谷氨酰胺转胺酶2重组兔单抗
Rrmab?兔单抗
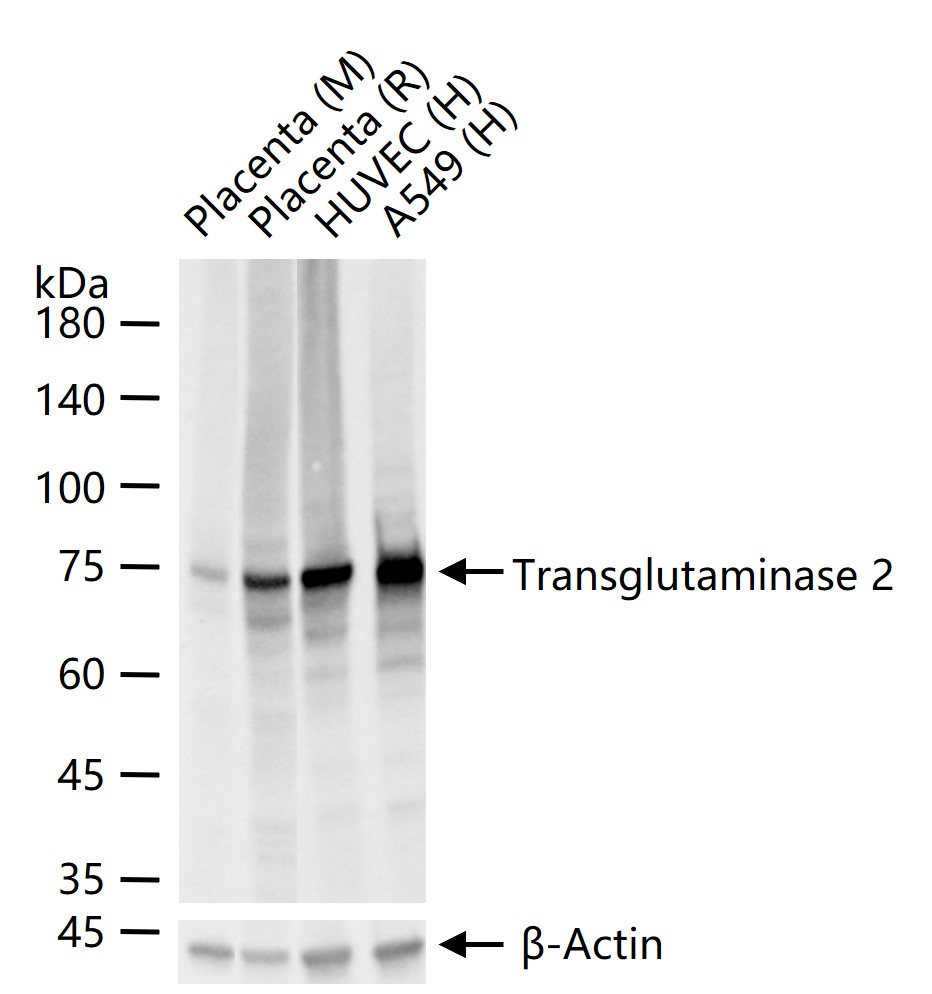
货号:bsm-55541R
产品详情
相关标记
相关产品
相关文献
常见问题
概述
产品编号
bsm-55541R
产品类型
重组兔单抗、mIHC精品抗体
英文名称
Transglutaminase 2 Recombinant Rabbit mAb
中文名称
谷氨酰胺转胺酶2重组兔单抗
英文别名
G(h); TG(C); TGC; hTG2; tTG; G[a]h; TG2; TGase2; tTGas; TGM2_HUMAN; TGM2; Erythrocyte transglutaminase; Heart G alpha(h) (hhG alpha(h)); Isopeptidase TGM2; Protein G alpha(h) (G(h)); Protein-glutamine deamidase TGM2; Protein-glutamine dopaminyltransferase TGM2; Protein-glutamine histaminyltransferase TGM2; Protein-glutamine noradrenalinyltransferase TGM2; Protein-glutamine serotonyltransferase TGM2; Tissue transglutaminase (tTG | tTgase); Transglutaminase C (TG(C) | TGC | TGase C); Transglutaminase H (TGase H); Transglutaminase II (TGase II); Transglutaminase-2 (TG2 | TGase-2 | hTG2); 2.3.2.13; TGM2_MOUSE; Tissue transglutaminase (tTG); Transglutaminase-2 (TG2 | TGase-2 | TGase2);
抗体来源
Rabbit
免疫原
A synthesized peptide derived from human TGM2: 560-615/687
亚型
IgG
性状
Liquid
纯化方法
Affinity Purification
克隆类型
Recombinant
克隆号
17E10
理论分子量
78 kDa
检测分子量
78 kDa
储存液
PBS with 100 μg/ml BSA,0.15% ProClin300 and 50% glycerol.
