Smad4重组兔单抗
Rrmab?兔单抗
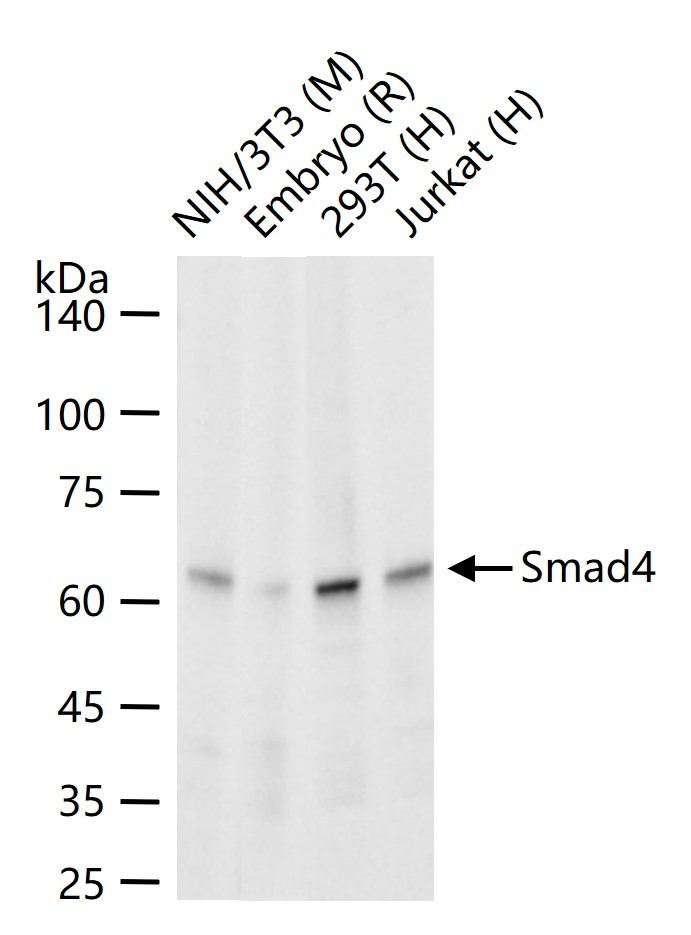
货号:bsm-52225R
产品详情
相关标记
相关产品
相关文献
常见问题
概述
产品编号
bsm-52225R
产品类型
重组兔单抗
英文名称
Smad4 Recombinant Rabbit mAb
中文名称
Smad4重组兔单抗
英文别名
DPC4; JIP; MADH4; MYHRS; D18Wsu70e; SMAD4_HUMAN; SMAD4; MAD homolog 4; Mothers against DPP homolog 4; Deletion target in pancreatic carcinoma 4; SMAD family member 4 (SMAD 4 | Smad4 | hSMAD4); SMAD4_MOUSE; Deletion target in pancreatic carcinoma 4 homolog; SMAD family member 4 (SMAD 4 | Smad4); SMAD4_RAT;
抗体来源
Rabbit
免疫原
A synthesized peptide derived from human SMAD4: 500-552/552
亚型
IgG
性状
Liquid
纯化方法
affinity purified by Protein A
克隆类型
Recombinant
克隆号
3A1
理论分子量
60 kDa
浓度
1mg/ml
储存液
0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol.
