神经细胞胞浆蛋白9.5重组兔单抗
Rrmab?兔单抗
货号:bsm-41257R
产品详情
相关标记
相关产品
相关文献
常见问题
概述
产品编号
bsm-41257R
产品类型
重组兔单抗、mIHC精品抗体
英文名称
PGP9.5 Recombinant Rabbit mAb
中文名称
神经细胞胞浆蛋白9.5重组兔单抗
英文别名
HEL-117; HEL-S-53; NDGOA; PARK5; PGP 9.5; PGP9.5; PGP95; SPG79; SPG79A; UCHL-1; Uch-L1; gad; UCHL1_HUMAN; UCHL1; Neuron cytoplasmic protein 9.5; PGP 9.5 (PGP9.5); Ubiquitin thioesterase L1; 3.4.19.12; UCHL1_MOUSE; UCHL1_PIG; UCHL1_RAT;
抗体来源
Rabbit
免疫原
Recombinant human UCHL1 protein
亚型
IgG
性状
Liquid
纯化方法
affinity purified by Protein A
克隆类型
Recombinant
克隆号
18C19
理论分子量
25 kDa
浓度
1mg/ml
储存液
0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol.
SWISS
Gene ID
保存条件
Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
注意事项
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
数据库链接
产品介绍
该抗原是一种神经特异性蛋白,广泛分布于中枢与外周神经系统的神经元和神经纤维、神经内分泌细胞、肾小管段、睾丸精原细胞、Leydig细胞、卵细胞以及妊娠与非妊娠黄体内的某些细胞。用于标记神经元,对研究几种人慢性神经变性性疾病中广泛存在的细胞包涵体特征较有意义。
背景资料
catalyzes the hydrolysis of ubiquitin carboxy-terminal thiolesters to form ubiquitin and a thiol; may play a role in neuropathic pain [RGD].