研究领域
Cell Biology > Apoptosis > Intracellular > Associated Proteins
Immunology > Immune System Diseases > Autoimmune
Metabolism > Pathways and Processes > Metabolic signaling pathways > Amino acid metabolism
Metabolism > Types of disease > Cancer
Signal Transduction > Metabolism > Amino Acids
Signal Transduction > Signaling Pathway > Calcium Signaling > Calcium Binding Proteins
SWISS
Gene ID
保存条件
Store at -20 ℃ for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
注意事项
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
数据库链接
产品介绍
谷氨酰胺转移酶2(TGM2)是一种钙离子依赖酶,通过催化赖氨酸与谷氨酰胺残基之间形成化学键,可以将胞质和细胞外基质蛋白进行交联。这种双功能酶也有内在GTP酶活性,研究表明,转酰氨基酶活性的调节有可能通过G蛋白偶联受体信号转导通路进行调节。在交联肽中,TGM2可以帮助调节细胞骨架结构、细胞迁移、凋亡和细胞基质粘附。另外,该酶在创伤愈合与免疫应答中起重要作用。TGM2显示有体外激酶活性,胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白3(IGFBP-3)为其潜在底物。这种广泛表达的蛋白定位于胞质与胞核之中,但是从细胞表面与细胞外基质中也有分离,由于其与许多不同的底物有相互作用,以及在损伤应答中的作用,TGM2与许多人疾病病理有关。TGM2长期被认为是腹腔疾病的自身抗原,其表达或活性变化可能与阿尔茨海默病、亨廷顿病、动脉硬化、糖尿病以及与多种癌症有关联。
背景资料
Calcium-dependent acyltransferase that catalyzes the formation of covalent bonds between peptide-bound glutamine and various primary amines, such as gamma-amino group of peptide-bound lysine, or mono- and polyamines, thereby producing cross-linked or aminated proteins, respectively. Involved in many biological processes, such as bone development, angiogenesis, wound healing, cellular differentiation, chromatin modification and apoptosis. Acts as a protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase by mediating the cross-linking of proteins, such as ACO2, HSPB6, FN1, HMGB1, RAP1GDS1, SLC25A4/ANT1, SPP1 and WDR54. Under physiological conditions, the protein cross-linking activity is inhibited by GTP; inhibition is relieved by Ca(2+) in response to various stresses. When secreted, catalyzes cross-linking of proteins of the extracellular matrix, such as FN1 and SPP1 resulting in the formation of scaffolds. Plays a key role during apoptosis, both by (1) promoting the cross-linking of cytoskeletal proteins resulting in condensation of the cytoplasm, and by (2) mediating cross-linking proteins of the extracellular matrix, resulting in the irreversible formation of scaffolds that stabilize the integrity of the dying cells before their clearance by phagocytosis, thereby preventing the leakage of harmful intracellular components.

