粘蛋白-1重组兔单抗
Rrmab?兔单抗
货号:bsm-55523R
产品详情
相关标记
相关产品
相关文献
常见问题
概述
产品编号
bsm-55523R
产品类型
重组兔单抗、mIHC精品抗体
英文名称
MUC1/CD227 Recombinant Rabbit mAb
中文名称
粘蛋白-1重组兔单抗
英文别名
ADMCKD; ADMCKD1; ADTKD2; CA 15-3; CD227; Ca15-3; EMA; H23AG; KL-6; MAM6; MCD; MCKD; MCKD1; MUC-1; MUC-1/SEC; MUC-1/X; MUC1/ZD; PEM; PEMT; PUM; MUC1_HUMAN; MUC1; Breast carcinoma-associated antigen DF3; Cancer antigen 15-3 (CA 15-3); Carcinoma-associated mucin; Episialin; Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6); Peanut-reactive urinary mucin (PUM); Polymorphic epithelial mucin (PEM); Tumor-associated epithelial membrane antigen (EMA); Tumor-associated mucin; MUC1_MOUSE;
抗体来源
Rabbit
免疫原
Synthesized peptide derived from Human MUC1
亚型
IgG
性状
Liquid
纯化方法
Affinity Purification
克隆类型
Recombinant
克隆号
SB48
储存液
PBS with 100 μg/ml BSA,0.15% ProClin300 and 50% glycerol.
研究领域
SWISS
Gene ID
保存条件
Store at -20 ℃ for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
