containing cytoplasmic granules which stain bright blue with the usual hematologic stains. The syndrome is the consequence of an inherited metabolic defect analogous to Gaucher disease and other sphingolipidoses.
Defects in APOE are a cause of lipoprotein glomerulopathy (LPG) [MIM:611771]. LPG is an uncommon kidney disease characterized by proteinuria, progressive kidney failure, and distinctive lipoprotein thrombi in glomerular capillaries. It mainly affects people of Japanese and Chinese origin. The disorder has rarely been described in Caucasians.
标记抗体
暂无标记数据
同靶标产品
暂无同靶标产品
相关文献
暂无相关文献
常见问题
暂无常见问题