犬细小病毒VP2蛋白单克隆抗体
货号:bsm-49051M
产品详情
相关标记
相关产品
相关文献
常见问题
概述
产品编号
bsm-49051M
英文名称
CPV VP2 Mouse mAb
中文名称
犬细小病毒VP2蛋白单克隆抗体
英文别名
CAPSD_PAVC; Coat protein VP2;
抗体来源
Mouse
免疫原
Recombinant Canine parvovirus Capsid protein VP2: 201-584/584
亚型
IgG
性状
Size : 50ul/100ul/200ul
Liquid
Size : 200ug (PBS only)
Lyophilized
Note: Centrifuge tubes before opening. Reconstitute the lyophilized product in distilled water. Optimal concentration should be determined by the end user.
Liquid
Size : 200ug (PBS only)
Lyophilized
Note: Centrifuge tubes before opening. Reconstitute the lyophilized product in distilled water. Optimal concentration should be determined by the end user.
纯化方法
affinity purified by Protein A
克隆类型
Monoclonal
克隆号
4G2
理论分子量
65 kDa
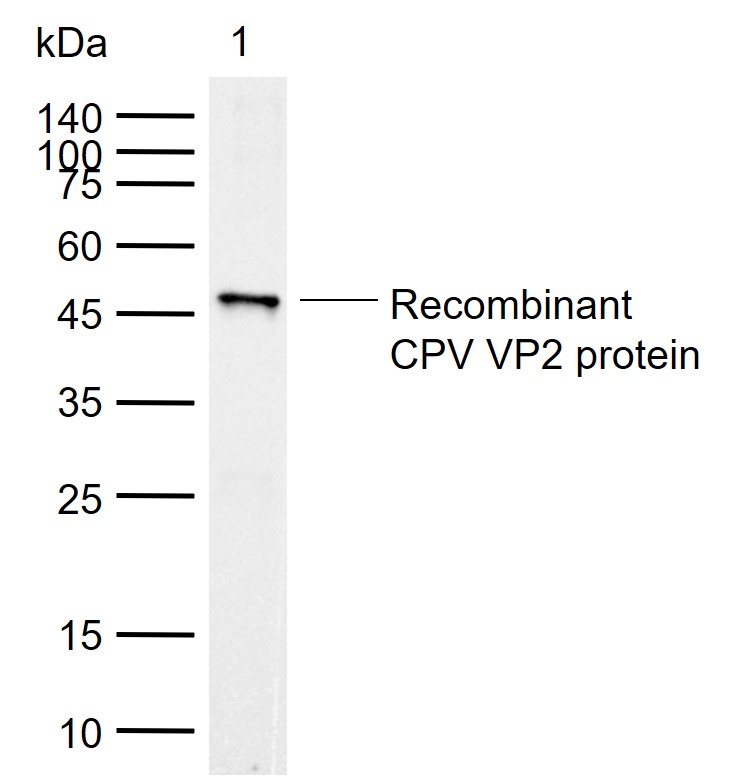
检测分子量
47 kDa
浓度
1mg/ml
储存液
Size : 50ul/100ul/200ul
0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol.
Size : 200ug (PBS only)
0.01M PBS
0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol.
Size : 200ug (PBS only)
0.01M PBS
保存条件
Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20℃ for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
注意事项
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
背景资料
Capsid protein self-assembles to form an icosahedral capsid with a T=1 symmetry, about 22 nm in diameter, and consisting of 60 copies of two size variants of the capsid proteins, VP1 and VP2, which differ by the presence of an N-terminal extension in the minor protein VP1. The capsid encapsulates the genomic ssDNA. Capsid proteins are responsible for the attachment to host cell receptor TFRC. This attachment induces virion internalization predominantly through clathrin-endocytosis. Binding to the host receptors also induces capsid rearrangements leading to surface exposure of VP1 N-terminus, specifically its phospholipase A2-like region and nuclear localization signal(s). VP1 N-terminus might serve as a lipolytic enzyme to breach the endosomal membrane during entry into host cell. Intracytoplasmic transport involves microtubules and interaction between capsid proteins and host dynein. Exposure of nuclear localization signal probably allows nuclear import of capsids.

产品应用
| 应用 | 已检合格种属 | 预测种属 | 推荐稀释比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| WB | CPV | 1:500-2000 | |
| ELISA | CPV | 1:5000-10000 |
交叉反应
交叉反应: CPV
相关产品
暂无相关产品
靶标
基因名
CPV-2
蛋白名
Capsid protein VP2
亚基
Interacts with host TFRC.
亚细胞定位
Virion; Host nucleus
相似性
Belongs to the parvoviridae capsid protein family.
功能
Capsid protein self-assembles to form an icosahedral capsid with a T=1 symmetry, about 22 nm in diameter, and consisting of 60 copies of two size variants of the capsid proteins, VP1 and VP2, which differ by the presence of an N-terminal extension in the minor protein VP1. The capsid encapsulates the genomic ssDNA. Capsid proteins are responsible for the attachment to host cell receptor TFRC. This attachment induces virion internalization predominantly through clathrin-endocytosis. Binding to the host receptors also induces capsid rearrangements leading to surface exposure of VP1 N-terminus, specifically its phospholipase A2-like region and nuclear localization signal(s). VP1 N-terminus might serve as a lipolytic enzyme to breach the endosomal membrane during entry into host cell. Intracytoplasmic transport involves microtubules and interaction between capsid proteins and host dynein. Exposure of nuclear localization signal probably allows nuclear import of capsids.
标记抗体
暂无标记数据
同靶标产品
暂无同靶标产品
相关文献
提示: 发表研究结果有使用 bsm-49051M 时请让我们知道,以便我们可以引用参考文章。作为回馈,资料提供者将获得我们送上的小礼品。
暂无相关文献
常见问题
暂无常见问题