研究领域
Cancer > Cancer Metabolism > Response to hypoxia
Cancer > Oncoproteins/suppressors > Tumor suppressors
Cardiovascular > Heart > Apoptosis
Cardiovascular > Heart > Cardiogenesis > Transcription factors/regulators
Cardiovascular > Heart > Hypertrophy > Transcription factors
Cardiovascular > Vasculature > Endothelium
Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling > Nuclear Signaling Pathways > SMADs
Metabolism > Pathways and Processes > Metabolism processes > Hypoxia
Signal Transduction > Signaling Pathway > Nuclear Signaling > SMADs
SWISS
Gene ID
保存条件
Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20℃ for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
注意事项
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
数据库链接
产品介绍
转录调节因子(Transcriptin Regulators)
Smad4(deletedinpancreaticcarcinomalocus4,DPC4)是一种抑癌基因,其主要功能是参与转化生长因子β(TGF-β)超家族的细胞内信号转导,在TGF-β超家族的信号转导途径中处于重要地位,目前多用于肿瘤方面的研究。
Smad4(deletedinpancreaticcarcinomalocus4,DPC4)是一种抑癌基因,其主要功能是参与转化生长因子β(TGF-β)超家族的细胞内信号转导,在TGF-β超家族的信号转导途径中处于重要地位,目前多用于肿瘤方面的研究。
背景资料
Smad 4 is a member of the Mothers Against Dpp (MAD)-related family of proteins. So far, eight Smads have been identified and can be divided in 3 subgroups based on their structure and functions; pathway-restricted, common mediator and inhibitory Smad. Smad 4 is the common Smad (co-Smad). Previously identified as the tumor suppressor DPC4 (deleted in pancreatic carcinoma, locus 4), Smad 4 is functionally distinct among the Smad family, and is required for the assembly and transcriptional activation of diverse, Smad-DNA complexes. In contrast to the R-Smads, Smad 4 is not regulated by phosphorylation, but acts as a common mediator of TGF-Beta, activin, and bone morphogenetic protein signaling responses. Smad 4 is frequently inactivated in pancreatic, biliary and colorectal tumors.

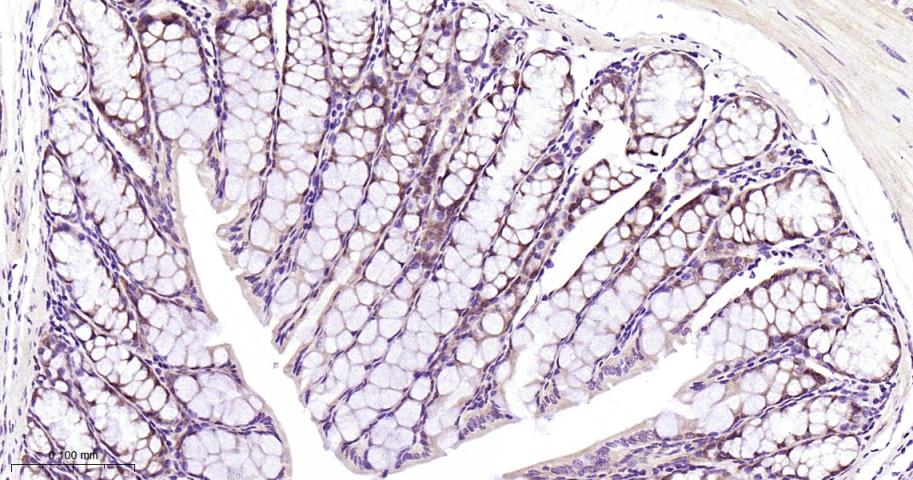