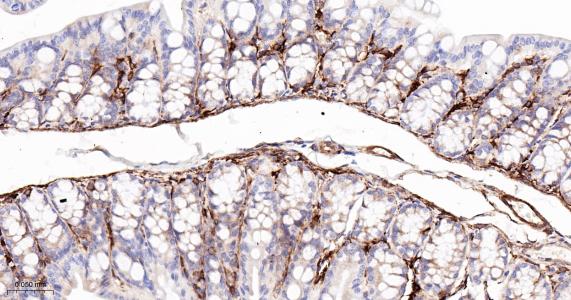
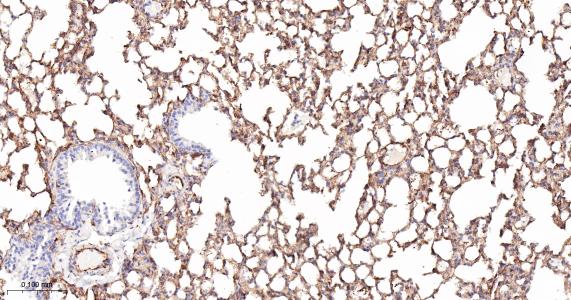
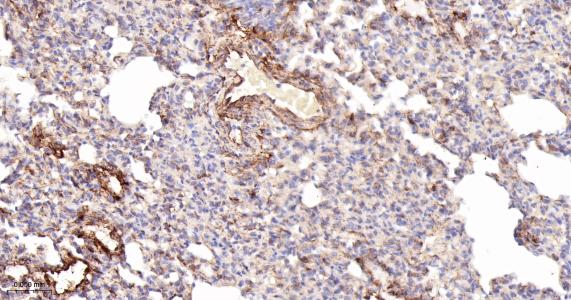
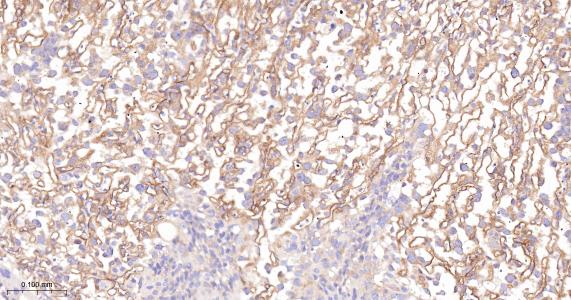
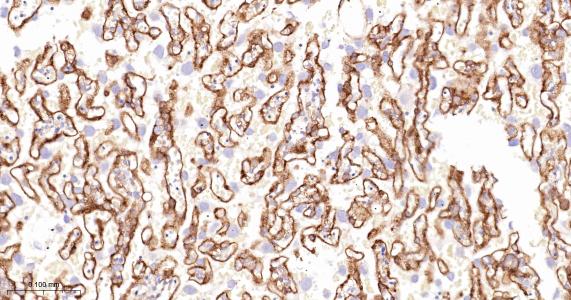
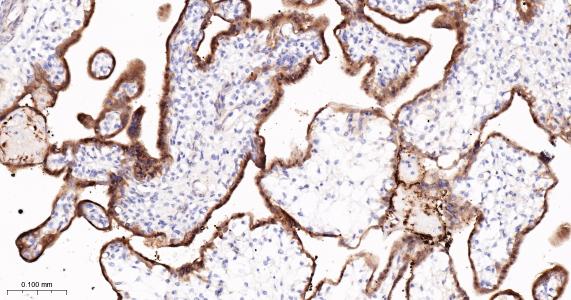
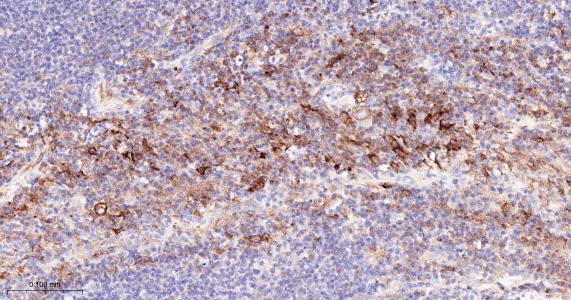
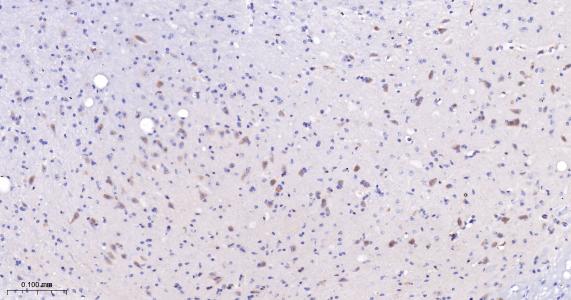
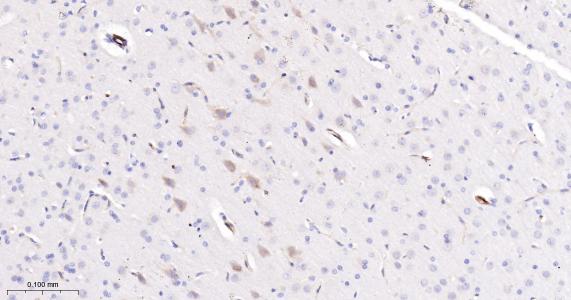
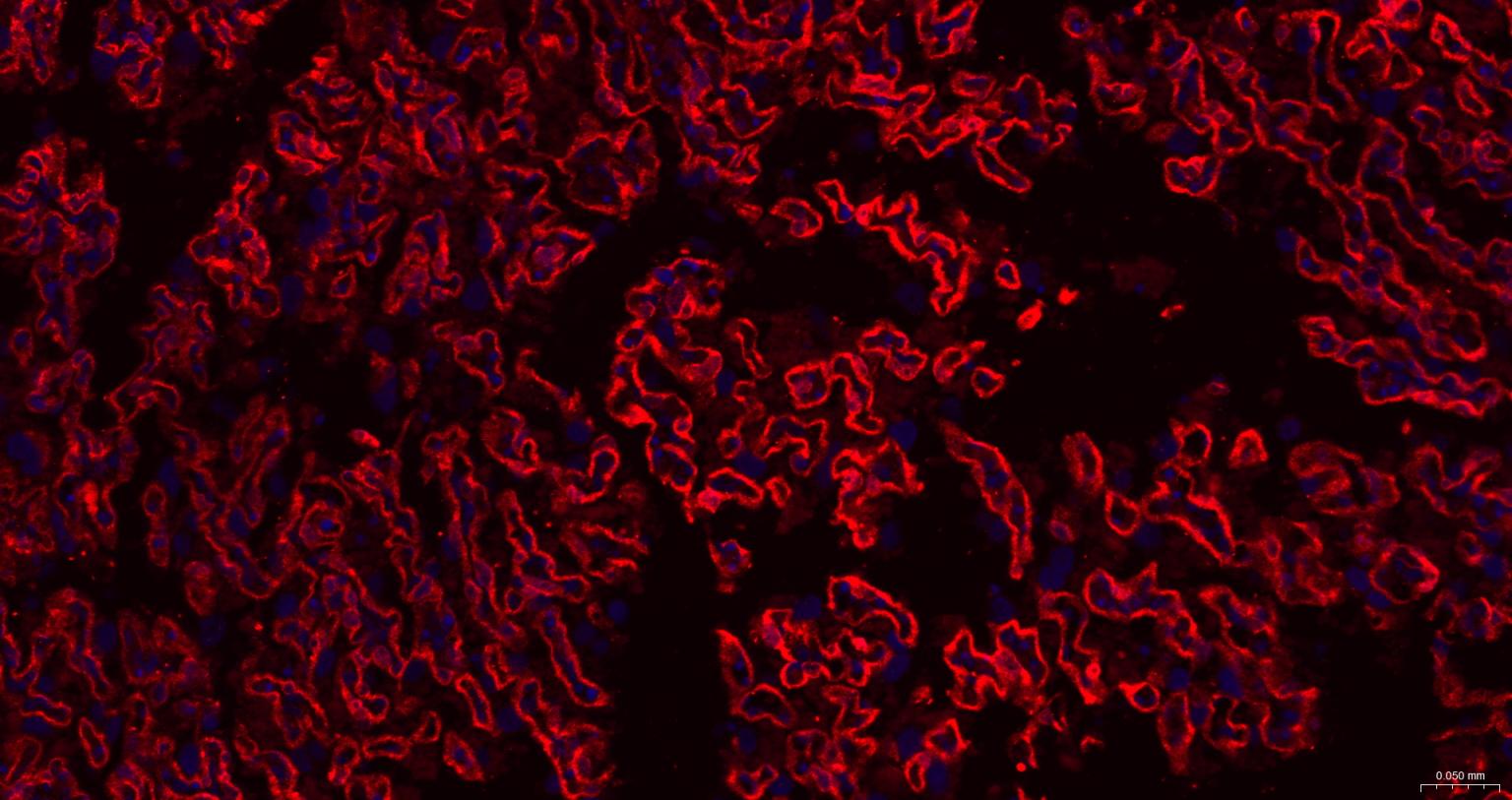
