p38 MAPK重组兔单抗
Rrmab?兔单抗
货号:bsm-55529R
产品详情
相关标记
相关产品
相关文献
常见问题
概述
产品编号
bsm-55529R
产品类型
重组兔单抗
英文名称
p38 Recombinant Rabbit mAb
中文名称
p38 MAPK重组兔单抗
英文别名
CSBP; CSBP1; CSBP2; CSPB1; EXIP; Mxi2; PRKM14; PRKM15; RK; SAPK2A; p38; p38ALPHA; Crk1; p38-alpha; p38MAPK; p38a; Hog; p38Hog; MK14_CANLF; MAPK14; MAP kinase 14; MAPK 14; Mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 alpha (MAP kinase p38 alpha); 2.7.11.24; MK14_HUMAN; Cytokine suppressive anti-inflammatory drug-binding protein (CSAID-binding protein | CSBP); MAP kinase MXI2; MAX-interacting protein 2; Stress-activated protein kinase 2a (SAPK2a); MK14_MOUSE; MK14_RAT;
抗体来源
Rabbit
免疫原
KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from Human p38
亚型
IgG
性状
Liquid
纯化方法
Affinity Purification
克隆类型
Recombinant
克隆号
SB94
理论分子量
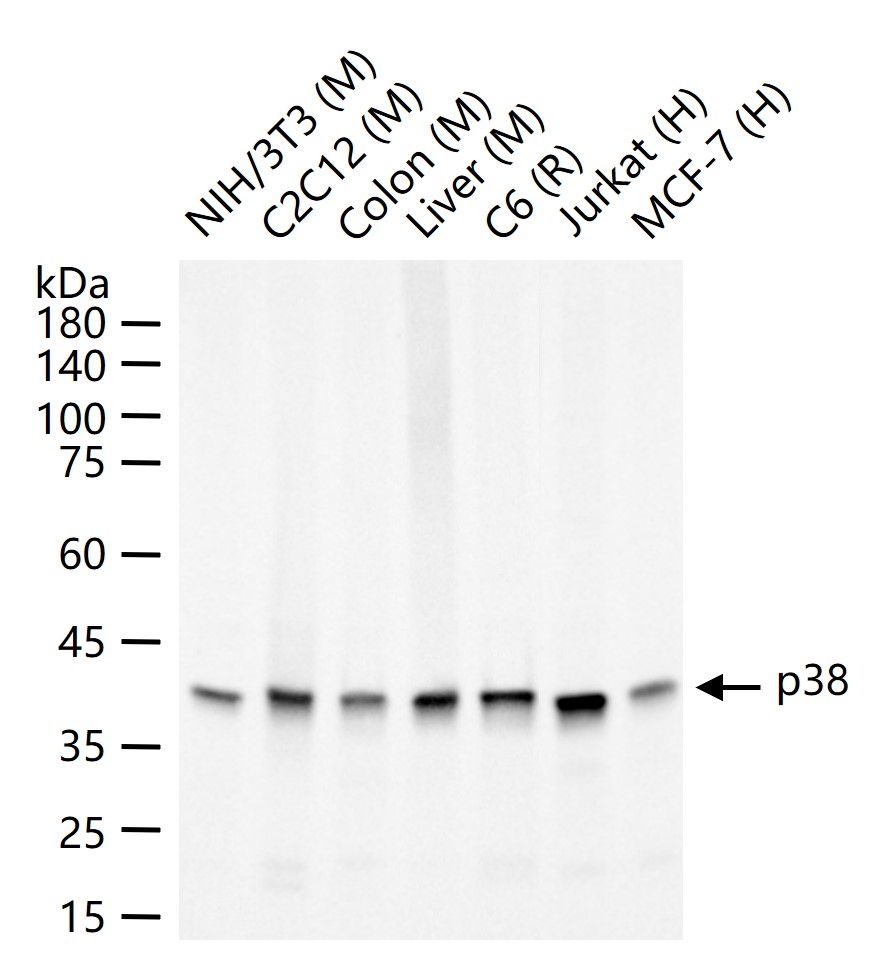
38 kDa
检测分子量
40 kDa
储存液
PBS with 100 μg/ml BSA,0.15% ProClin300 and 50% glycerol.