Found in neuronal cell bodies and processes throughout the neocortex (at protein level). Expressed in neurons and cells of the diffuse neuroendocrine system and their tumors. Weakly expressed in ovary. Down-regulated in brains from Parkinson disease and Alzheimer disease patients.
Found in neuronal cell bodies and processes throughout the neocortex (at protein level). Expressed in neurons and cells of the diffuse neuroendocrine system and their tumors. Weakly expressed in ovary. Down-regulated in brains from Parkinson disease and Alzheimer disease patients.

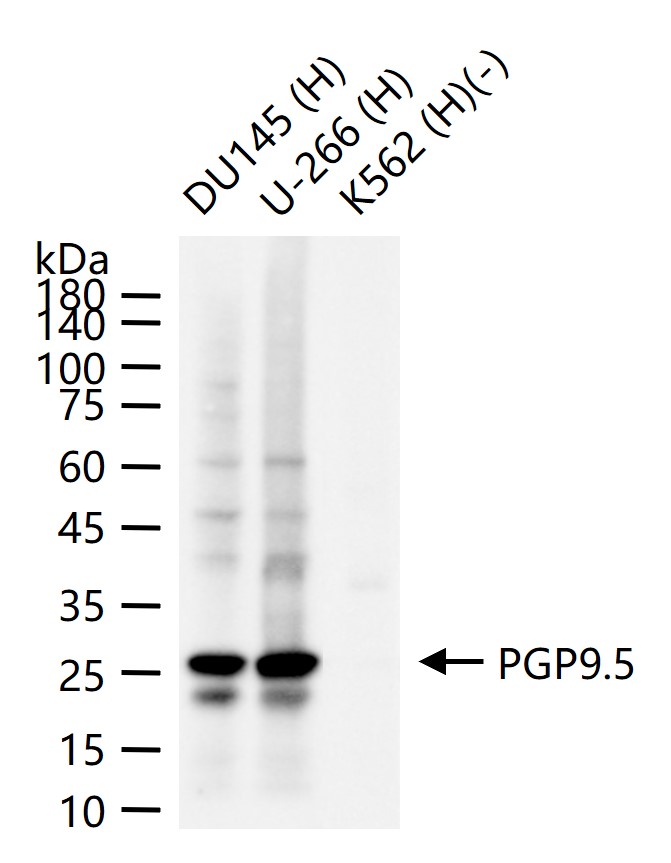