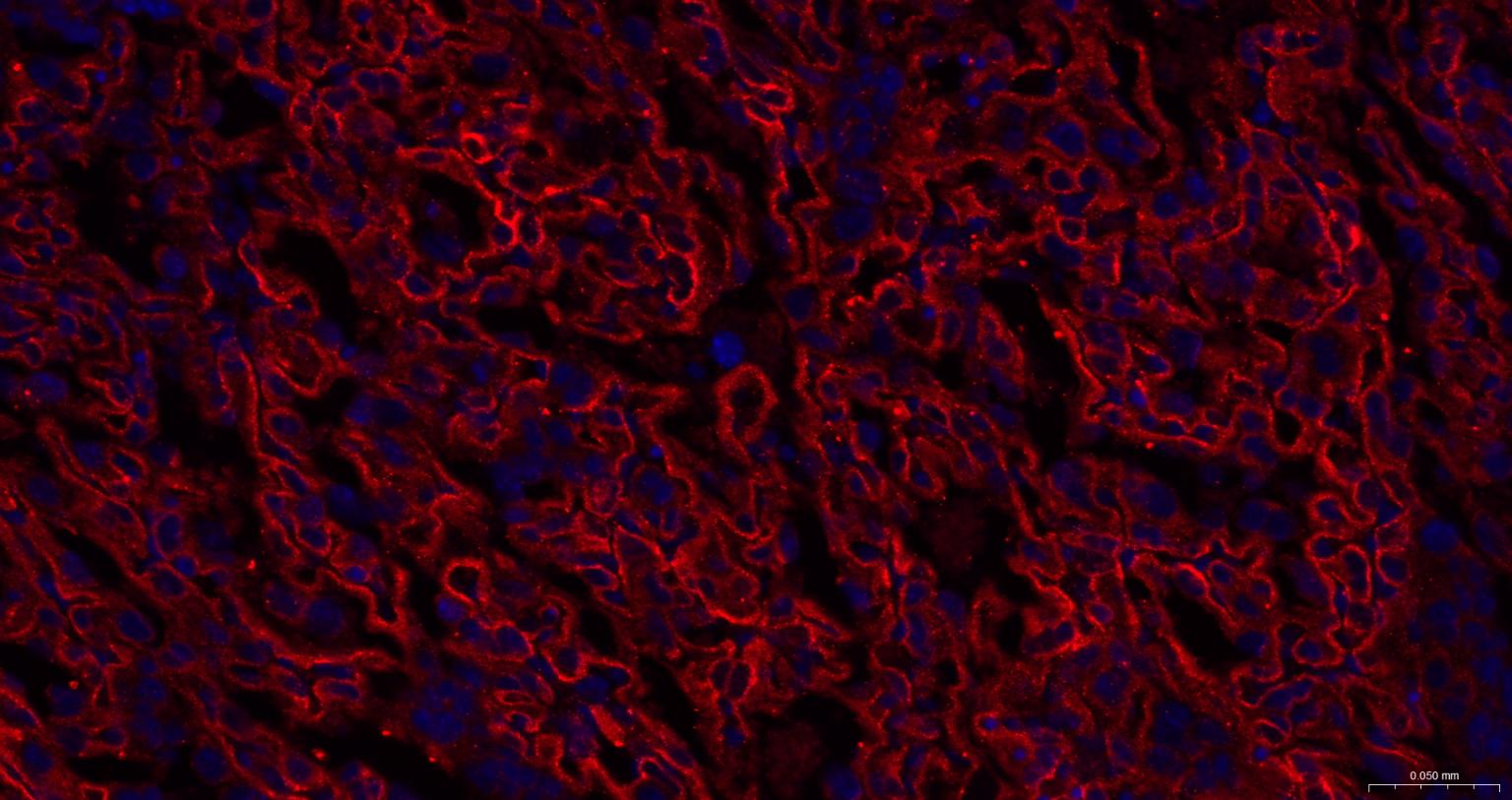
产品应用
| 应用 | 已检合格种属 | 预测种属 | 推荐稀释比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| WB | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1: 500- 2000 | |
| IHC-P | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1: 100- 500 | |
| IHC-F | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1: 100- 500 | |
| IF | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1: 100- 500 |
交叉反应
交叉反应: Human, Mouse, Rat
相关产品
暂无相关产品
靶标
基因名
TGM2
蛋白名
Protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase 2
亚基
Monomer.
相似性
Belongs to the transglutaminase superfamily. Transglutaminase family.
功能
Catalyzes the cross-linking of proteins and the conjugation of polyamines to proteins.
标记抗体
暂无标记数据
同靶标产品
暂无同靶标产品
相关文献
提示: 发表研究结果有使用 bsm-55541R 时请让我们知道,以便我们可以引用参考文章。作为回馈,资料提供者将获得我们送上的小礼品。
暂无相关文献
常见问题
暂无常见问题