注意事项
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
数据库链接
产品介绍
Mucin(CD227)是糖蛋白家族的一员,以重复结构域和密集的O-糖基化为特征。MUC1在呼吸道、胃肠道等所有上皮组织、皮脂腺和唾液腺以及造血细胞中都有表达,MUC1的非上皮性表达已被描述发生在白细胞上,包括T细胞、B细胞、骨髓单核细胞、单核细胞和树突状细胞(DCs)等。MUC1可进行蛋白质水解裂解,并且较大的胞外域与较小的羧基末端结构域有关,后者包含一个跨膜片段和一个含72个残基的胞质尾区。MUC1对正常的上皮起润滑和保护作用,同时还介导信号转导和细胞黏附功能,免疫活化和抑制作用等。在肿瘤组织中,MUC1常出现异常表达,非极性分布,且由于糖基转移酶活性增高而导致的糖基化不完全,使正常情况下隐蔽的表位暴露出来,成为肿瘤生物学治疗的靶点。
背景资料
Mucins represent a family of glycoproteins characterized by repeat domains and dense O-glycosylation . MUC1 (or mucin 1) is aberrantly overexpressed in most human carcinomas. Increased expression of MUC1 in carcinomas reduces cell-cell and cell-ECM interactions. MUC1 is cleaved proteolytically, and the large ectodomain can remain associated with the small 25 kDa carboxy-terminal domain that contains a transmembrane segment and a 72-residue cytoplasmic tail. MUC1 interacts with ErbB family receptors