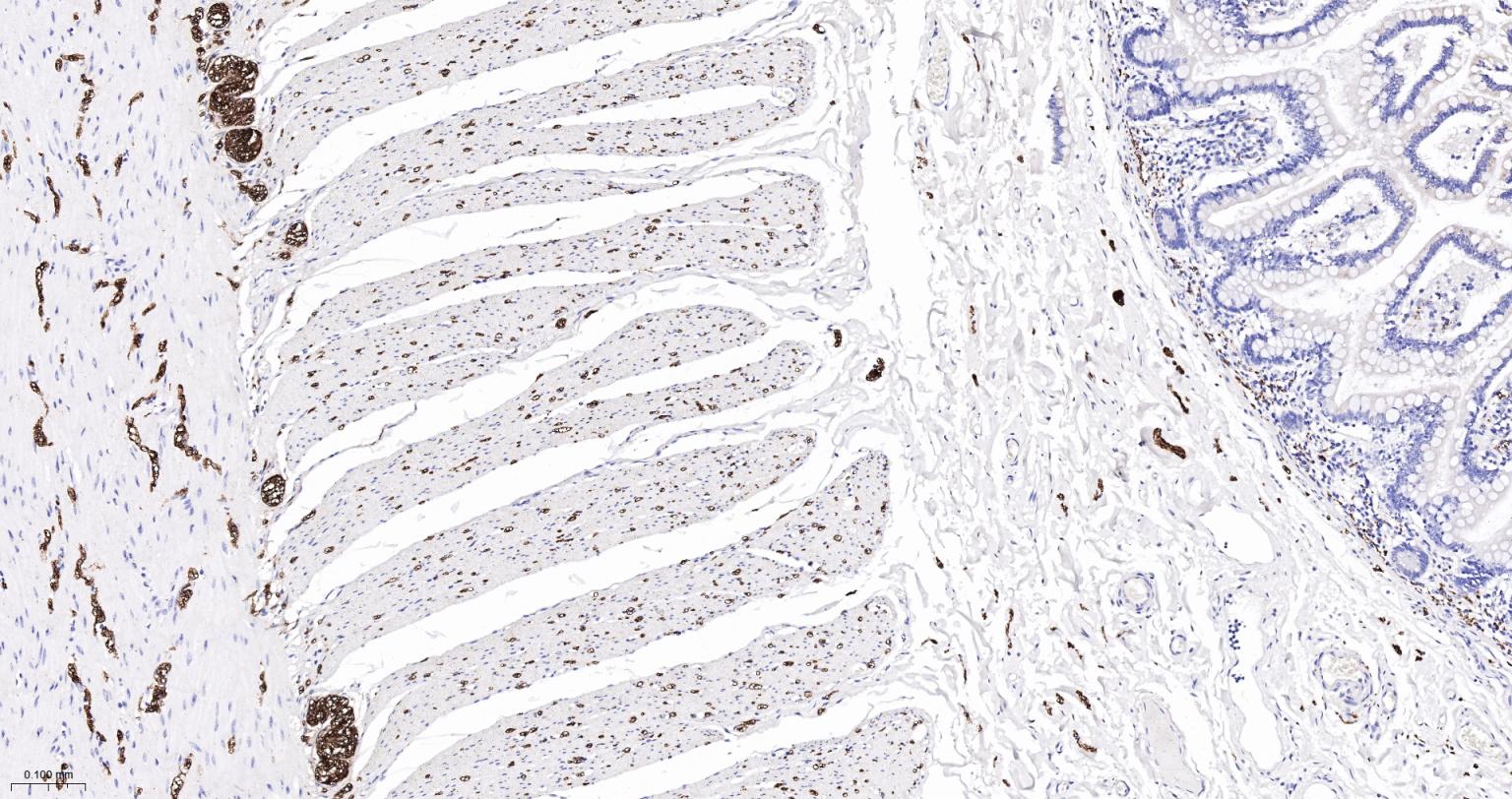
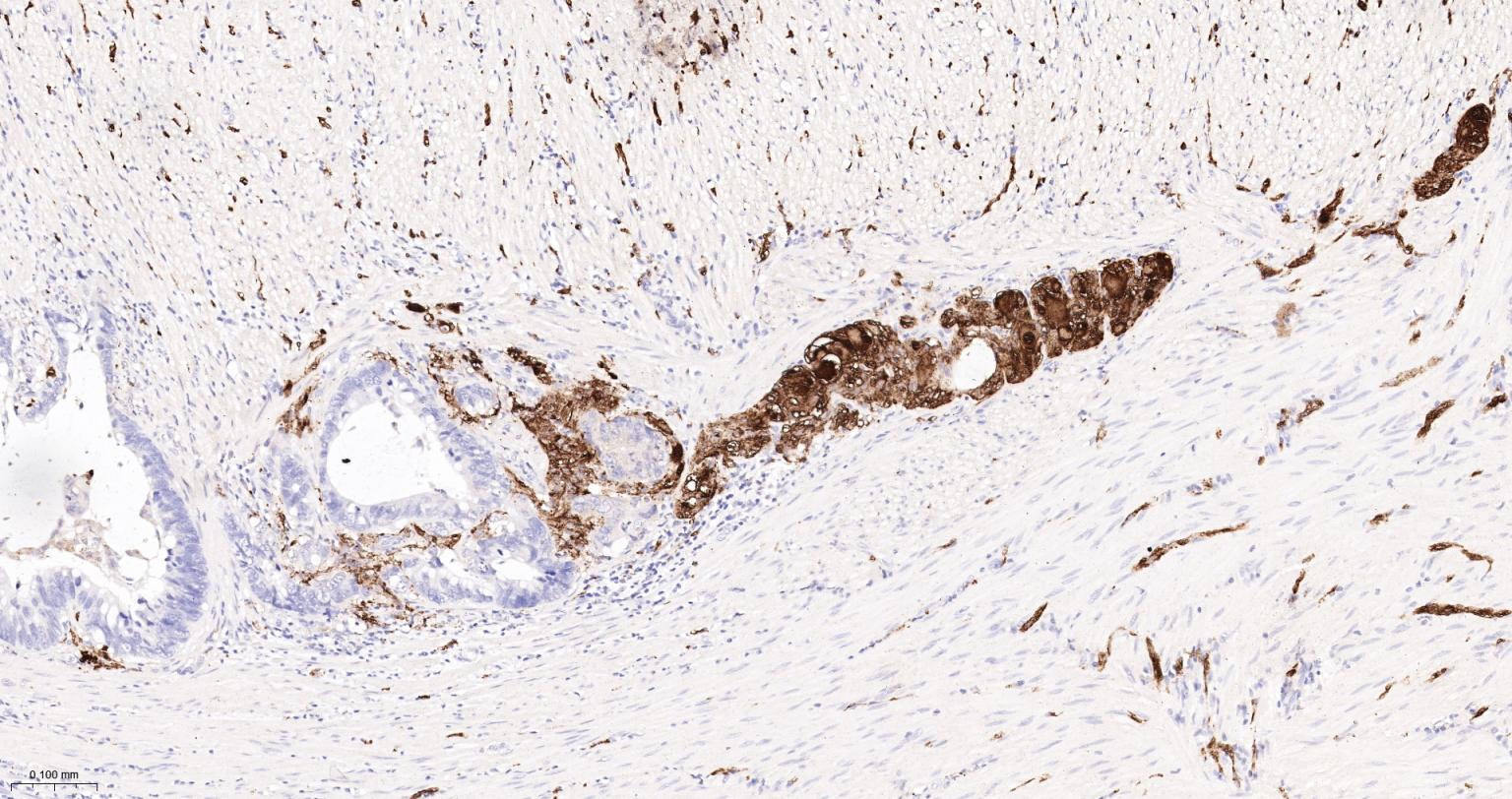
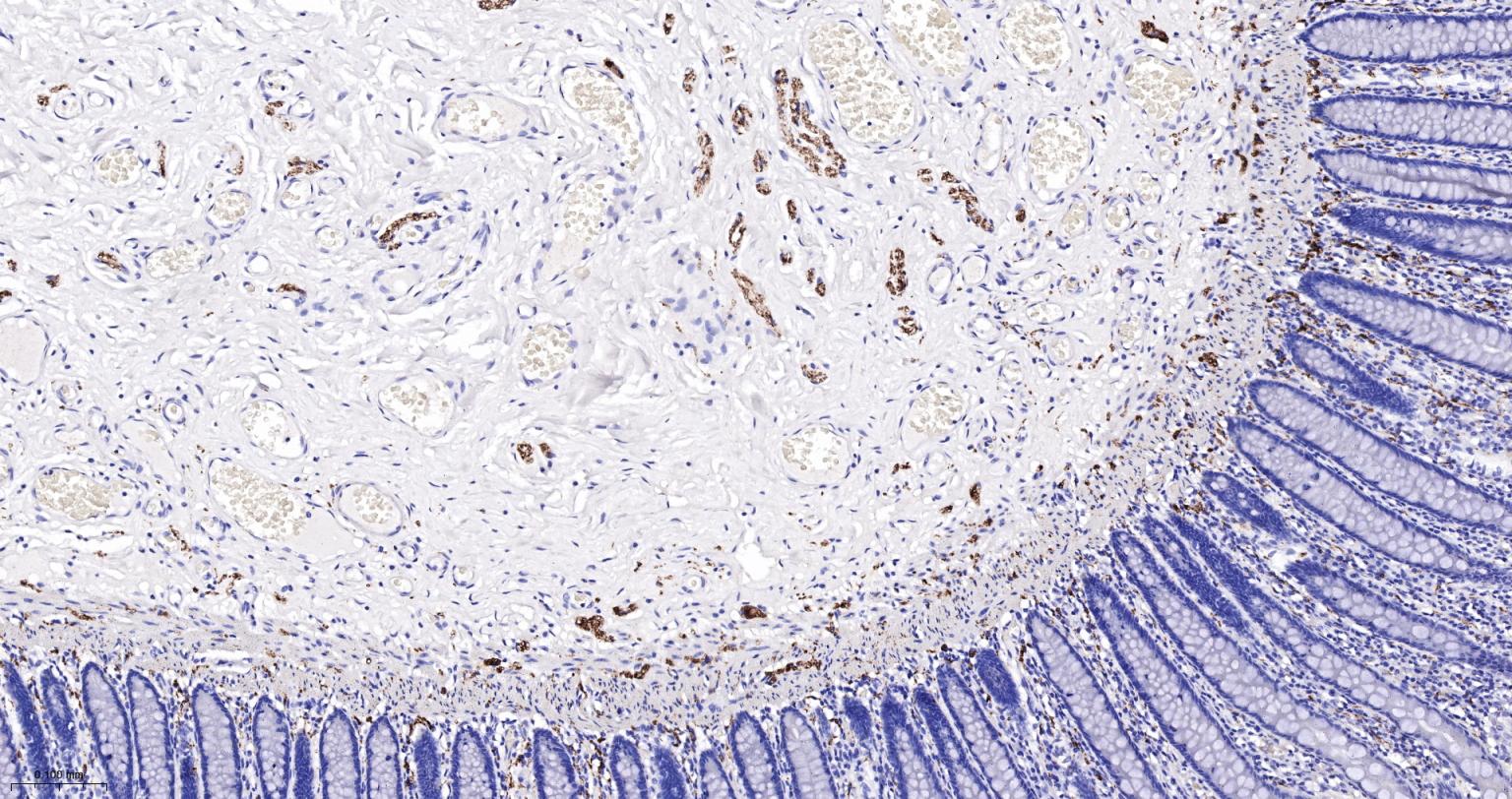
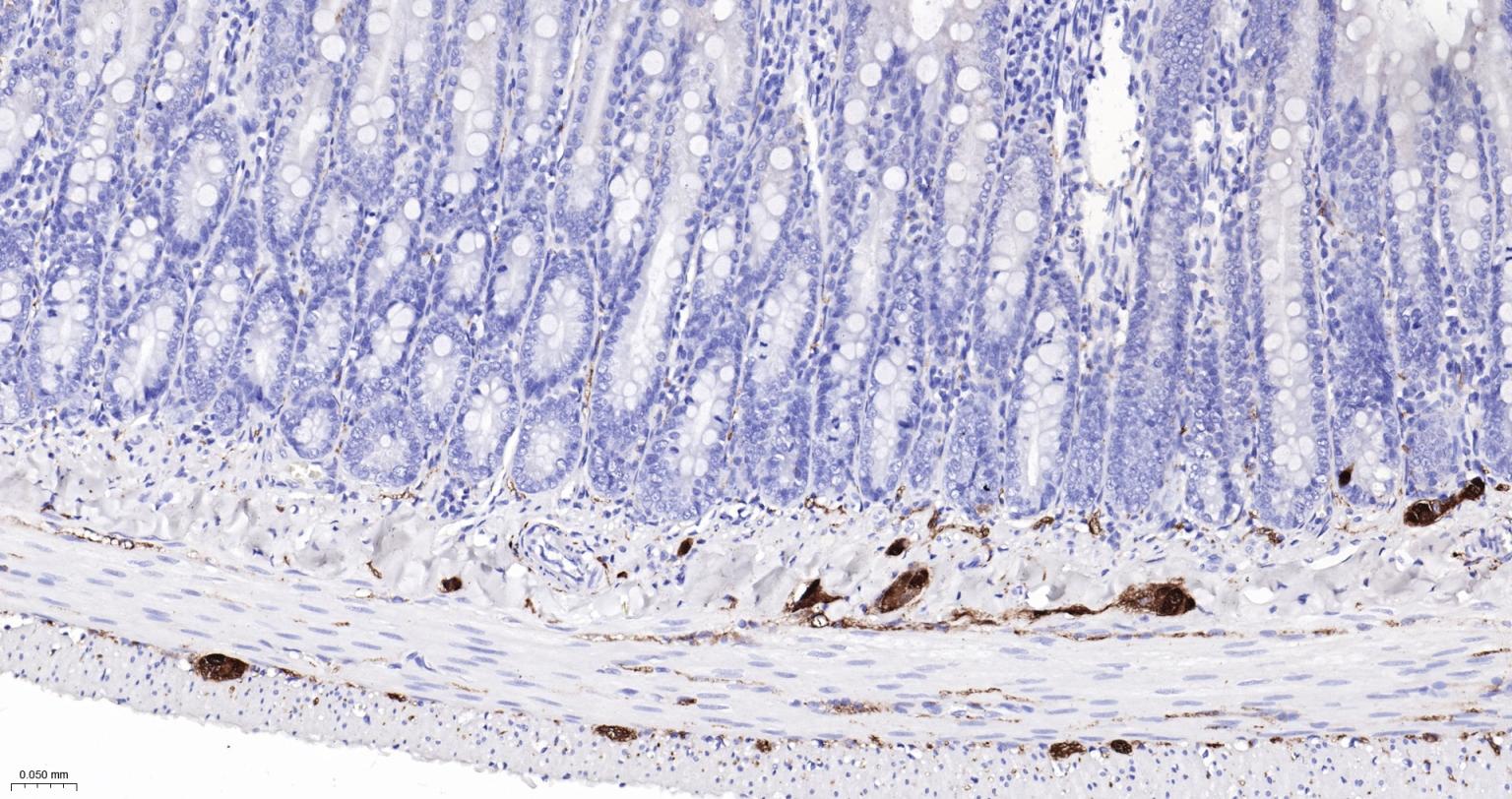
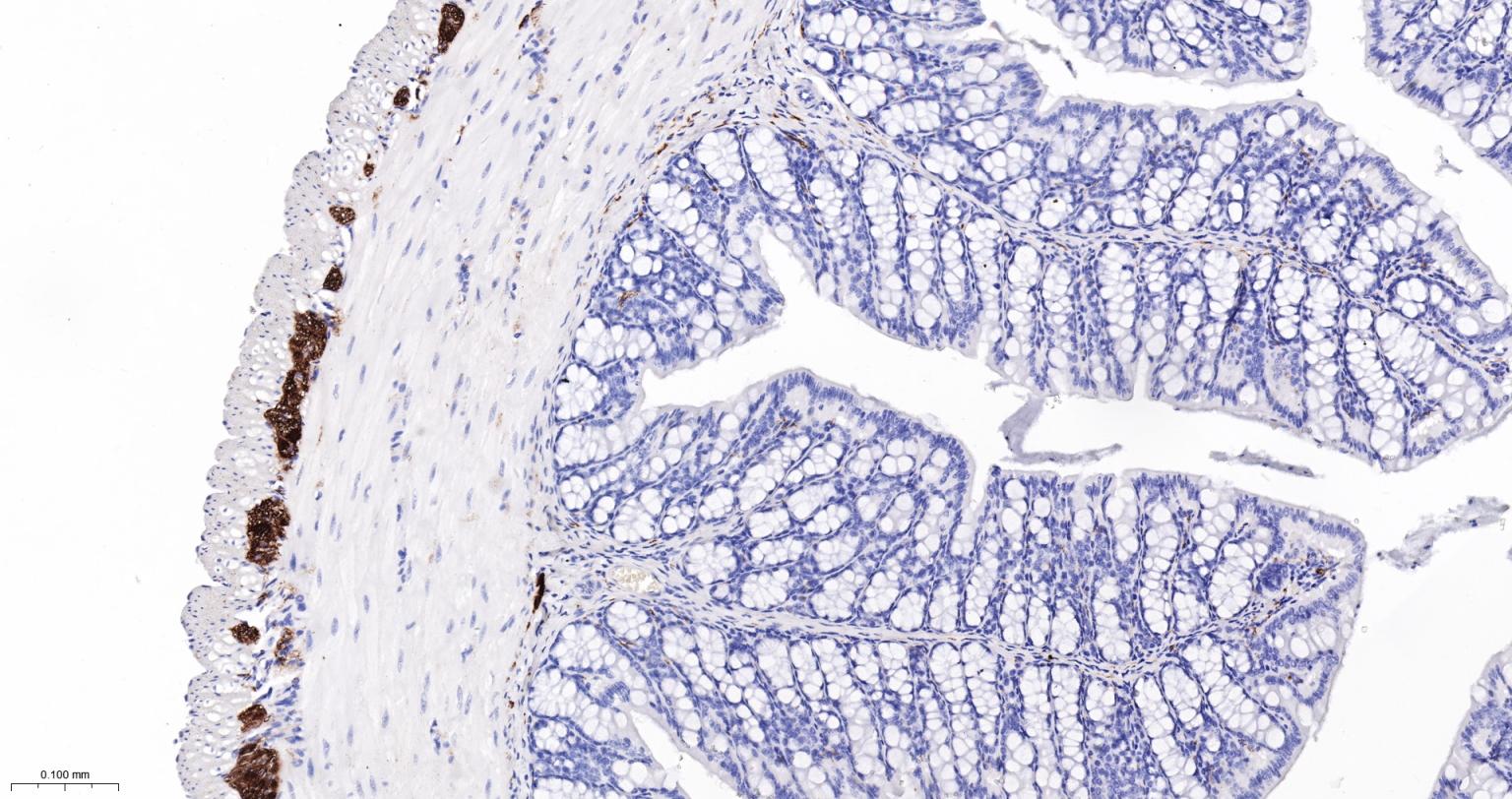
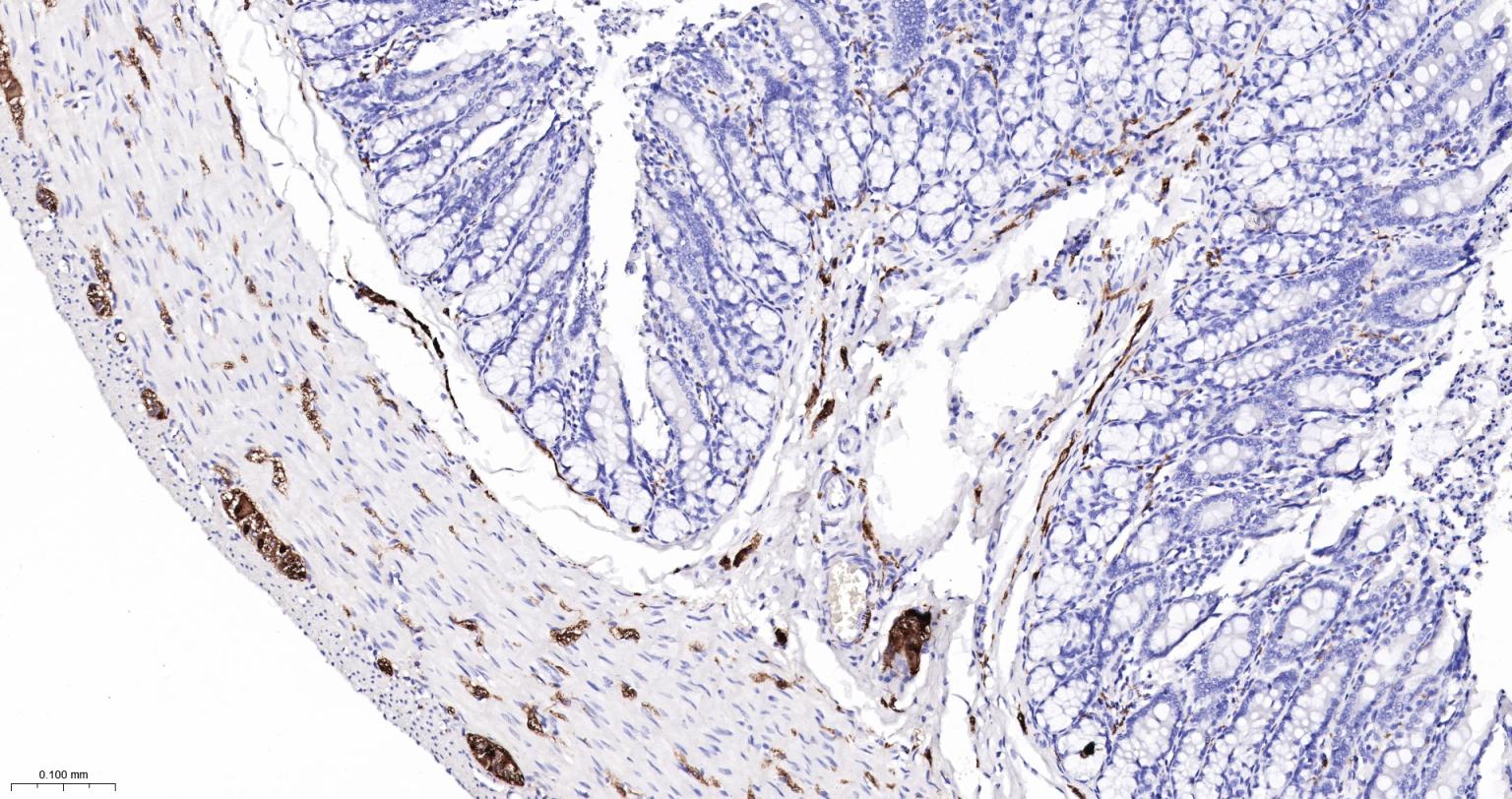
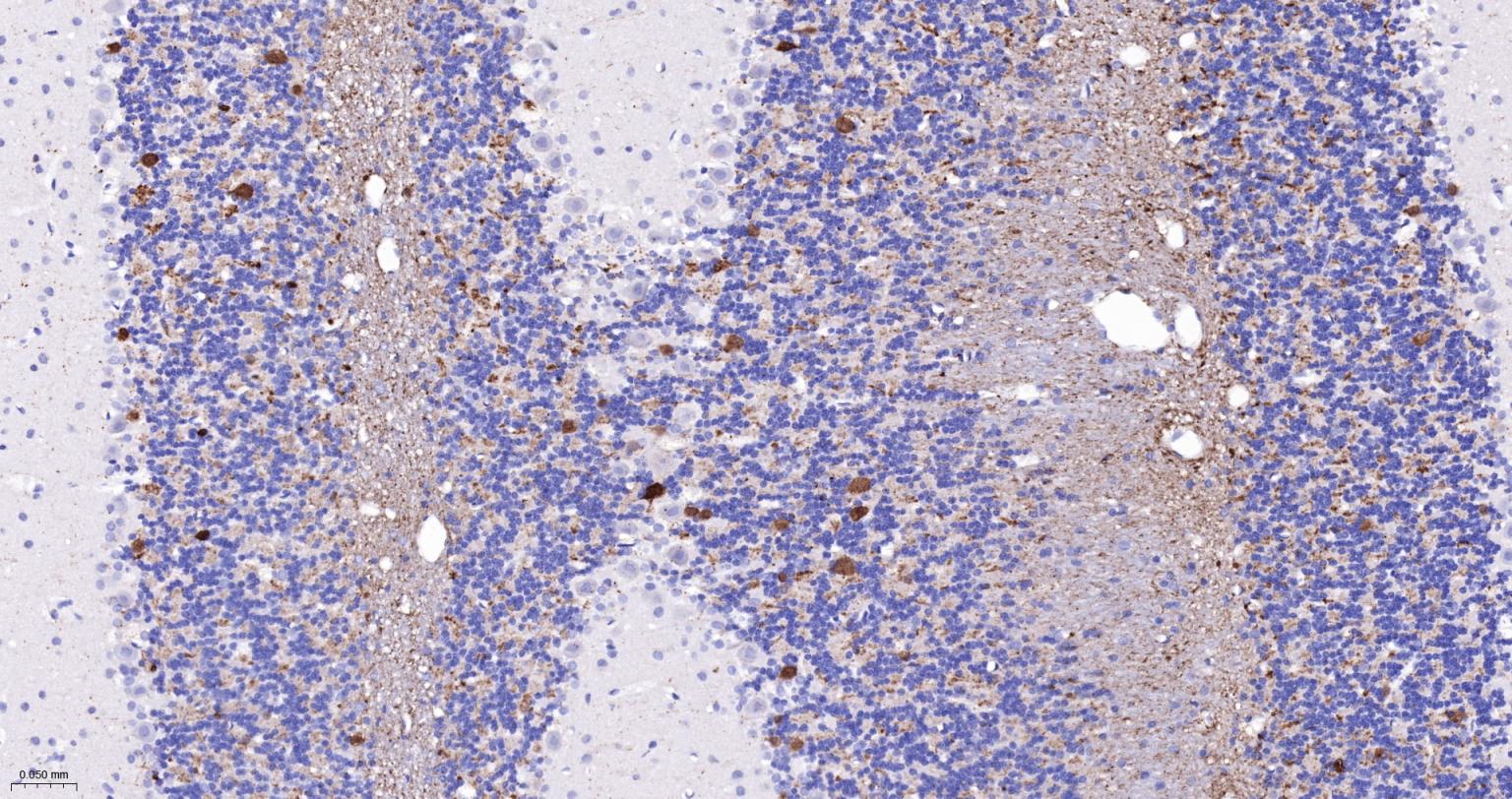
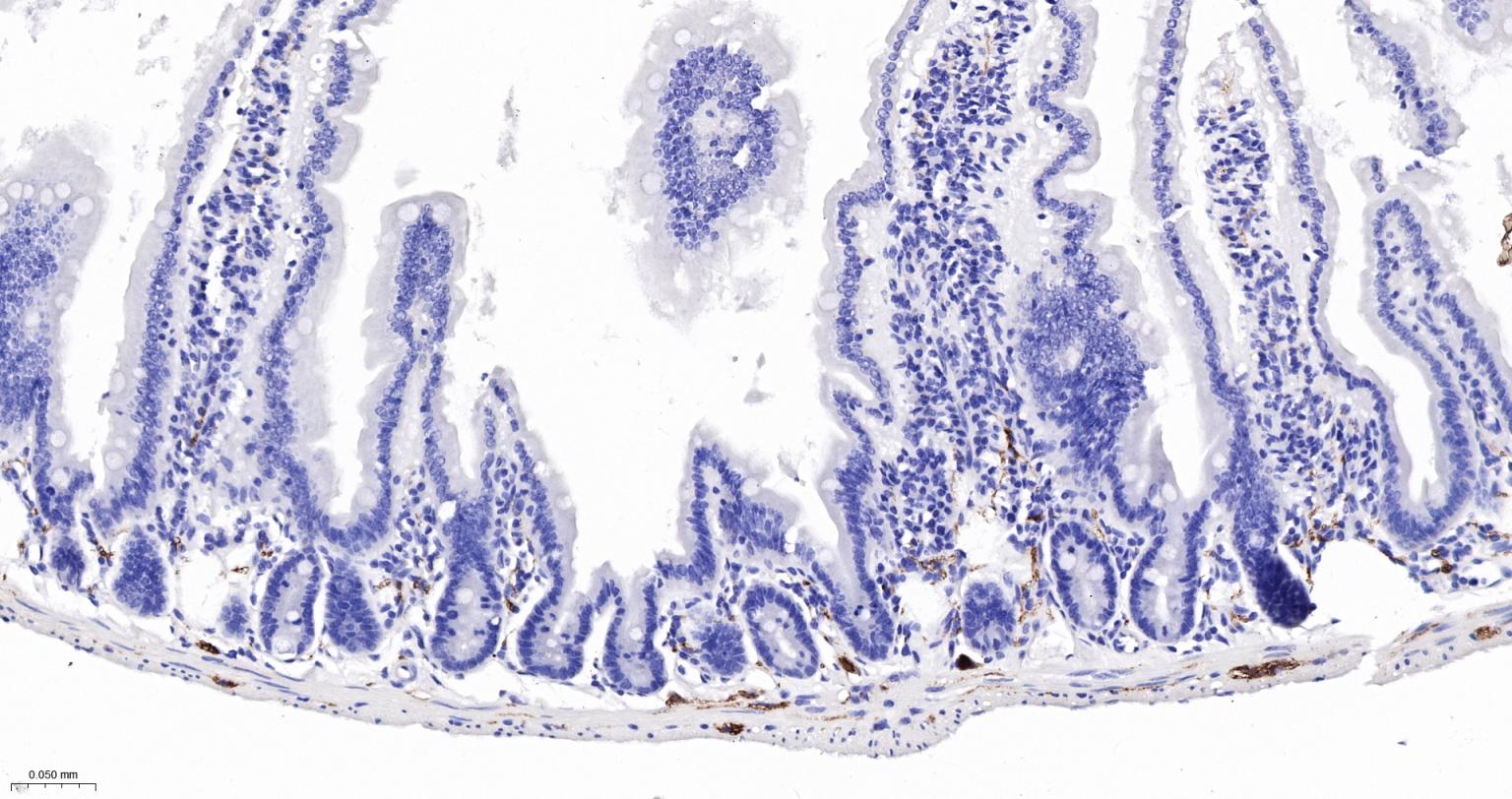
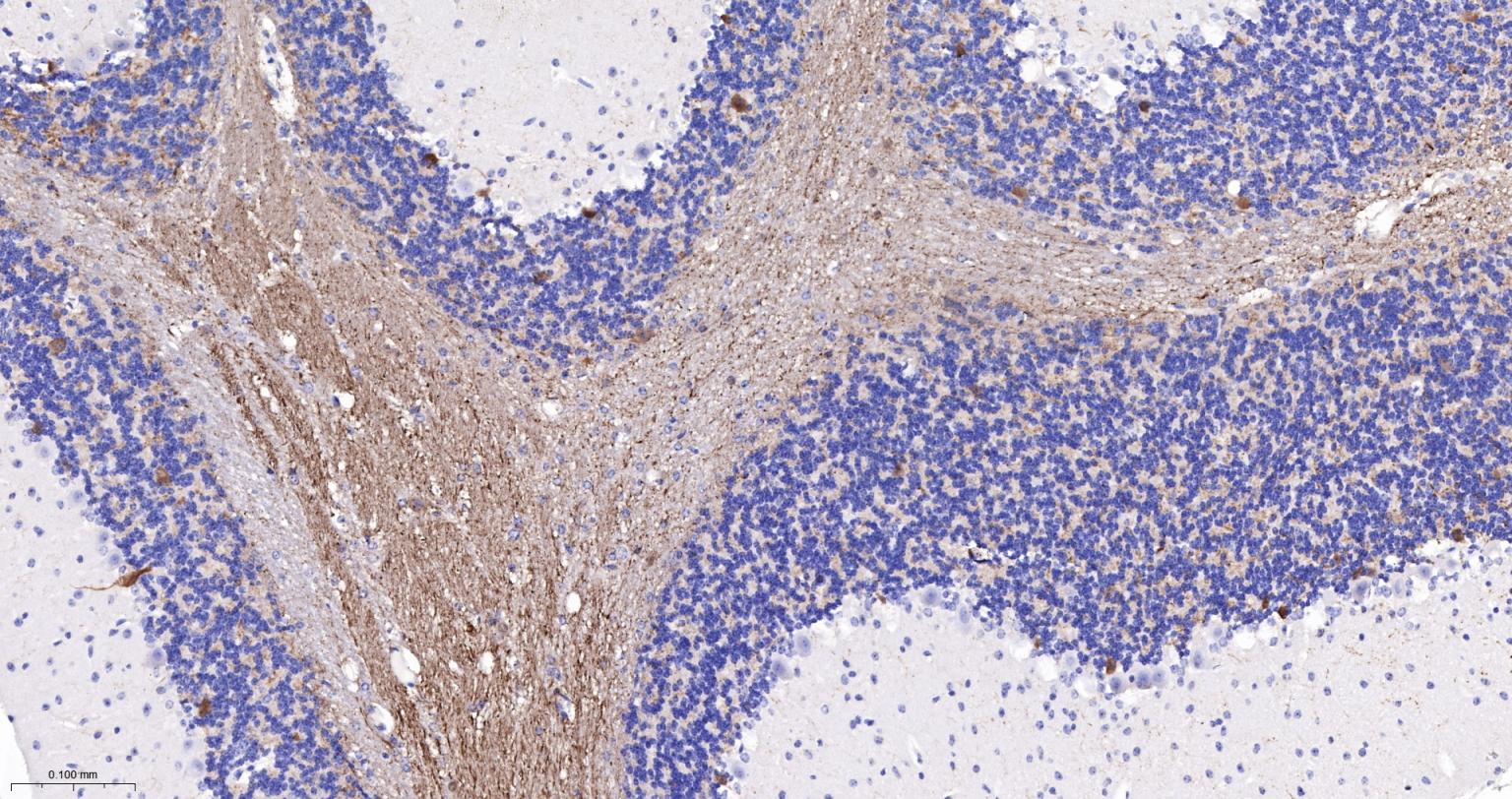
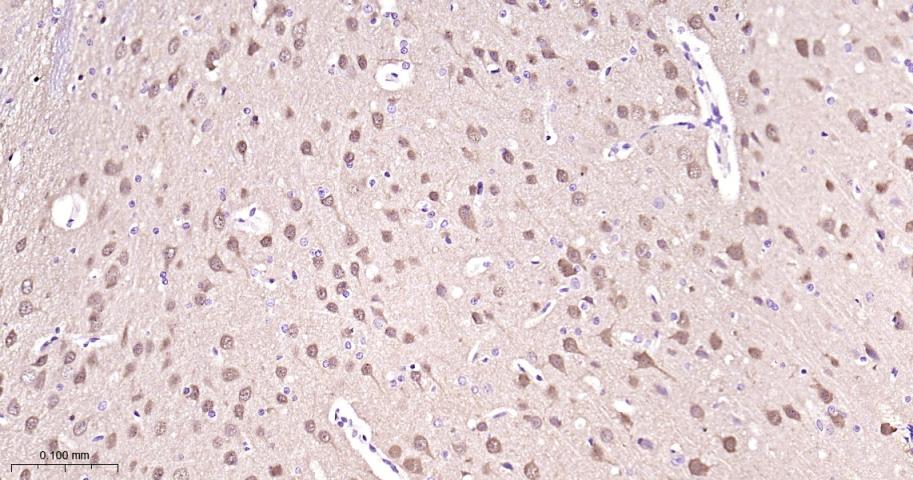
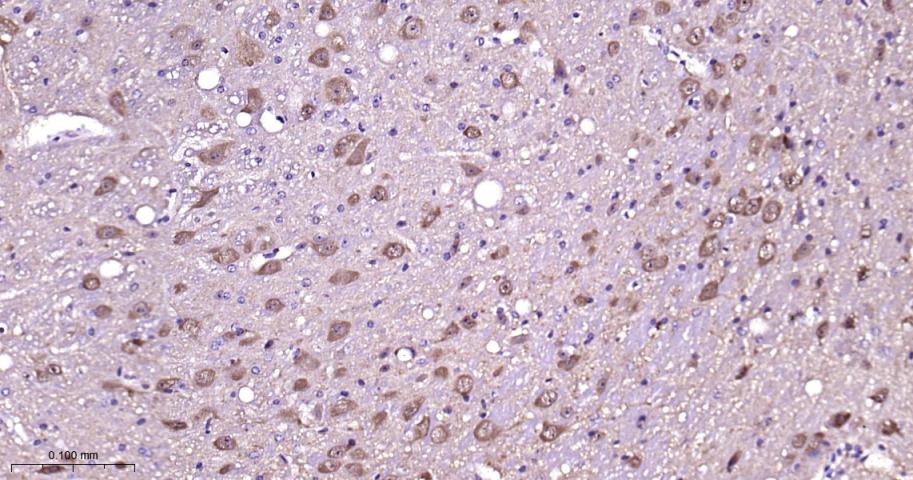
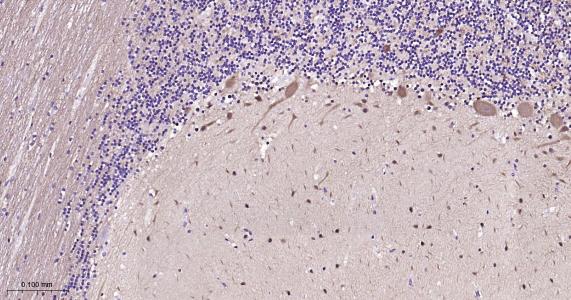
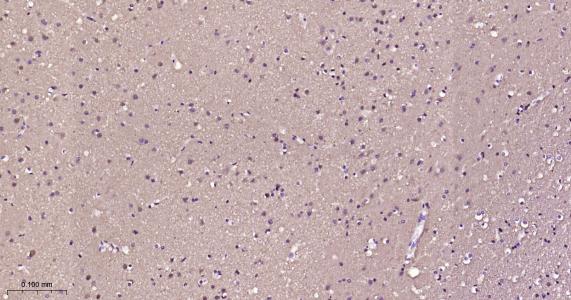
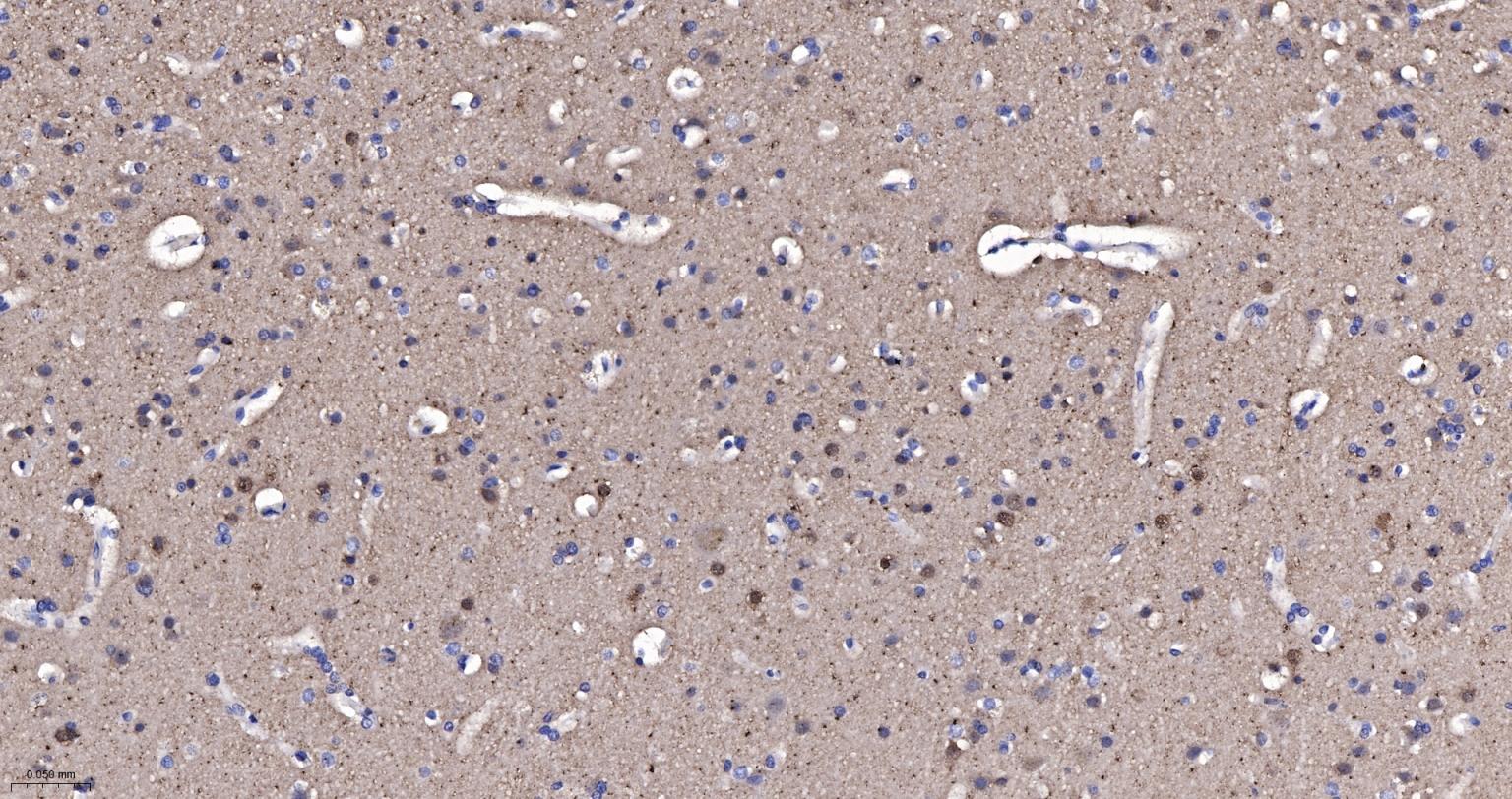
