α-1抗胰糜蛋白酶/SERPINA3重组兔单克隆抗体
Rrmab?兔单抗
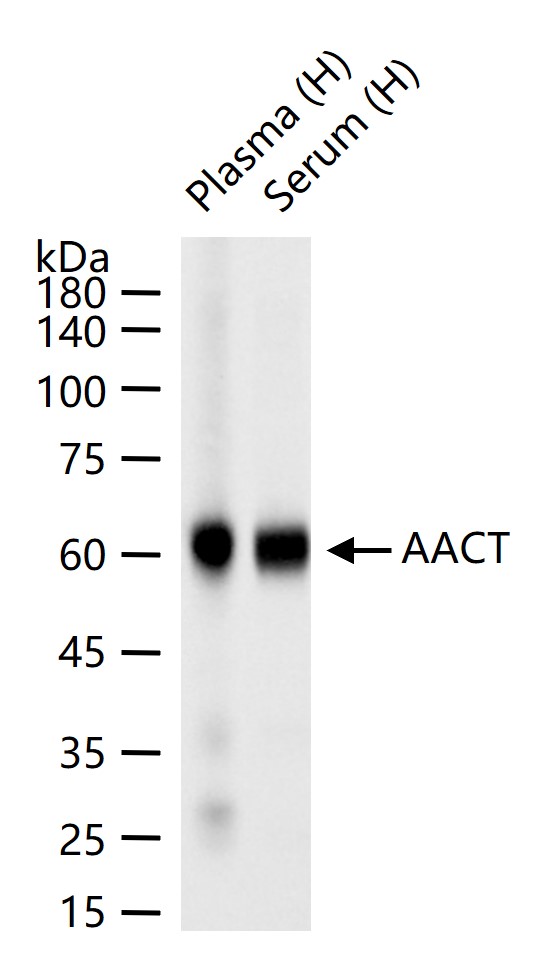
货号:bsm-60780R
产品详情
相关标记
相关产品
相关文献
常见问题
概述
产品编号
bsm-60780R
产品类型
重组兔单抗、mIHC精品抗体
英文名称
AACT Recombinant Rabbit mAb
中文名称
α-1抗胰糜蛋白酶/SERPINA3重组兔单克隆抗体
英文别名
AACT; ACT; GIG24; GIG25; AACT_HUMAN; SERPINA3; Cell growth-inhibiting gene 24/25 protein; Serpin A3;
抗体来源
Rabbit
免疫原
Full length native Protein: 1-423/423
亚型
IgG
性状
Lyophilized or Liquid
纯化方法
affinity purified by Protein A
克隆类型
Recombinant
克隆号
A12D5
理论分子量
45 kDa
浓度
1mg/ml
储存液
PBS, Glycerol, BSA.
研究领域
SWISS
Gene ID
保存条件
Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20℃ for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
注意事项
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
数据库链接
产品介绍
AACT是由神经胶质细胞分泌并参与淀粉样纤维生成和沉积的一种色氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂,被认为是Aβ肽的假性底物,与Aβ肽具有很高的亲合性,可促进Aβ肽的纤维化以生成淀粉样沉积。