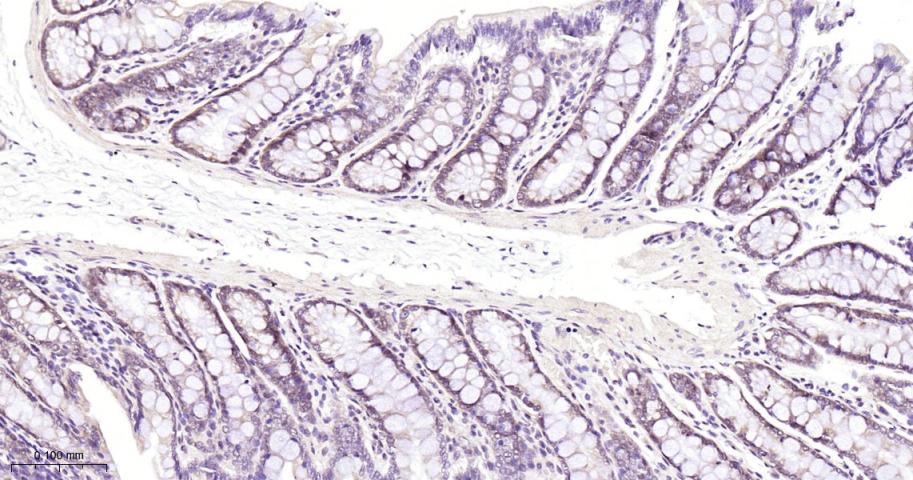
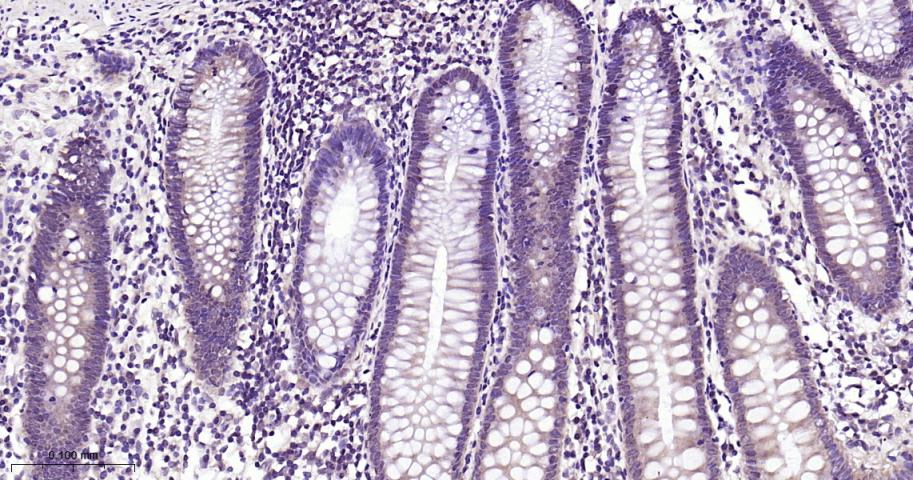
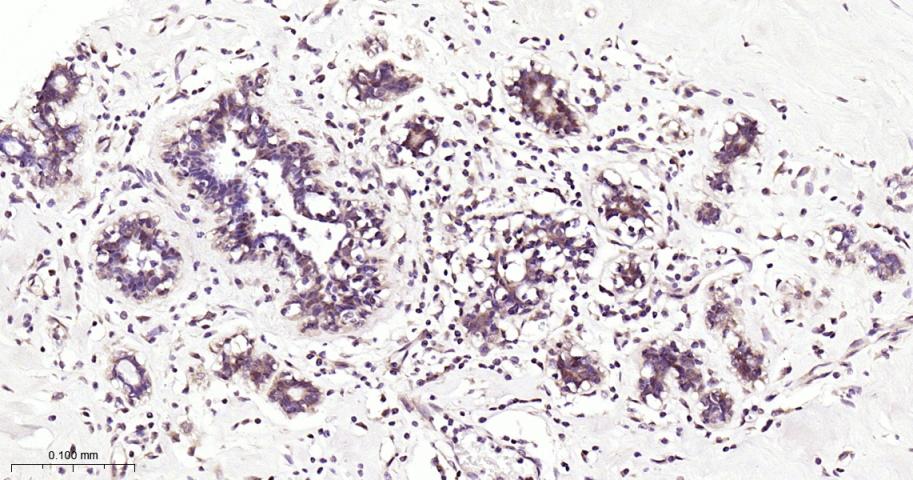
产品应用
| 应用 | 已检合格种属 | 预测种属 | 推荐稀释比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| WB | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:500-2000 | |
| IHC-P | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:50-200 | |
| IHC-F | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:50-200 | |
| IF | Human, Mouse, Rat | 1:50-200 |
交叉反应
交叉反应: Human, Mouse, Rat
相关产品
暂无相关产品
靶标
基因名
SMAD4
蛋白名
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4
亚基
Interacts with CITED2 (By similarity). Monomer; in the absence of TGF-beta activation. Heterodimer; on TGF-beta activation. Composed of two molecules of a C-terminally phosphorylated R-SMAD molecule, SMAD2 or SMAD3, and one molecule of SMAD4 to form the transcriptional active SMAD2/SMAD3-SMAD4 complex. Found in a ternary complex composed of SMAD4, STK11/LKB1 and STK11IP. Interacts with ATF2, COPS5, DACH1, MSG1, SKI, STK11/LKB1, STK11IP and TRIM33. Interacts with ZNF423; the interaction takes place in response to BMP2 leading to activation of transcription of BMP target genes. Interacts with ZNF521; the interaction takes place in response to BMP2 leading to activation of transcription of BMP target genes. Interacts with USP9X. Interacts (via the MH1 and MH2 domains) with RBPMS. Interacts with WWTR1 (via coiled-coil domain). Component of the multimeric complex SMAD3/SMAD4/JUN/FOS which forms at the AP1 promoter site; required for syngernistic transcriptional activity in response to TGF-beta. Interacts with CITED1. Interacts with PDPK1 (via PH domain). Interacts with VPS39; this interaction affects heterodimer formation with SMAD3, but not with SMAD2, and leads to inhibition of SMAD3-dependent transcription activation. Interactions with VPS39 and SMAD2 may be mutually exclusive.