and potentiates ERK1/2 activation. MUC1 also interacts with β-catenin, which is regulated by GSK-3β, PKCγ, and Src through phosphorylation at Ser44, Thr41, and Tyr46 of the MUC1 cytoplasmic tail. Overexpression of MUC1 potentiates transformation and attenuates stress-induced apoptosis through the Akt or p53 pathways

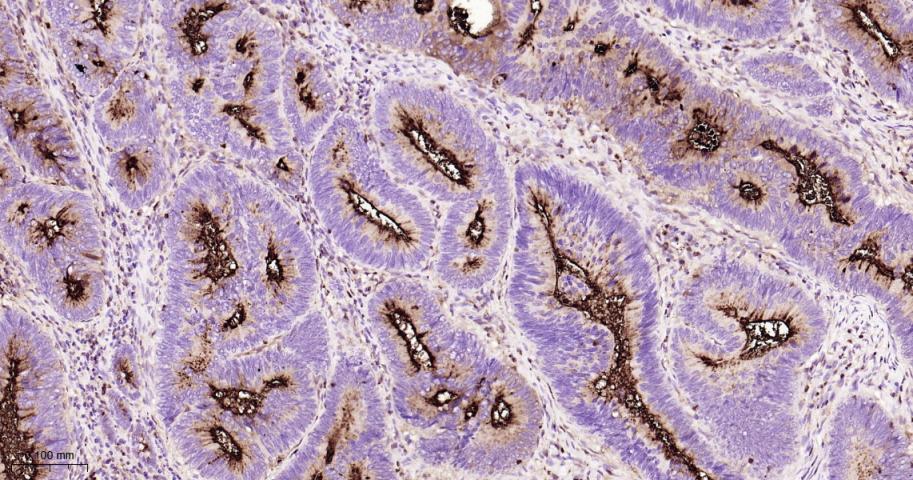
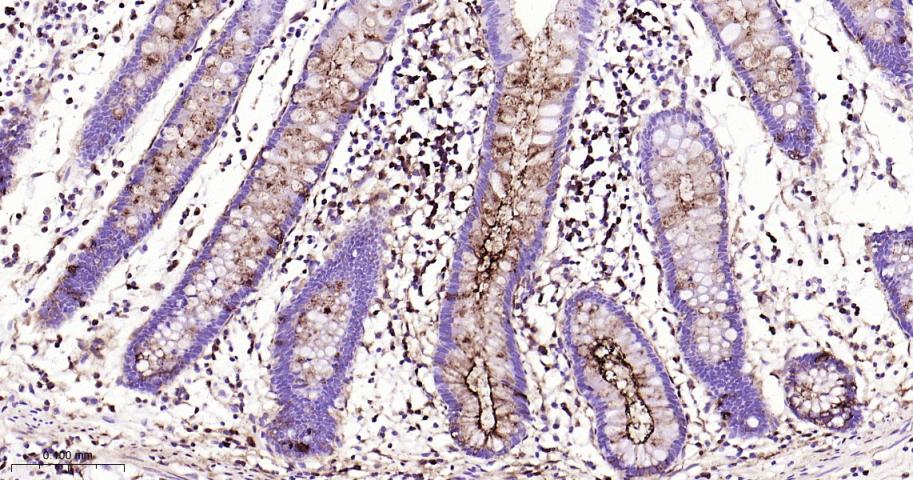
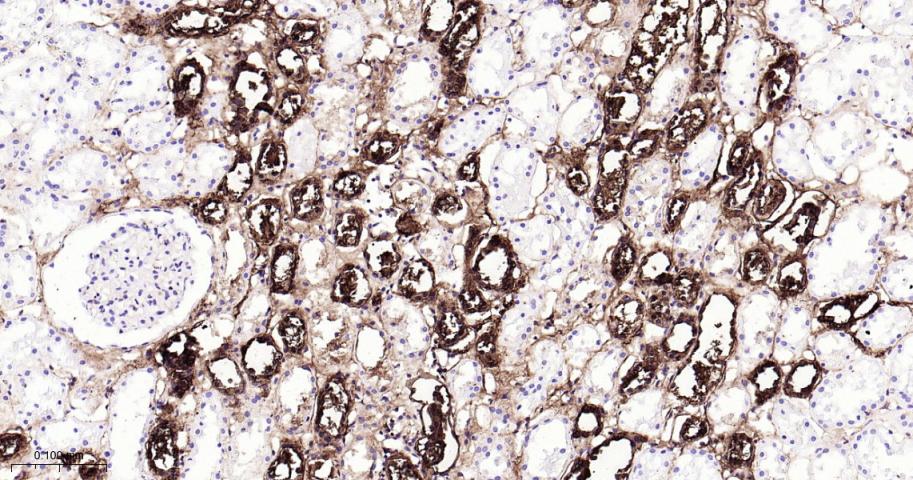
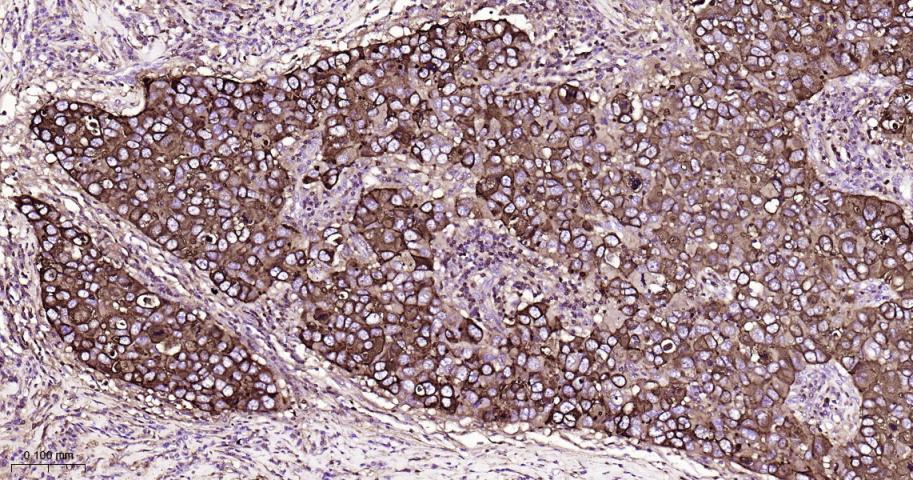
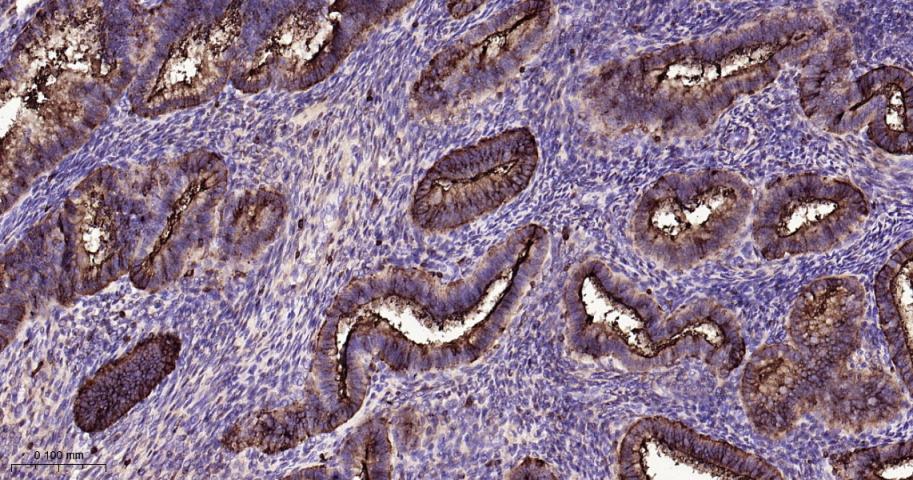
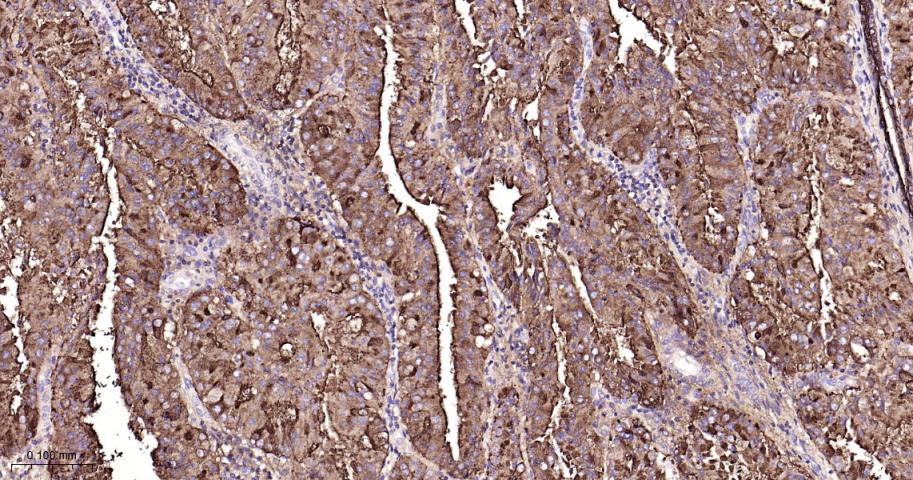
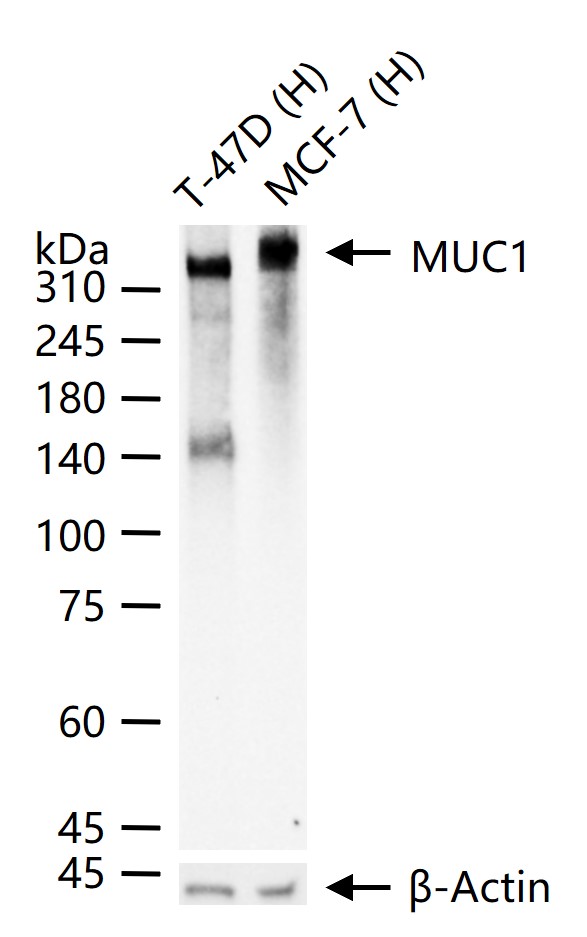
产品应用
| 应用 | 已检合格种属 | 预测种属 | 推荐稀释比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| WB | Human | 1: 500-2000 | |
| IHC-P | Human | 1: 200-1000 | |
| IHC-F | Human | 1: 200-1000 | |
| IF | Human | 1: 200-1000 |
交叉反应
交叉反应: Human
相关产品
暂无相关产品
靶标
基因名
MUC1
蛋白名
Mucin-1
亚基
The alpha subunit forms a tight, non-covalent heterodimeric complex with the proteolytically-released beta-subunit.
亚细胞定位
Secreted; Cell membrane. Cytoplasm. Nucleus. On EGF and PDGFRB stimulation, transported to the nucleus through interaction with CTNNB1, a process which is stimulated by phosphorylation. On HRG stimulation, colocalizes with JUP/gamma-catenin at the nucleus and Apical cell membrane. Exclusively located in the apical domain of the plasma membrane of highly polarized epithelial cells. After endocytosis, internalized and recycled to the cell membrane. Located to microvilli and to the tips of long filopodial protusions.
组织特异性
Expressed on the apical surface of epithelial cells, especially of airway passages, breast and uterus. Also expressed in activated and unactivated T-cells.
Overexpressed in epithelial tumors, such as breast or ovarian cancer and also in non-epithelial tumor cells. Isoform 7 is expressed in tumor cells only.