ApoE作为AD的另一种病理伴随性物质,也可识别并与Aβ肽相结合,促进Aβ肽沉积生成淀粉样老年斑块。由于AACT和ApoE在AD发病中具有共同的作用途径,因此探讨其相互作用可能是AD治疗中一个新的途径。
AACT是一种丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂,可以中和糜蛋白酶等酶活性的蛋白酶,存在于大多数的组织细胞、巨噬细胞以及多种胃肠道和肺部肿瘤中,但多形核白细胞中无此物质,它可以作为组织细胞瘤和良性/恶性纤维组织细胞瘤的标志。此抗体与人的AACT反应,主要用于恶性纤维组织细胞瘤等恶性肿瘤的诊断,也可用于胃癌﹑肺癌、肾癌等肿瘤的研究。
ApoE作为AD的另一种病理伴随性物质,也可识别并与Aβ肽相结合,促进Aβ肽沉积生成淀粉样老年斑块。由于AACT和ApoE在AD发病中具有共同的作用途径,因此探讨其相互作用可能是AD治疗中一个新的途径。
AACT是一种丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂,可以中和糜蛋白酶等酶活性的蛋白酶,存在于大多数的组织细胞、巨噬细胞以及多种胃肠道和肺部肿瘤中,但多形核白细胞中无此物质,它可以作为组织细胞瘤和良性/恶性纤维组织细胞瘤的标志。此抗体与人的AACT反应,主要用于恶性纤维组织细胞瘤等恶性肿瘤的诊断,也可用于胃癌﹑肺癌、肾癌等肿瘤的研究。
背景资料
Alpha 1-Antichymotrypsin, a member of the serine proteinase inhibitor (serpin) family, inhibits neutrophil proteinase cathepsin G and mast cell chymases, and protects the lower respiratory tract from