尿路上皮特异蛋白3重组兔单抗
Rrmab?兔单抗
货号:bsm-61004R
产品详情
相关标记
相关产品
相关文献
常见问题
概述
产品编号
bsm-61004R
产品类型
重组兔单抗、mIHC精品抗体
英文名称
UPK3A Recombinant Rabbit mAb
中文名称
尿路上皮特异蛋白3重组兔单抗
英文别名
UP3A; UPIII; UPIIIA; UPK3; UPK3A_HUMAN; UPK3A; Uroplakin III (UPIII); Q32N05_HUMAN;
抗体来源
Rabbit
免疫原
A synthesized peptide derived from human Uroplakin 3a: 220-287/287
亚型
IgG
性状
Liquid
纯化方法
affinity purified by Protein A
克隆类型
Recombinant
克隆号
19A15
理论分子量
29 kDa
浓度
1mg/ml
储存液
0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol.
保存条件
Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
注意事项
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
数据库链接
背景资料
The asymmetric unit membrane (AUM) forms numerous plaques, which cover the apical surface of the urothelium. These plaques are thought to strengthen the urothelium and reduce the risk of rupturing during ladder distention. They are composed of four major integral membrane proteins called uroplakins (UP). The uroplakin family comprises UPIa, UPIb, UPII, and UPIII. Family members are conserved among several species, including human, mouse, rat, rabbit, dog, pig and sheep. UPIa and UPIb form tightly packed structures with UPII and UPIII, respectively. This pairing is required for normal urothelial plaque formation and is regulated by proteolytic processing of the uroplakin proteins. Uroplakins are expressed in normal urothelium and are used as specific markers of urothelial differentiation. They are also expressed in a majority of transitional cell carcinomas of the bladder (TCCs), which make the uroplakins a useful marker for detecting bladder cancer metastasis and for staging and monitoring chemotherapeutic response.

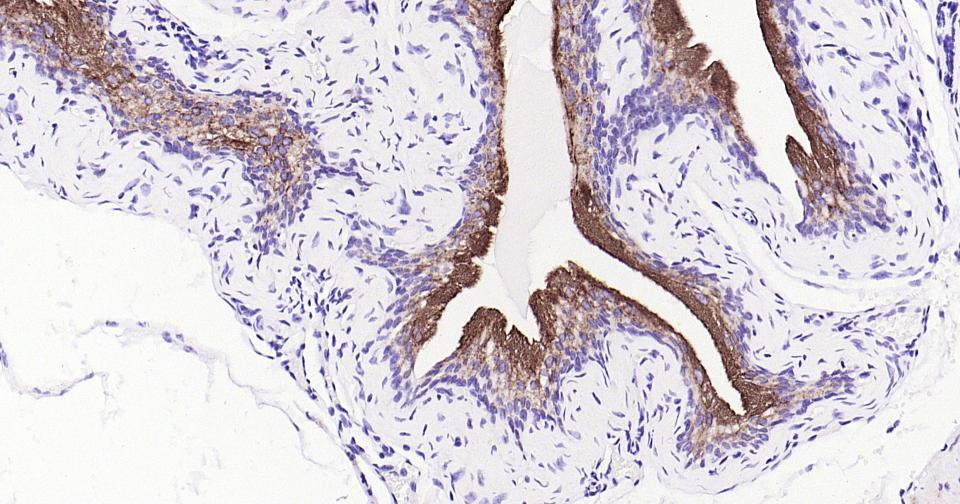
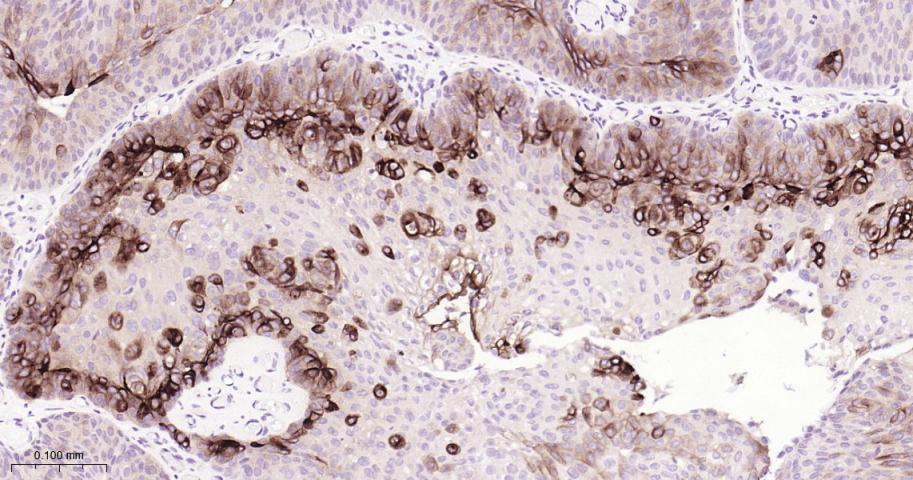
产品应用
| 应用 | 已检合格种属 | 预测种属 | 推荐稀释比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IHC-P | Human, Mouse | 1:100-500 | |
| IHC-F | Human, Mouse | 1:100-500 | |
| IF | Human, Mouse | 1:100-500 |
交叉反应
交叉反应: Human, Mouse
相关产品
暂无相关产品
靶标
基因名
UPK3A
蛋白名
Uroplakin-3a
亚细胞定位
Endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Heterodimer formation with UPK1B is a prerequisite to exit out of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
组织特异性
Expressed in ureter.
疾病
Defects in UPK3A are a cause of renal adysplasia (RADYS) [MIM:191830]; also known as renal agenesis or renal aplasia. Renal agenesis refers to the absence of one (unilateral) or both (bilateral) kidneys at birth. Bilateral renal agenesis belongs to a group of perinatally lethal renal diseases, including severe bilateral renal dysplasia, unilateral renal agenesis with contralateral dysplasia and severe obstructive uropathy.
相似性
Belongs to the uroplakin-3 family.
功能
Component of the asymmetric unit membrane (AUM); a highly specialized biomembrane elaborated by terminally differentiated urothelial cells. May play an important role in AUM-cytoskeleton interaction in terminally differentiated urothelial cells. It also contributes to the formation of urothelial glycocalyx which may play an important role in preventing bacterial adherence.
标记抗体
暂无标记数据
同靶标产品
暂无同靶标产品
相关文献
提示: 发表研究结果有使用 bsm-61004R 时请让我们知道,以便我们可以引用参考文章。作为回馈,资料提供者将获得我们送上的小礼品。
暂无相关文献
常见问题
暂无常见问题