亚细胞定位
Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Note=Cytoplasmic in the absence of ligand. Migrates to the nucleus when complexed with R-SMAD. PDPK1 prevents its nuclear translocation in response to TGF-beta.
翻译后修饰
Phosphorylated by PDPK1.
Monoubiquitinated on Lys-519 by E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM33. Monoubiquitination hampers its ability to form a stable complex with activated SMAD2/3 resulting in inhibition of TGF-beta/BMP signaling cascade. Deubiqitination by USP9X restores its competence to mediate TGF-beta signaling.
Monoubiquitinated on Lys-519 by E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM33. Monoubiquitination hampers its ability to form a stable complex with activated SMAD2/3 resulting in inhibition of TGF-beta/BMP signaling cascade. Deubiqitination by USP9X restores its competence to mediate TGF-beta signaling.
疾病
Pancreatic cancer (PNCA) [MIM:260350]: A malignant neoplasm of the pancreas. Tumors can arise from both the exocrine and endocrine portions of the pancreas, but 95% of them develop from the exocrine portion, including the ductal epithelium, acinar cells, connective tissue, and lymphatic tissue. Note=The gene represented in this entry may be involved in disease pathogenesis.
Juvenile polyposis syndrome (JPS) [MIM:174900]: Autosomal dominant gastrointestinal hamartomatous polyposis syndrome in which patients are at risk for developing gastrointestinal cancers. The lesions are typified by a smooth histological appearance, predominant stroma, cystic spaces and lack of a smooth muscle core. Multiple juvenile polyps usually occur in a number of Mendelian disorders. Sometimes, these polyps occur without associated features as in JPS; here, polyps tend to occur in the large bowel and are associated with an increased risk of colon and other gastrointestinal cancers. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.
Juvenile polyposis/hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia syndrome (JP/HHT) [MIM:175050]: JP/HHT syndrome phenotype consists of the coexistence of juvenile polyposis (JIP) and hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) [MIM:187300] in a single individual. JIP and HHT are autosomal dominant disorders with distinct and non-overlapping clinical features. The former, an inherited gastrointestinal malignancy predisposition, is caused by mutations in SMAD4 or BMPR1A, and the latter is a vascular malformation disorder caused by mutations in ENG or ACVRL1. All four genes encode proteins involved in the transforming-growth-factor-signaling pathway. Although there are reports of patients and families with phenotypes of both disorders combined, the genetic etiology of this association is unknown. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) [MIM:114500]: A complex disease characterized by malignant lesions arising from the inner wall of the large intestine (the colon) and the rectum. Genetic alterations are often associated with progression from premalignant lesion (adenoma) to invasive adenocarcinoma. Risk factors for cancer of the colon and rectum include colon polyps, long-standing ulcerative colitis, and genetic family history. Note=The disease may be caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.
Note=SMAD4 variants may be associated with susceptibility to pulmonary hypertension, a disorder characterized by plexiform lesions of proliferating endothelial cells in pulmonary arterioles. The lesions lead to elevated pulmonary arterial pression, right ventricular failure, and death. The disease can occur from infancy throughout life and it has a mean age at onset of 36 years. Penetrance is reduced. Although familial pulmonary hypertension is rare, cases secondary to known etiologies are more common and include those associated with the appetite-suppressant drugs.
Myhre syndrome (MYHRS) [MIM:139210]: A syndrome characterized by pre- and postnatal growth deficiency, mental retardation, generalized muscle hypertrophy and striking muscular build, decreased joint mobility, cryptorchidism, and unusual facies. Dysmorphic facial features include microcephaly, midface hypoplasia, prognathism, and blepharophimosis. Typical skeletal anomalies are short stature, square body shape, broad ribs, iliac hypoplasia, brachydactyly, flattened vertebrae, and thickened calvaria. Other features, such as congenital heart disease, may also occur. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.