研究领域
SWISS
Gene ID
保存条件
Store at -20 ℃ for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
注意事项
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
数据库链接
产品介绍
p38 MAP 激酶(MAPK)也称为 RK 或 CSBP,参与控制细胞因子和应激引起的细胞反应的信号转导级联。现已发现p38 的四种同工型:p38α、β、γ(也称 Erk6 或 SAPK3)和 δ(也称 SAPK4)。与 SAPK/JNK 通路相似,p38 MAPK 被多种细胞应激激活,包括渗透压休克、炎性细胞因子、脂多糖(LPS)、紫外线和生长因子。MKK3、MKK6 和 SEK 通过磷酸化 Thr180 和 Tyr182 位点激活 p38 MAPK。激活的 p38 MAPK 已证实可磷酸化和激活 MAPKAP 激酶 2,并磷酸化转录因子 ATF-2、Max 和 MEF2。
背景资料
Serine/threonine kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway. MAPK12 is one of the four p38 MAPKs which play an important role in the cascades of cellular responses evoked by extracellular stimuli such as pro-inflammatory cytokines or physical stress leading to direct activation of transcription factors such as ELK1 and ATF2.

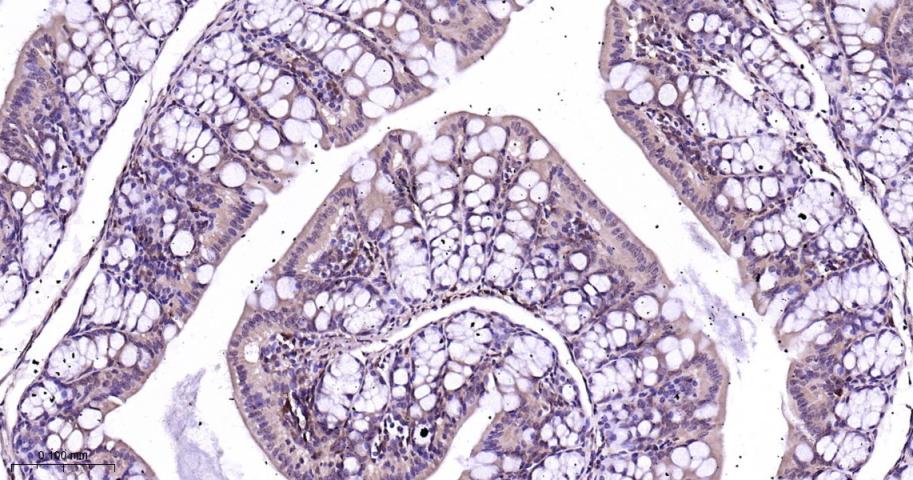
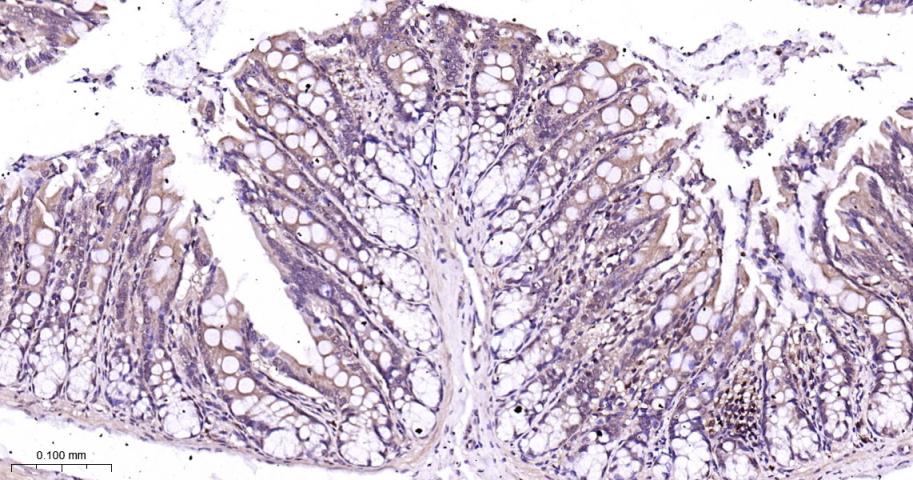
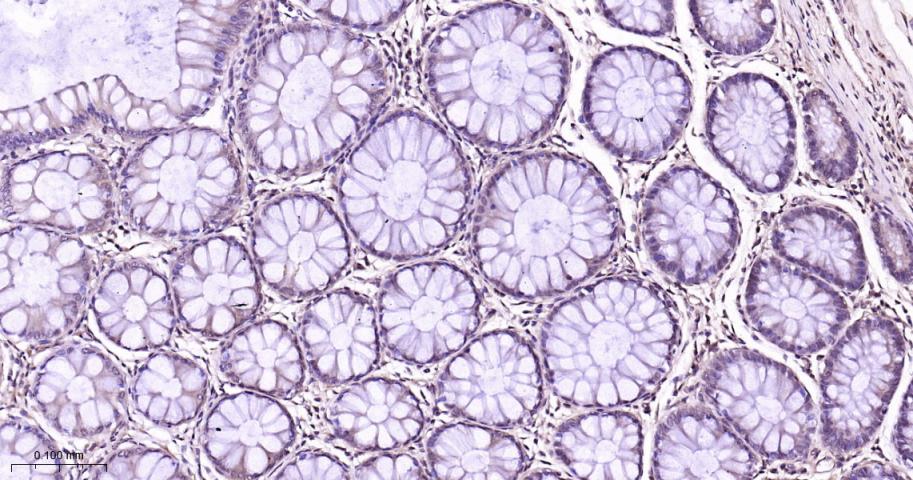
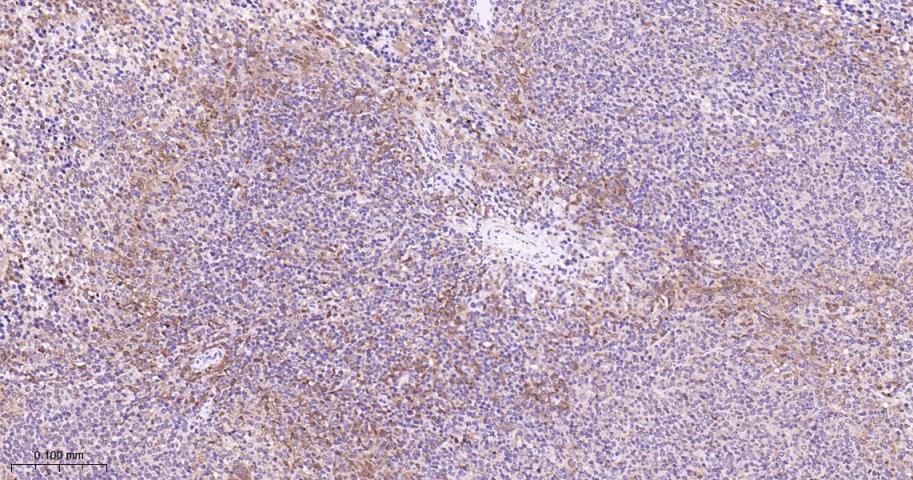
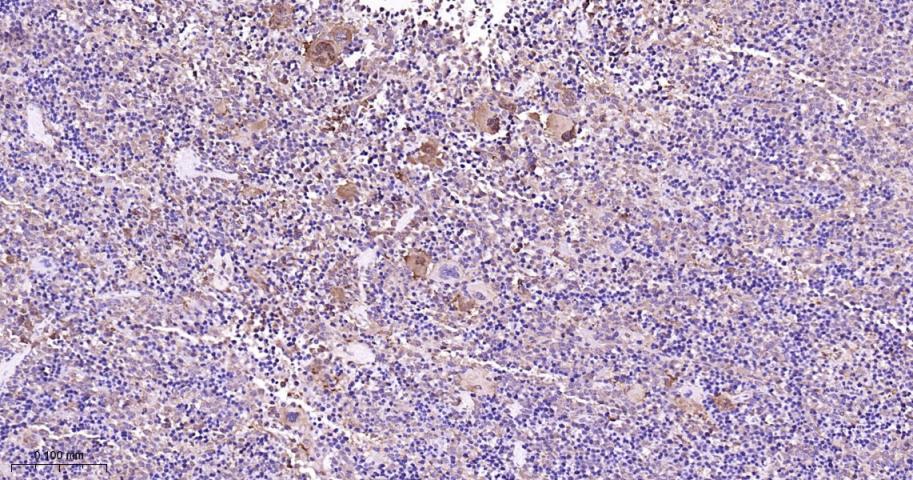
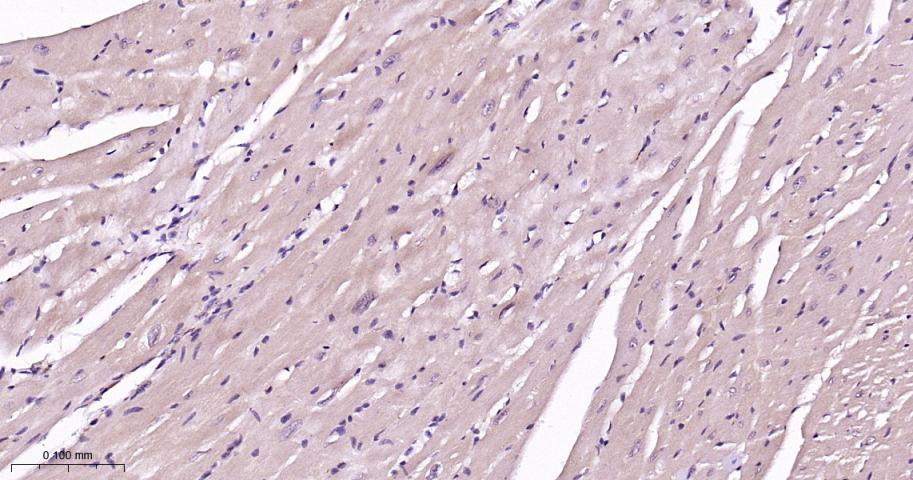
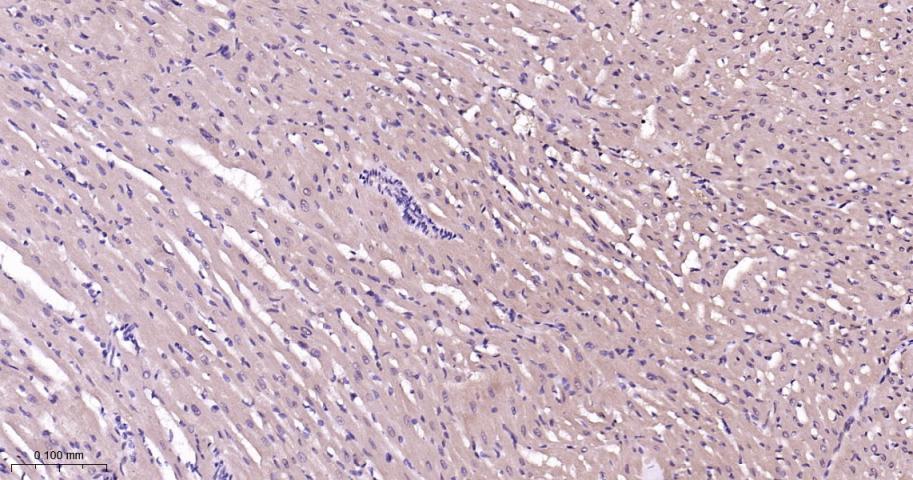
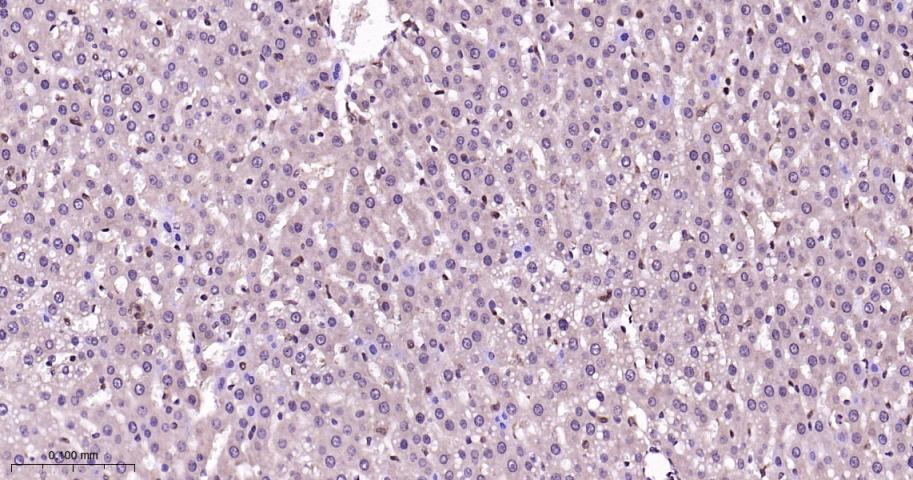
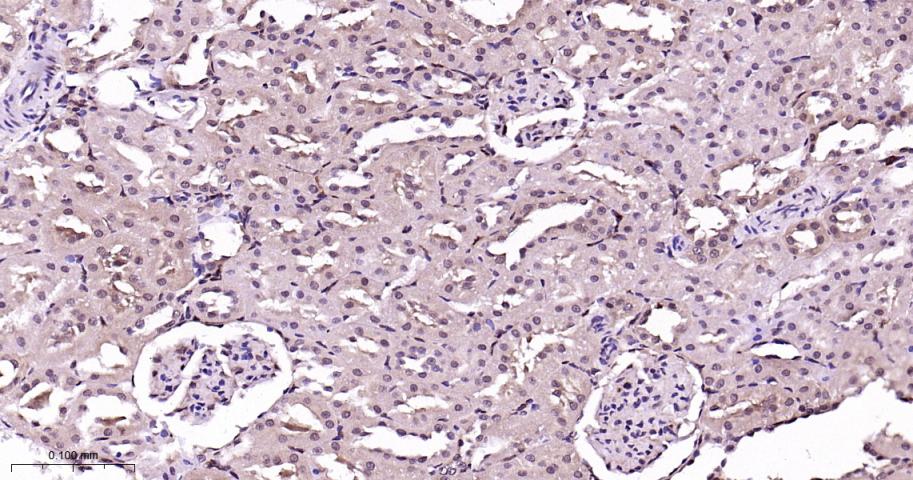