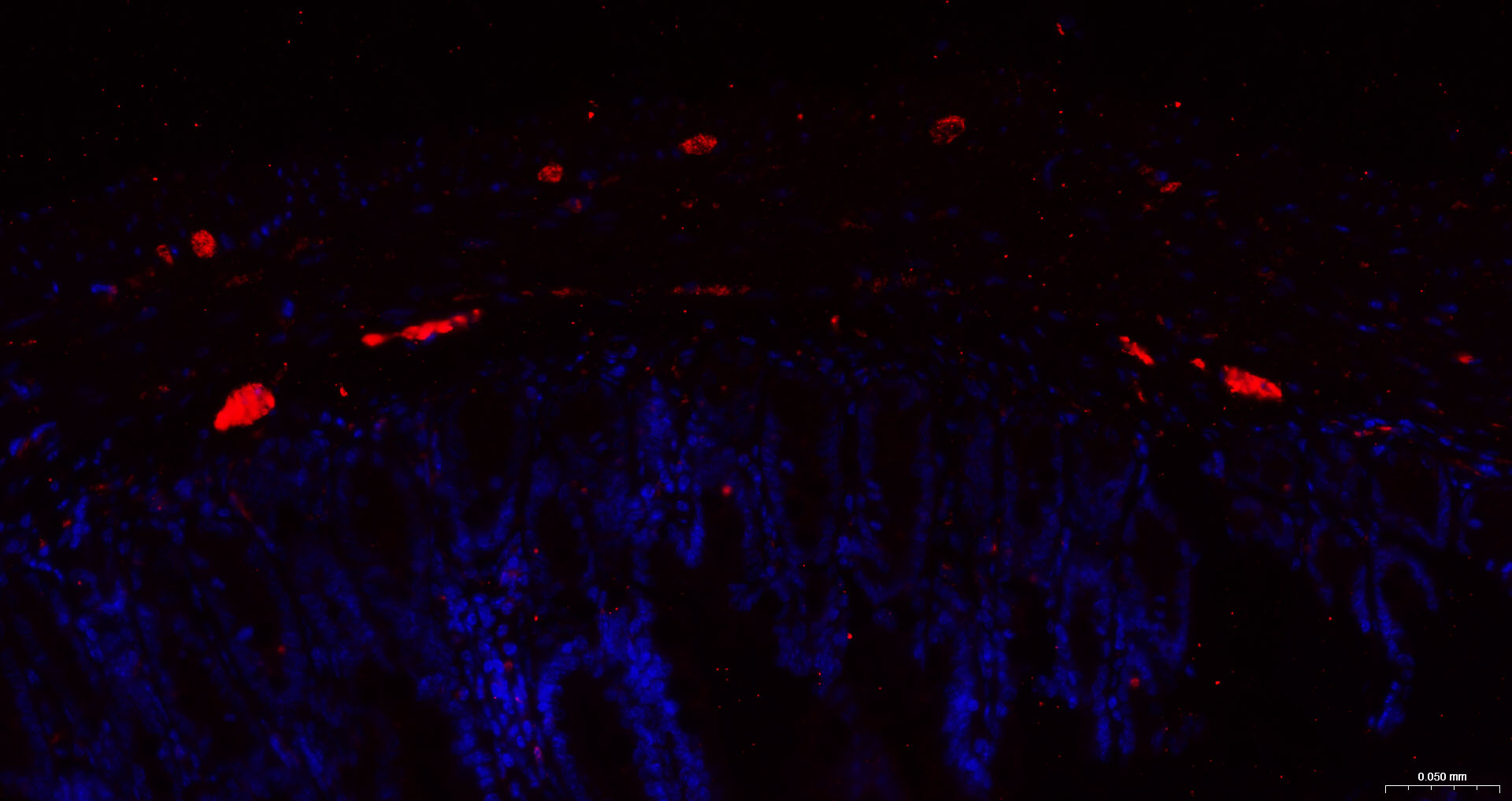
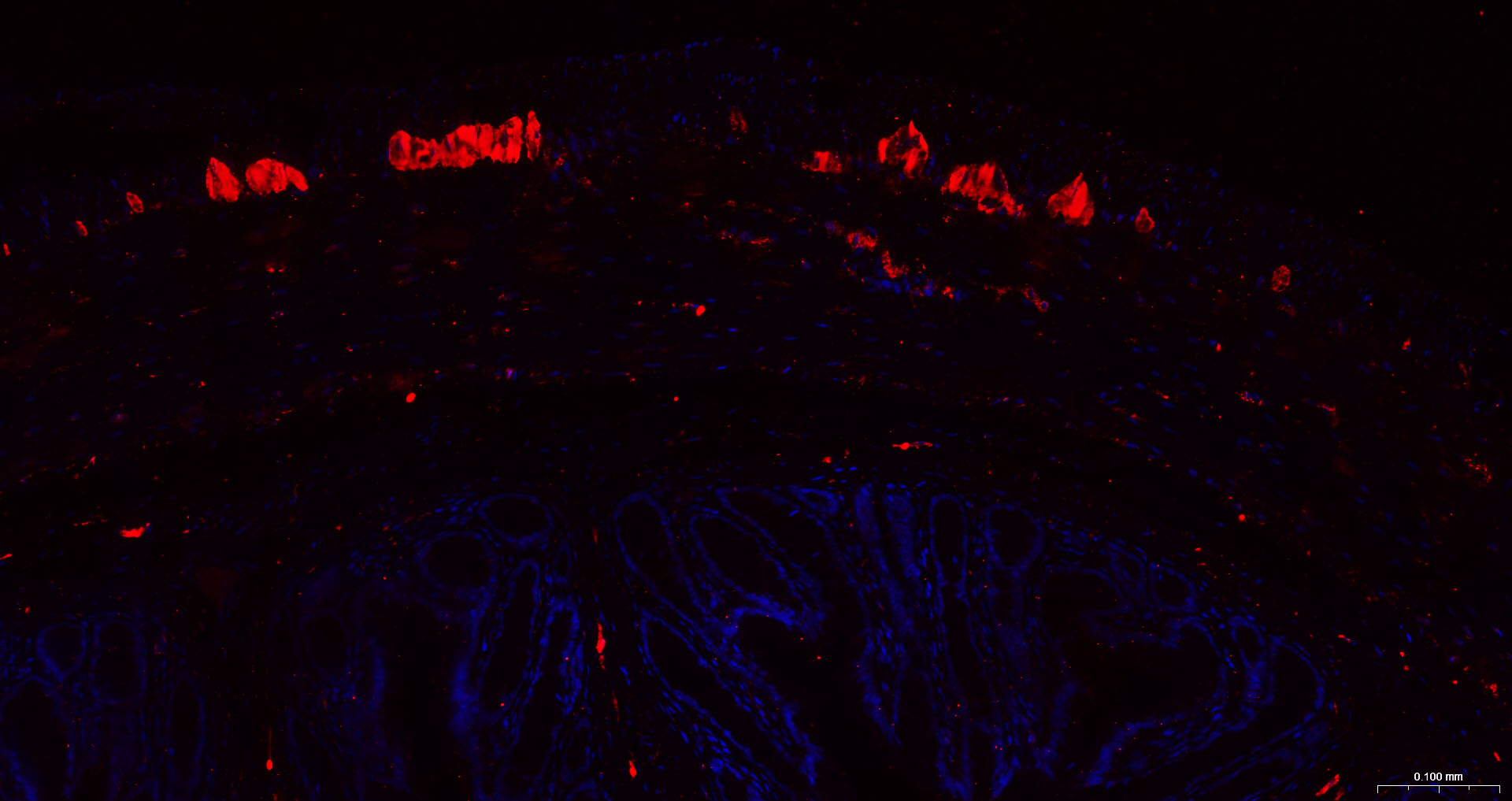
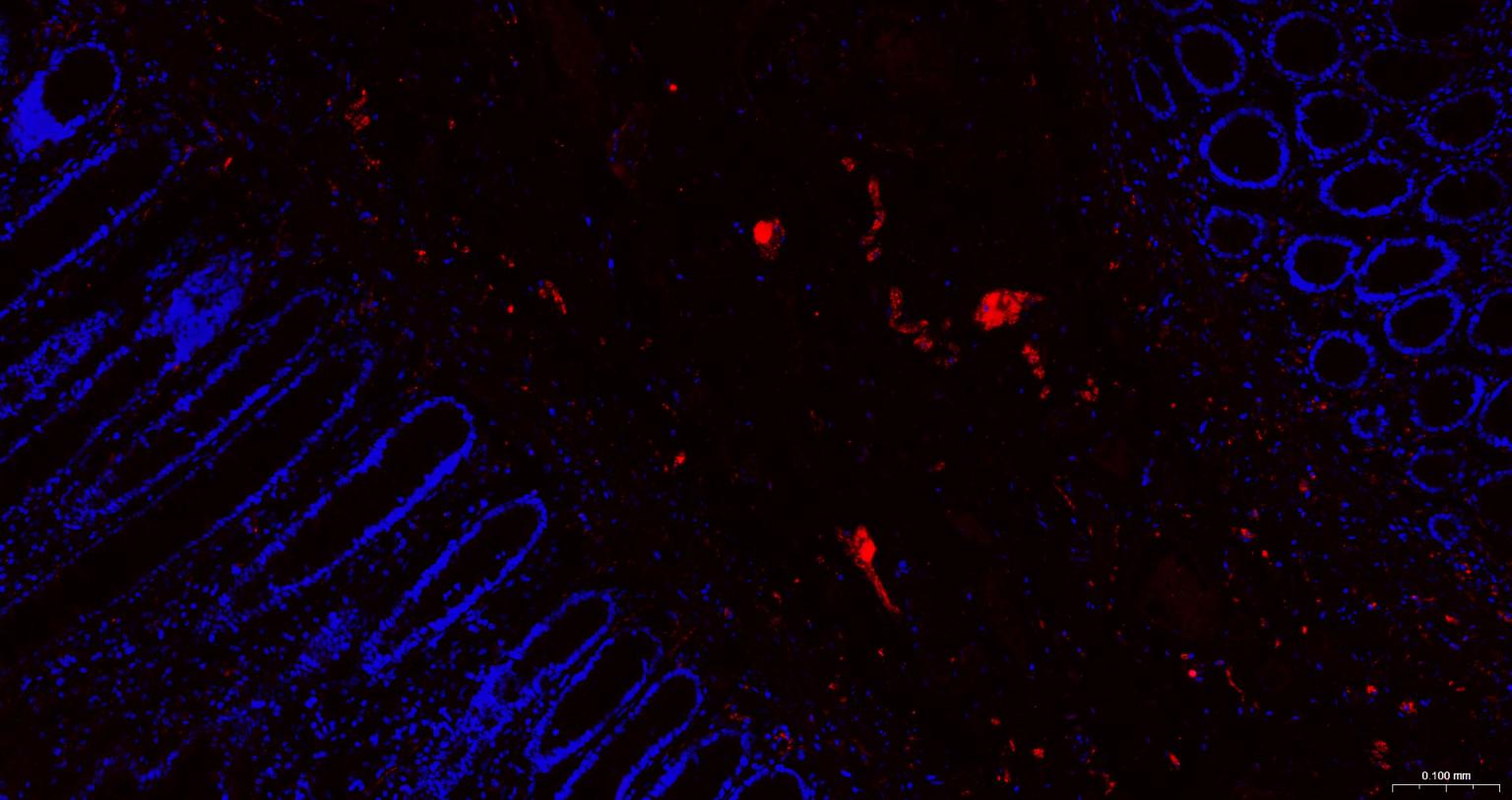
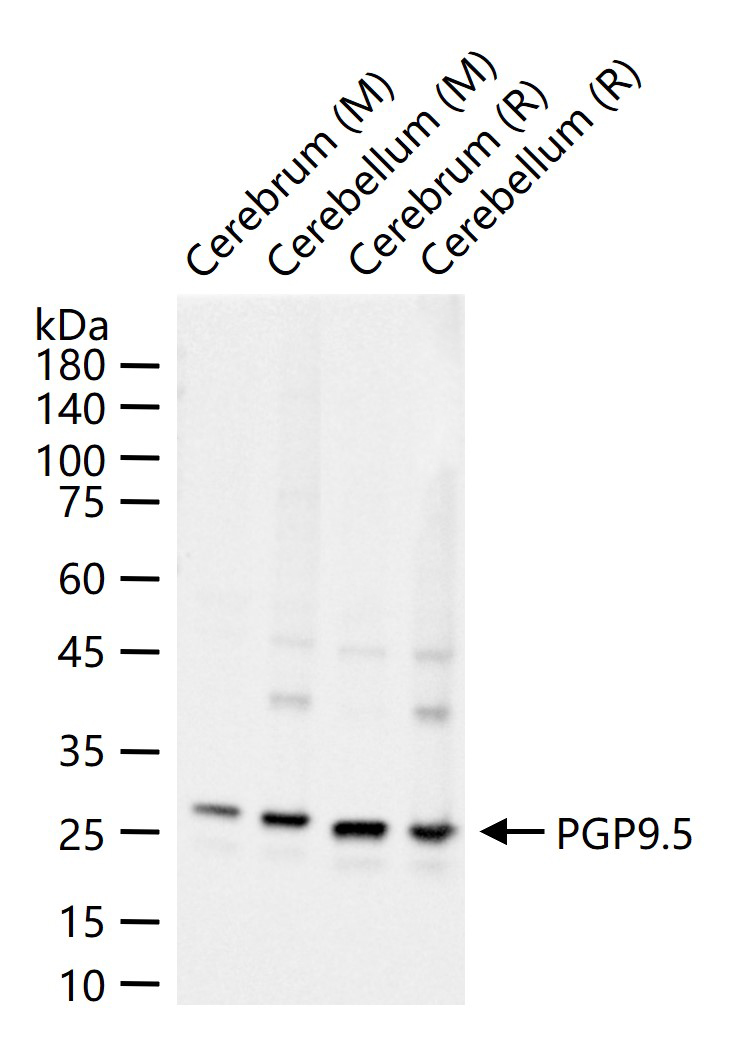
产品应用
| 应用 | 已检合格种属 | 预测种属 | 推荐稀释比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| WB | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:1000-5000 | |
| IHC-P | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:200-2000 | |
| IHC-F | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:200-2000 | |
| IF | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:200-2000 |