Juvenile polyposis syndrome (JPS) [MIM:174900]: Autosomal dominant gastrointestinal hamartomatous polyposis syndrome in which patients are at risk for developing gastrointestinal cancers. The lesions are typified by a smooth histological appearance, predominant stroma, cystic spaces and lack of a smooth muscle core. Multiple juvenile polyps usually occur in a number of Mendelian disorders. Sometimes, these polyps occur without associated features as in JPS; here, polyps tend to occur in the large bowel and are associated with an increased risk of colon and other gastrointestinal cancers. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.
Juvenile polyposis/hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia syndrome (JP/HHT) [MIM:175050]: JP/HHT syndrome phenotype consists of the coexistence of juvenile polyposis (JIP) and hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) [MIM:187300] in a single individual. JIP and HHT are autosomal dominant disorders with distinct and non-overlapping clinical features. The former, an inherited gastrointestinal malignancy predisposition, is caused by mutations in SMAD4 or BMPR1A, and the latter is a vascular malformation disorder caused by mutations in ENG or ACVRL1. All four genes encode proteins involved in the transforming-growth-factor-signaling pathway. Although there are reports of patients and families with phenotypes of both disorders combined, the genetic etiology of this association is unknown. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) [MIM:114500]: A complex disease characterized by malignant lesions arising from the inner wall of the large intestine (the colon) and the rectum. Genetic alterations are often associated with progression from premalignant lesion (adenoma) to invasive adenocarcinoma. Risk factors for cancer of the colon and rectum include colon polyps, long-standing ulcerative colitis, and genetic family history. Note=The disease may be caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.
Note=SMAD4 variants may be associated with susceptibility to pulmonary hypertension, a disorder characterized by plexiform lesions of proliferating endothelial cells in pulmonary arterioles. The lesions lead to elevated pulmonary arterial pression, right ventricular failure, and death. The disease can occur from infancy throughout life and it has a mean age at onset of 36 years. Penetrance is reduced. Although familial pulmonary hypertension is rare, cases secondary to known etiologies are more common and include those associated with the appetite-suppressant drugs.
Myhre syndrome (MYHRS) [MIM:139210]: A syndrome characterized by pre- and postnatal growth deficiency, mental retardation, generalized muscle hypertrophy and striking muscular build, decreased joint mobility, cryptorchidism, and unusual facies. Dysmorphic facial features include microcephaly, midface hypoplasia, prognathism, and blepharophimosis. Typical skeletal anomalies are short stature, square body shape, broad ribs, iliac hypoplasia, brachydactyly, flattened vertebrae, and thickened calvaria. Other features, such as congenital heart disease, may also occur. Note=The disease is caused by mutations affecting the gene represented in this entry.
相似性
Belongs to the dwarfin/SMAD family.
Contains 1 MH1 (MAD homology 1) domain.
Contains 1 MH2 (MAD homology 2) domain.
Contains 1 MH1 (MAD homology 1) domain.
Contains 1 MH2 (MAD homology 2) domain.
功能
Common SMAD (co-SMAD) is the coactivator and mediator of signal transduction by TGF-beta (transforming growth factor). Component of the heterotrimeric SMAD2/SMAD3-SMAD4 complex that forms in the nucleus and is required for the TGF-mediated signaling. Promotes binding of the SMAD2/SMAD4/FAST-1 complex to DNA and provides an activation function required for SMAD1 or SMAD2 to stimulate transcription. Component of the multimeric SMAD3/SMAD4/JUN/FOS complex which forms at the AP1 promoter site; required for syngernistic transcriptional activity in response to TGF-beta. May act as a tumor suppressor. Positively regulates PDPK1 kinase activity by stimulating its dissociation from the 14-3-3 protein YWHAQ which acts as a negative regulator.
标记抗体
暂无标记数据
同靶标产品
暂无同靶标产品
相关文献
提示: 发表研究结果有使用 bsm-52225R 时请让我们知道,以便我们可以引用参考文章。作为回馈,资料提供者将获得我们送上的小礼品。
暂无相关文献
常见问题
暂无常见问题