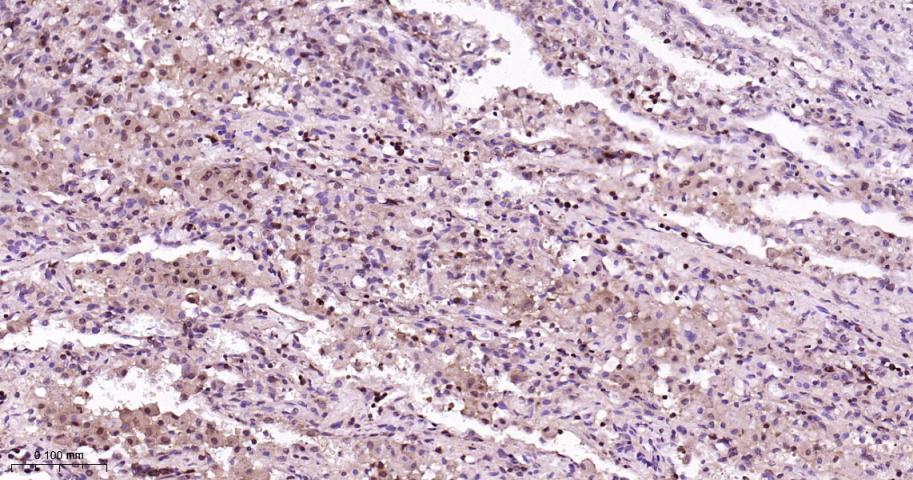
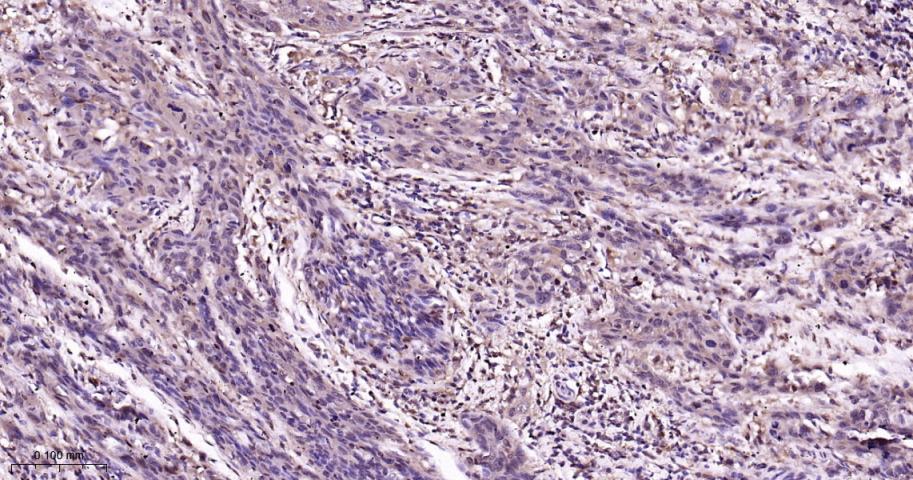
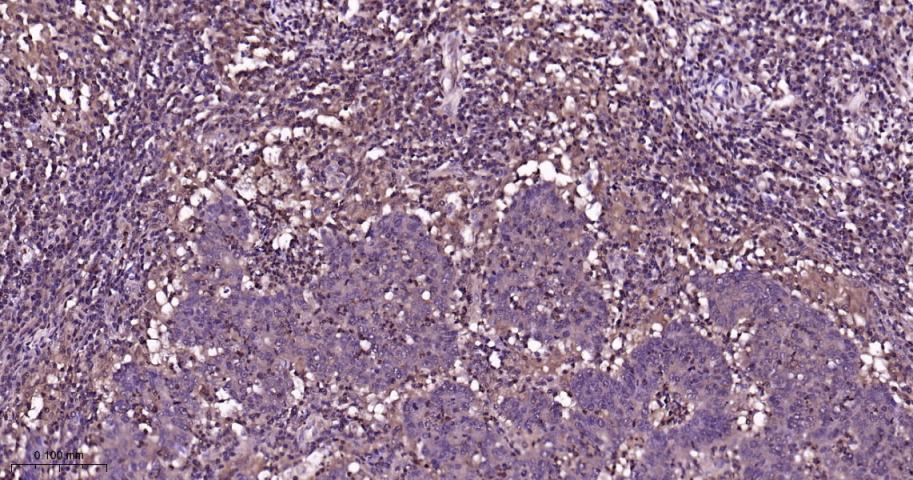
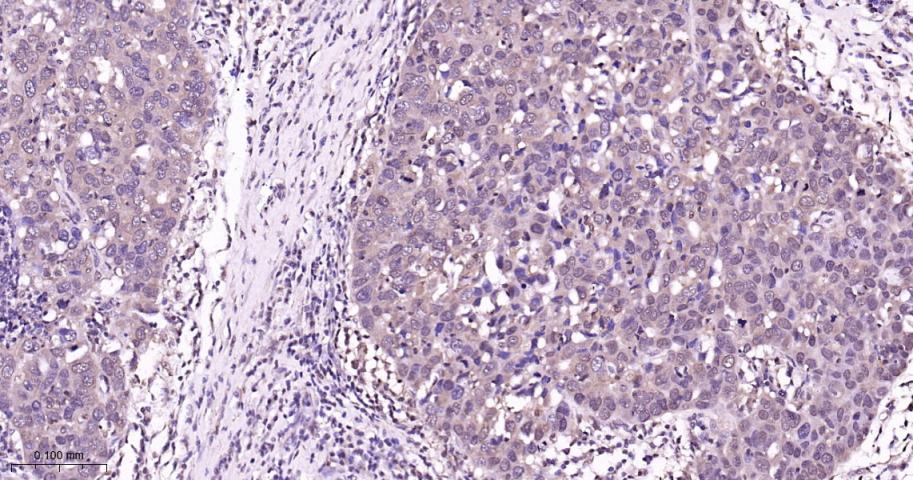
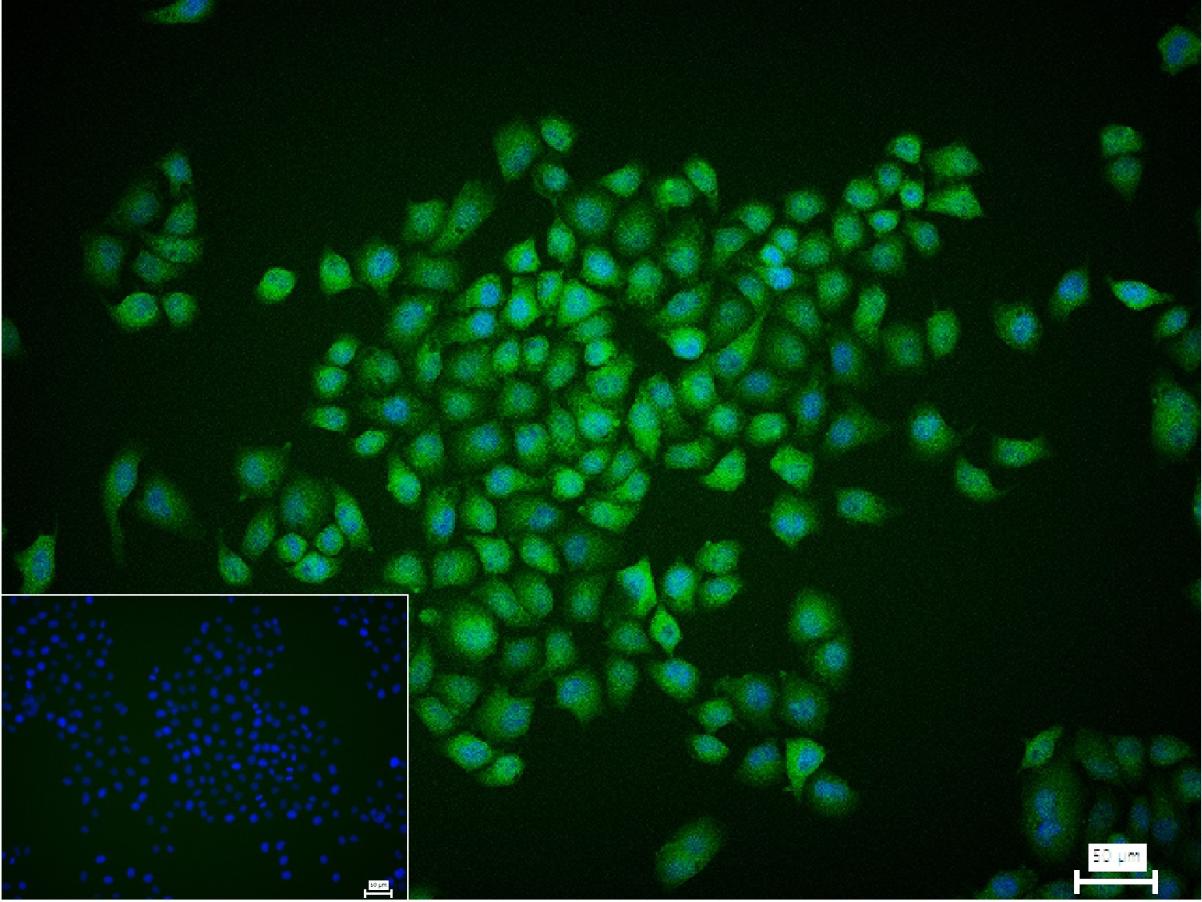
产品应用
| 应用 | 已检合格种属 | 预测种属 | 推荐稀释比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| WB | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1: 500-2000 | |
| IHC-P | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1: 50-200 | |
| IHC-F | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1: 50-200 | |
| IF | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1: 50-200 | |