交叉反应
交叉反应: Human, Mouse, Rat
相关产品
暂无相关产品
靶标
基因名
UCHL1
蛋白名
Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase isozyme L1
亚基
Monomer. Homodimer. Interacts with SNCA (By similarity). Interacts with COPS5.
亚细胞定位
Cytoplasm. Endoplasmic reticulum membrane. About 30% of total UCHL1 is associated with membranes in brain.
组织特异性
Found in neuronal cell bodies and processes throughout the neocortex (at protein level). Expressed in neurons and cells of the diffuse neuroendocrine system and their tumors. Weakly expressed in ovary. Down-regulated in brains from Parkinson disease and Alzheimer disease patients.
翻译后修饰
O-glycosylated.
疾病
Defects in UCHL1 are the cause of Parkinson disease type 5 (PARK5) [MIM:613643]; also known as Parkinson disease autosomal dominant 5. PARK5 is a complex neurodegenerative disorder with manifestations ranging from typical Parkinson disease to dementia with Lewy bodies. Clinical features include parkinsonian symptoms (resting tremor, rigidity, postural instability and bradykinesia), dementia, diffuse Lewy body pathology, autonomic dysfunction, hallucinations and paranoia.
相似性
Belongs to the peptidase C12 family.
功能
Ubiquitin-protein hydrolase involved both in the processing of ubiquitin precursors and of ubiquitinated proteins. This enzyme is a thiol protease that recognizes and hydrolyzes a peptide bond at the C-terminal glycine of ubiquitin. Also binds to free monoubiquitin and may prevent its degradation in lysosomes. The homodimer may have ATP-independent ubiquitin ligase activity.
标记抗体
暂无标记数据
同靶标产品
暂无同靶标产品
相关文献
提示: 发表研究结果有使用 bsm-41257R 时请让我们知道,以便我们可以引用参考文章。作为回馈,资料提供者将获得我们送上的小礼品。
暂无相关文献
常见问题
暂无常见问题