Overexpressed in epithelial tumors, such as breast or ovarian cancer and also in non-epithelial tumor cells. Isoform 7 is expressed in tumor cells only.
翻译后修饰
Highly glycosylated (N- and O-linked carbohydrates and sialic acid). O-glycosylated to a varying degree on serine and threonine residues within each tandem repeat, ranging from mono- to penta-glycosylation. The average density ranges from about 50% in human milk to over 90% in T47D breast cancer cells. Further sialylation occurs during recycling. Membrane-shed glycoproteins from kidney and breast cancer cells have preferentially sialyated core 1 structures, while secreted forms from the same tissues display mainly core 2 structures. The O-glycosylated content is overlapping in both these tissues with terminal fucose and galactose, 2- and 3-linked galactose, 3- and 3,6-linked GalNAc-ol and 4-linked GlcNAc predominating. Differentially O-glycosylated in breast carcinomas with 3,4-linked GlcNAc. N-glycosylation consists of high-mannose, acidic complex-type and hybrid glycans in the secreted form MUC1/SEC, and neutral complex-type in the transmembrane form, MUC1/TM.
Proteolytic cleavage in the SEA domain occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum by an autoproteolytic mechanism and requires the full-length SEA domain as well as requiring a Ser, Thr or Cys residue at the P + 1 site. Cleavage at this site also occurs on isoform MUC1/X but not on isoform MUC1/Y. Ectodomain shedding is mediated by ADAM17.
Proteolytic cleavage in the SEA domain occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum by an autoproteolytic mechanism and requires the full-length SEA domain as well as requiring a Ser, Thr or Cys residue at the P + 1 site. Cleavage at this site also occurs on isoform MUC1/X but not on isoform MUC1/Y. Ectodomain shedding is mediated by ADAM17.
疾病
Note=MUC1/CA 15-3 is used as a serological clinical marker of breast cancer to monitor response to breast cancer treatment and disease recurrence (PubMed:20816948). Decreased levels over time may be indicative of a positive response to treatment. Conversely, increased levels may indicate disease progression. At an early stage disease, only 21% of patients exhibit high MUC1/CA 15-3 levels, that is why CA 15-3 is not a useful screening test. Most antibodies target the highly immunodominant core peptide domain of 20 amino acid (APDTRPAPGSTAPPAHGVTS) tandem repeats. Some antibodies recognize glycosylated epitopes.
相似性
Contains 1 SEA domain.
功能
The alpha subunit has cell adhesive properties. Can act both as an adhesion and an anti-adhesion protein. May provide a protective layer on epithelial cells against bacterial and enzyme attack.
The beta subunit contains a C-terminal domain which is involved in cell signaling, through phosphorylations and protein-protein interactions. Modulates signaling in ERK, SRC and NF-kappa-B pathways. In activated T-cells, influences directly or indirectly the Ras/MAPK pathway. Promotes tumor progression. Regulates TP53-mediated transcription and determines cell fate in the genotoxic stress response. Binds, together with KLF4, the PE21 promoter element of TP53 and represses TP53 activity.
The beta subunit contains a C-terminal domain which is involved in cell signaling, through phosphorylations and protein-protein interactions. Modulates signaling in ERK, SRC and NF-kappa-B pathways. In activated T-cells, influences directly or indirectly the Ras/MAPK pathway. Promotes tumor progression. Regulates TP53-mediated transcription and determines cell fate in the genotoxic stress response. Binds, together with KLF4, the PE21 promoter element of TP53 and represses TP53 activity.
标记抗体
暂无标记数据
同靶标产品
暂无同靶标产品
相关文献
提示: 发表研究结果有使用 bsm-55523R 时请让我们知道,以便我们可以引用参考文章。作为回馈,资料提供者将获得我们送上的小礼品。
暂无相关文献
常见问题
暂无常见问题