| ICC/IF | Human | Mouse, Rat | 1:50-200 |
交叉反应
交叉反应: Human, Mouse, Rat
相关产品
暂无相关产品
靶标
基因名
MAPK14
蛋白名
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14
亚基
Binds to a kinase interaction motif within the protein tyrosine phosphatase, PTPRR (By similarity). This interaction retains MAPK14 in the cytoplasm and prevents nuclear accumulation. Interacts with SPAG9 and GADD45A. Interacts with CDC25B, CDC25C, DUSP1, DUSP10, DUSP16, NP60, FAM48A and TAB1. Interacts with casein kinase II subunits CSNK2A1 and CSNK2B.
亚细胞定位
Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
组织特异性
Brain, heart, placenta, pancreas and skeletal muscle. Expressed to a lesser extent in lung, liver and kidney.
翻译后修饰
Dually phosphorylated on Thr-180 and Tyr-182 by the MAP2Ks MAP2K3/MKK3, MAP2K4/MKK4 and MAP2K6/MKK6 in response to inflammatory citokines, environmental stress or growth factors, which a ctivates the enzyme. Dual phosphorylation can also be mediated by TAB1-mediated autophosphorylation. TCR engagement in T-cells also leads to Tyr-323 phosphorylation by ZAP70. Dephosphorylated and inactivated by DUPS1, DUSP10 and DUSP16.
Acetylated at Lys-53 and Lys-152 by KAT2B and EP300. Acetylation at Lys-53 increases the affinity for ATP and enhances kinase activity. Lys-53 and Lys-152 are deacetylated by HDAC3.
Ubiquitinated. Ubiquitination leads to degradation by the proteasome pathway.
Acetylated at Lys-53 and Lys-152 by KAT2B and EP300. Acetylation at Lys-53 increases the affinity for ATP and enhances kinase activity. Lys-53 and Lys-152 are deacetylated by HDAC3.
Ubiquitinated. Ubiquitination leads to degradation by the proteasome pathway.
相似性
Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family. MAP kinase subfamily.
Contains 1 protein kinase domain.
Contains 1 protein kinase domain.