damage by proteolytic enzymes. It contains a reactive centre loop, which interacts with cognate proteinases, resulting in loop cleavage and a major conformational change. Recently, alpha 1-antichymotrypsin has been identified as a major constituent of the neurofibrillary plaques associated with Alzheimers disease, and in vitro studies have shown that it enhances the rate of amyloid-fibril formation. These observations and recent genetic evidence suggest that alpha 1-antichymotrypsin is important in the pathogenesis of Alzheimers disease.

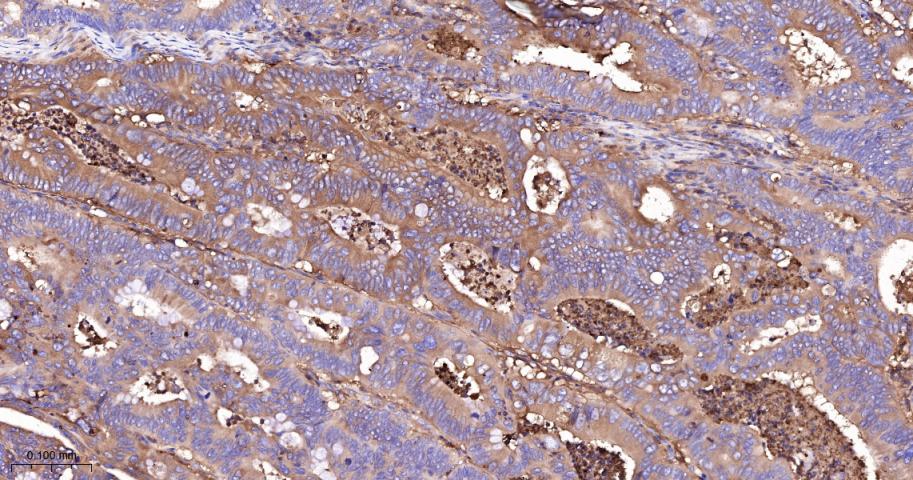
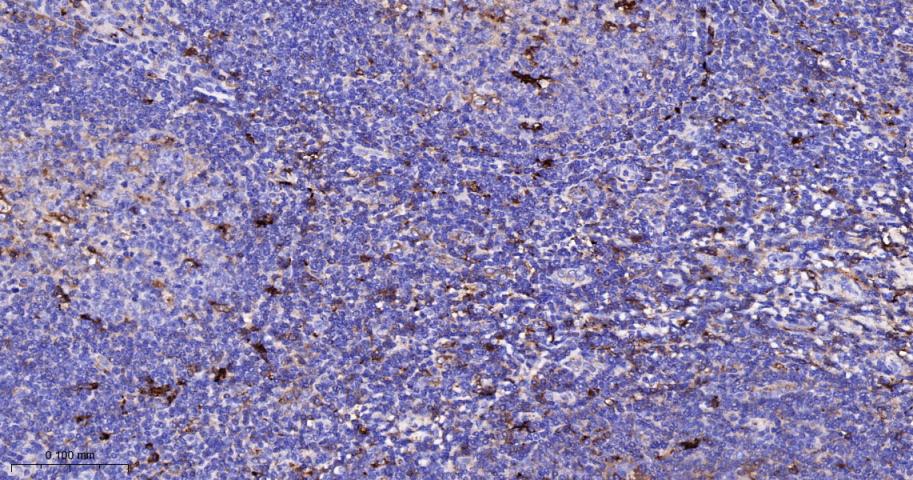
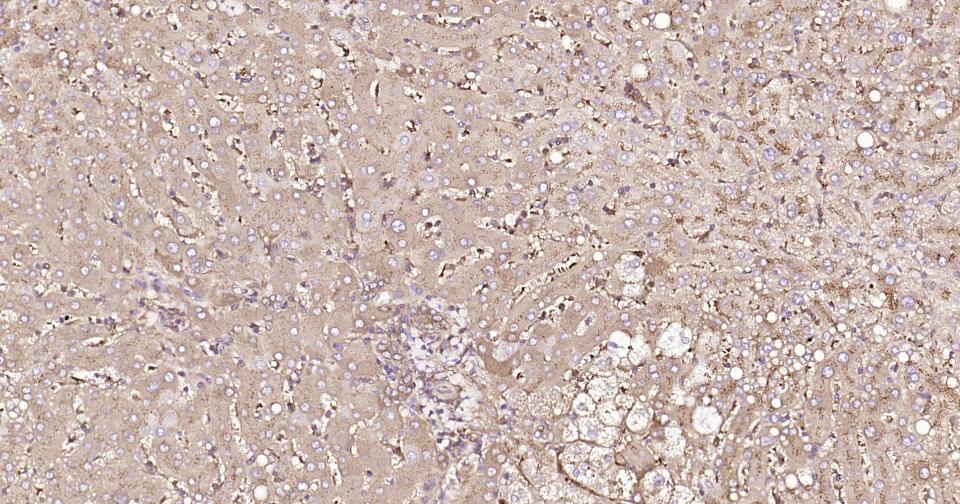
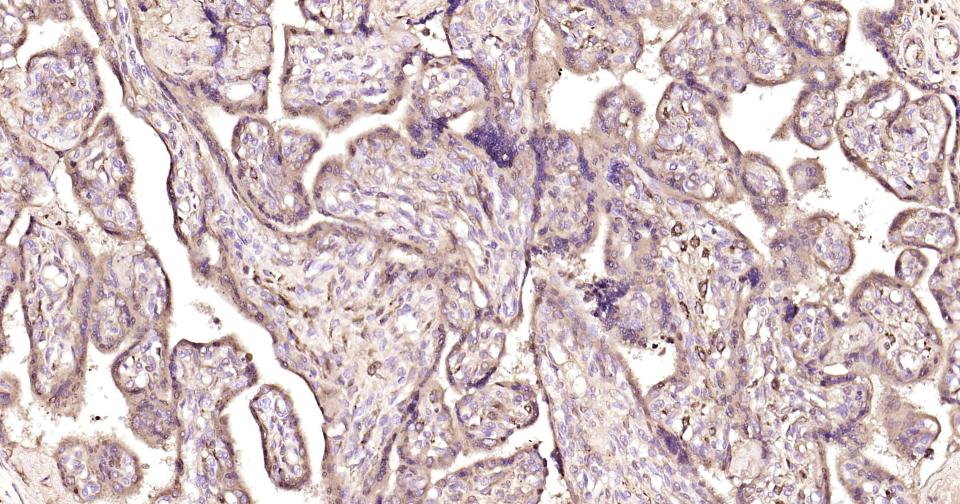
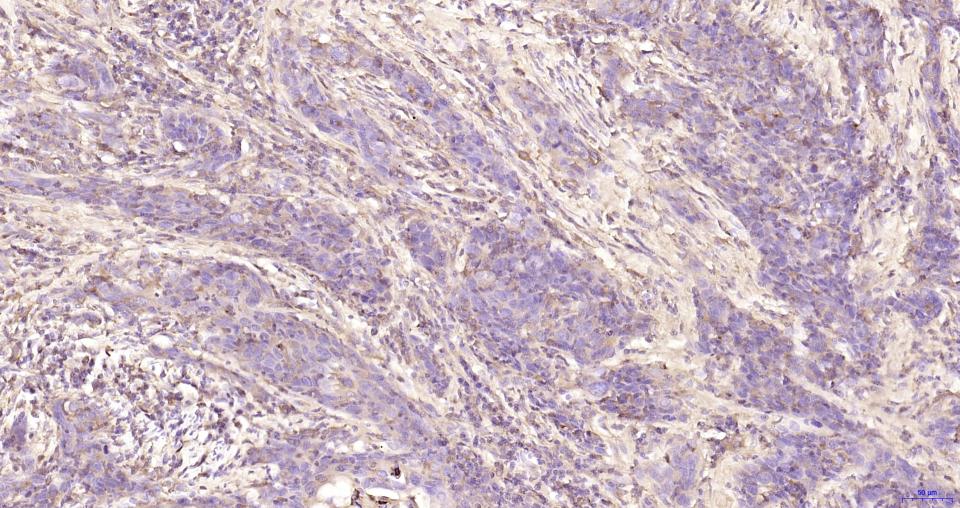
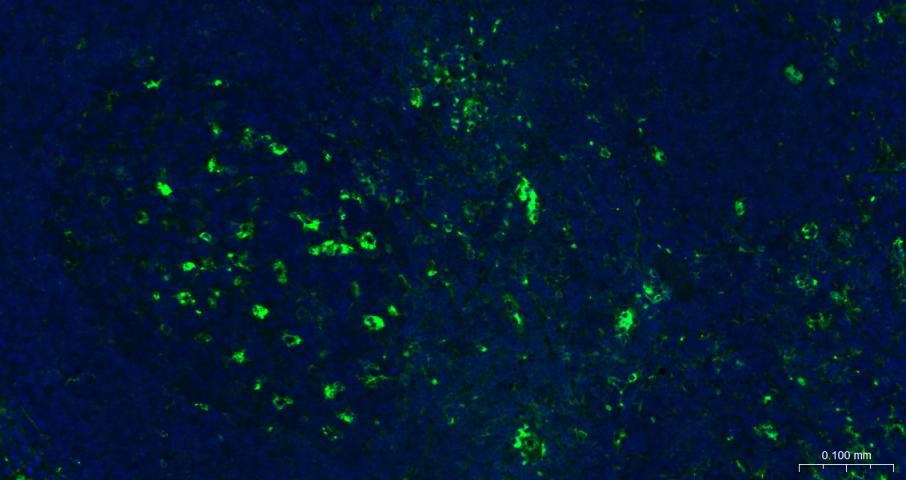
产品应用
| 应用 | 已检合格种属 | 预测种属 | 推荐稀释比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| WB | Human | 1:2000-10000 | |
| IHC-P | Human | 1:200-800 | |
| IHC-F | Human | 1:200-800 | |
| IF | Human | 1:200-800 |
交叉反应
交叉反应: Human
相关产品
暂无相关产品
靶标
基因名
SERPINA3
蛋白名
alpha-1-antichymotrypsin
亚基
Interacts with DNAJC1.
亚细胞定位
Secreted.
组织特异性
Plasma. Synthesized in the liver. Like the related alpha-1-antitrypsin, its concentration increases in the acute phase of inflammation or infection. Found in the amyloid plaques from the hippocampus of Alzheimer disease brains.
相似性
Belongs to the serpin family.
功能
Although its physiological function is unclear, it can inhibit neutrophil cathepsin G and mast cell chymase, both of which can convert angiotensin-1 to the active angiotensin-2.
标记抗体
暂无标记数据
同靶标产品
暂无同靶标产品
相关文献
提示: 发表研究结果有使用 bsm-60780R 时请让我们知道,以便我们可以引用参考文章。作为回馈,资料提供者将获得我们送上的小礼品。
暂无相关文献
常见问题
暂无常见问题