功能
Serine/threonine kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway. MAPK14 is one of the four p38 MAPKs which play an important role in the cascades of cellular responses evoked by extracellular stimuli such as proinflammatory cytokines or physical stress leading to direct activation of transcription factors. Accordingly, p38 MAPKs phosphorylate a broad range of proteins and it has been estimated that they may have approximately 200 to 300 substrates each. Some of the targets are downstream kinases which are activated through phosphorylation and further phosphorylate additional targets. RPS6KA5/MSK1 and RPS6KA4/MSK2 can directly phosphorylate and activate transcription factors such as CREB1, ATF1, the NF-kappa-B isoform RELA/NFKB3, STAT1 and STAT3, but can also phosphorylate histone H3 and the nucleosomal protein HMGN1. RPS6KA5/MSK1 and RPS6KA4/MSK2 play important roles in the rapid induction of immediate-early genes in response to stress or mitogenic stimuli, either by inducing chromatin remodeling or by recruiting the transcription machinery. On the other hand, two other kinase targets, MAPKAPK2/MK2 and MAPKAPK3/MK3, participate in the control of gene expression mostly at the post-transcriptional level, by phosphorylating ZFP36 (tristetraprolin) and ELAVL1, and by regulating EEF2K, which is important for the elongation of mRNA during translation. MKNK1/MNK1 and MKNK2/MNK2, two other kinases activated by p38 MAPKs, regulate protein synthesis by phosphorylating the initiation factor EIF4E2. MAPK14 interacts also with casein kinase II, leading to its activation through autophosphorylation and further phosphorylation of TP53/p53. In the cytoplasm, the p38 MAPK pathway is an important regulator of protein turnover. For example, CFLAR is an inhibitor of TNF-induced apoptosis whose proteasome-mediated degradation is regulated by p38 MAPK phosphorylation. In a similar way, MAPK14 phosphorylates the ubiquitin ligase SIAH2, regulating its activity towards EGLN3. MAPK14 may also inhibit the lysosomal degradation pathway of autophagy by interfering with the intracellular trafficking of the transmembrane protein ATG9. Another function of MAPK14 is to regulate the endocytosis of membrane receptors by different mechanisms that impinge on the small GTPase RAB5A. In addition, clathrin-mediated EGFR internalization induced by inflammatory cytokines and UV irradiation depends on MAPK14-mediated phosphorylation of EGFR itself as well as of RAB5A effectors. Ectodomain shedding of transmembrane proteins is regulated by p38 MAPKs as well. In response to inflammatory stimuli, p38 MAPKs phosphorylate the membrane-associated metalloprotease ADAM17. Such phosphorylation is required for ADAM17-mediated ectodomain shedding of TGF-alpha family ligands, which results in the activation of EGFR signaling and cell proliferation. Another p38 MAPK substrate is FGFR1. FGFR1 can be translocated from the extracellular space into the cytosol and nucleus of target cells, and regulates processes such as rRNA synthesis and cell growth. FGFR1 translocation requires p38 MAPK activation. In the nucleus, many transcription factors are phosphorylated and activated by p38 MAPKs in response to different stimuli. Classical examples include ATF1, ATF2, ATF6, ELK1, PTPRH, DDIT3, TP53/p53 and MEF2C and MEF2A. The p38 MAPKs are emerging as important modulators of gene expression by regulating chromatin modifiers and remodelers. The promoters of several genes involved in the inflammatory response, such as IL6, IL8 and IL12B, display a p38 MAPK-dependent enrichment of histone H3 phosphorylation on 'Ser-10' (H3S10ph) in LPS-stimulated myeloid cells. This phosphorylation enhances the accessibility of the cryptic NF-kappa-B-binding sites marking promoters for increased NF-kappa-B recruitment. Phosphorylates CDC25B and CDC25C which is required for binding to 14-3-3 proteins and leads to initiation of a G2 delay after ultraviolet radiation. Phosphorylates TIAR following DNA damage, releasing TIAR from GADD45A mRNA and preventing mRNA degradation. The p38 MAPKs may also have kinase-independent roles, which are thought to be due to the binding to targets in the absence of phosphorylation. Protein O-Glc-N-acylation catalyzed by the OGT is regulated by MAPK14, and, although OGT does not seem to be phosphorylated by MAPK14, their interaction increases upon MAPK14 activation induced by glucose deprivation. This interaction may regulate OGT activity by recruiting it to specific targets such as neurofilament H, stimulating its O-Glc-N-acylation. Required in mid-fetal development for the growth of embryo-derived blood vessels in the labyrinth layer of the placenta. Also plays an essential role in developmental and stress-induced erythropoiesis, through regulation of EPO gene expression. Isoform MXI2 activation is stimulated by mitogens and oxidative stress and only poorly phosphorylates ELK1 and ATF2. Isoform EXIP may play a role in the early onset of apoptosis. Phosphorylates S100A9 at 'Thr-113'.
标记抗体
暂无标记数据
同靶标产品
暂无同靶标产品
相关文献
提示: 发表研究结果有使用 bsm-55529R 时请让我们知道,以便我们可以引用参考文章。作为回馈,资料提供者将获得我们送上的小礼品。
具体参考文献:bsm-55529R 被引用于4文献中
暂无相关文献
常见问题
暂无常见问题